Sui Move 调试Debugging和test_scenario单测工具使用
- LeonDev1024
- 发布于 2024-12-02 23:02
- 阅读 2218
熟练掌握 debug 和 test_scenario 这两个工具包,开发者在 Move 开发中遇到问题时,便能够高效地进行调试与模拟测试,极大提升开发效率与代码质量。
1. 概述
Move 当前不支持原生调试器。但可借助 std::debug 模块与测试工具包 test_scenario 进行有效的调试与模拟测试。通过这种方式监控变量的值和模拟测试环境进行交易和功能的验证,从而深入了解模块的逻辑。
-
引入
std::debug模块use std::debug; -
在需要打印变量值
v的地方,可以使用以下代码,无论其类型为何:// 打印变量值 v 的地方 debug::print(&v); // 如果 v 已经是一个引用,则使用以下代码: -
打印当前的堆栈跟踪
debug::print_stack_trace();
2. 在 my_module 中使用 debug 调试代码
2.1. 创建package
创建一个新的package
sui move new my_first_package这里用的测试源码是官网里面的案例/examples/move/my_first_package/example.move
// Copyright (c) Mysten Labs, Inc.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
// docs::#first
module my_first_package::example;
use std::debug;
// Part 1: These imports are provided by default
// use sui::object::{Self, UID};
// use sui::transfer;
// use sui::tx_context::{Self, TxContext};
// Part 2: struct definitions
public struct Sword has key, store {
id: UID,
magic: u64,
strength: u64,
}
public struct Forge has key {
id: UID,
swords_created: u64,
}
// Part 3: Module initializer to be executed when this module is published
fun init(ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let admin = Forge {
id: object::new(ctx),
swords_created: 0,
};
// Transfer the forge object to the module/package publisher
transfer::transfer(admin, ctx.sender());
}
// Part 4: Accessors required to read the struct fields
public fun magic(self: &Sword): u64 {
self.magic
}
public fun strength(self: &Sword): u64 {
self.strength
}
public fun swords_created(self: &Forge): u64 {
self.swords_created
}
// Part 5: Public/entry functions (introduced later in the tutorial)
// docs::#first-pause
public fun sword_create(magic: u64, strength: u64, ctx: &mut TxContext): Sword {
// Create a sword
Sword {
id: object::new(ctx),
magic: magic,
strength: strength,
}
}
/// 构造函数
public fun new_sword(forge: &mut Forge, magic: u64, strength: u64, ctx: &mut TxContext): Sword {
debug::print(forge);
forge.swords_created = forge.swords_created + 1;
debug::print(forge);
debug::print_stack_trace();
Sword {
id: object::new(ctx),
magic: magic,
strength: strength,
}
}
// docs::#first-resume
// Part 6: Tests
// docs::#first-test
#[test]
fun test_sword_create() {
// Create a dummy TxContext for testing
let mut ctx = tx_context::dummy();
// Create a sword
let sword = Sword {
id: object::new(&mut ctx),
magic: 42,
strength: 7,
};
// Check if accessor functions return correct values
assert!(sword.magic() == 42 && sword.strength() == 7, 1);
// docs::/#first-test}
// docs::#test-dummy
// Create a dummy address and transfer the sword
let dummy_address = @0xCAFE;
transfer::public_transfer(sword, dummy_address);
// docs::/#test-dummy
}
#[test]
fun test_sword_transactions() {
use sui::test_scenario;
// Create test addresses representing users
let initial_owner = @0xCAFE;
let final_owner = @0xFACE;
// First transaction executed by initial owner to create the sword
let mut scenario = test_scenario::begin(initial_owner);
{
// Create the sword and transfer it to the initial owner
let sword = sword_create(42, 7, scenario.ctx());
transfer::public_transfer(sword, initial_owner);
};
// Second transaction executed by the initial sword owner
scenario.next_tx(initial_owner);
{
// Extract the sword owned by the initial owner
let sword = scenario.take_from_sender<Sword>();
// Transfer the sword to the final owner
transfer::public_transfer(sword, final_owner);
};
// Third transaction executed by the final sword owner
scenario.next_tx(final_owner);
{
// Extract the sword owned by the final owner
let sword = scenario.take_from_sender<Sword>();
// Verify that the sword has expected properties
assert!(sword.magic() == 42 && sword.strength() == 7, 1);
// Return the sword to the object pool (it cannot be simply "dropped")
scenario.return_to_sender(sword)
};
scenario.end();
}
#[test]
fun test_module_init() {
use sui::test_scenario;
// Create test addresses representing users
let admin = @0xAD;
let initial_owner = @0xCAFE;
// First transaction to emulate module initialization
let mut scenario = test_scenario::begin(admin);
{
init(scenario.ctx());
};
// Second transaction to check if the forge has been created
// and has initial value of zero swords created
scenario.next_tx(admin);
{
// Extract the Forge object
let forge = scenario.take_from_sender<Forge>();
// Verify number of created swords
assert!(forge.swords_created() == 0, 1);
// Return the Forge object to the object pool
scenario.return_to_sender(forge);
};
// Third transaction executed by admin to create the sword
scenario.next_tx(admin);
{
let mut forge = scenario.take_from_sender<Forge>();
// Create the sword and transfer it to the initial owner
let sword = forge.new_sword(42, 7, scenario.ctx());
transfer::public_transfer(sword, initial_owner);
scenario.return_to_sender(forge);
};
scenario.end();
}
// docs::/#first
2.2. 运行测试案例
sui move test --skip-fetch-latest-git-deps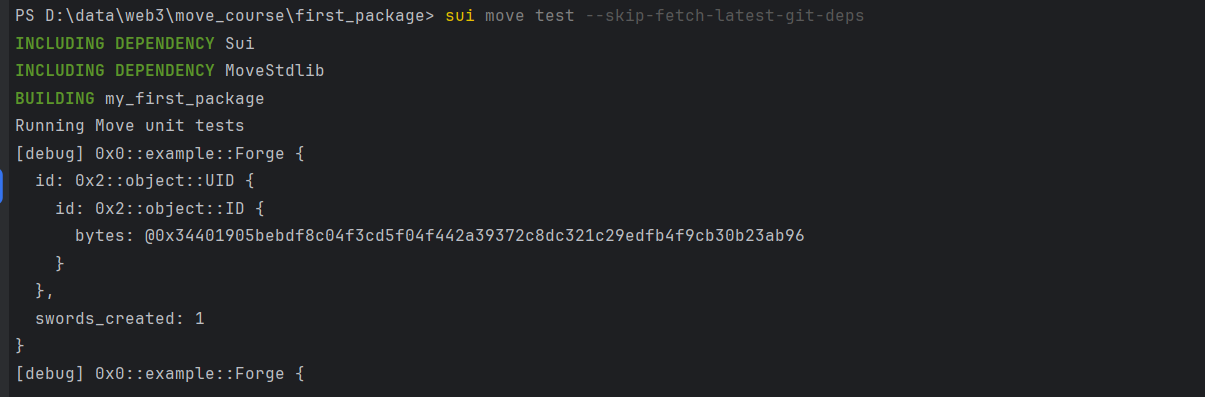
2.3. 查看debug打印的结果
PS D:\data\web3\move_course\first_package> sui move test --skip-fetch-latest-git-deps
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY Sui
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY MoveStdlib
BUILDING my_first_package
Running Move unit tests
[debug] 0x0::example::Forge {
id: 0x2::object::UID {
id: 0x2::object::ID {
bytes: @0x34401905bebdf8c04f3cd5f04f442a39372c8dc321c29edfb4f9cb30b23ab96
}
},
swords_created: 0
}
[debug] 0x0::example::Forge {
id: 0x2::object::UID {
id: 0x2::object::ID {
bytes: @0x34401905bebdf8c04f3cd5f04f442a39372c8dc321c29edfb4f9cb30b23ab96
}
},
swords_created: 1
}
Call Stack:
[0] 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000::example::test_module_init
Code:
[35] LdU64(7)
[36] MutBorrowLoc(3)
[37] Call(15)
> [38] Call(5)
[39] LdConst(0)
[40] CallGeneric(2)
[41] ImmBorrowLoc(3)
Locals:
[0] -
[1] -
[2] { { { 034401905bebdf8c04f3cd5f04f442a39372c8dc321c29edfb4f9cb30b23ab96 } }, 1 }
[3] { 2, { 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000ad, [2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], 0, 0, 0 } }
Operand Stack:
[ PASS ] my_first_package::example::test_module_init
[ PASS ] my_first_package::example::test_sword_create
[ PASS ] my_first_package::example::test_sword_transactions
Test result: OK. Total tests: 3; passed: 3; failed: 0
PS D:\data\web3\move_course\first_package>3. 使用测试工具包 test_scenario 模拟测试环境
在 Move 中,use sui::test_scenario; 是引入 Sui 的测试工具包 test_scenario 的语句。通过这个工具包,你可以创建模拟的测试环境,用于测试交易、模块和函数的行为。test_scenario 提供了一些有用的功能,帮助开发者在不依赖真实网络的情况下模拟和验证 Move 代码的逻辑。
主要功能
- 模拟交易(Transactions):创建和执行模拟的交易,包括状态的转移、对象的转移等。
- 测试函数(Testing Functions):通过模拟的交易环境,可以测试模块中的函数行为。
- 创建虚拟地址和对象(Virtual Addresses and Objects):模拟用户账户和对象的创建与转移。
3.1 测试 Sword 对象在多个交易中的创建和转移流程
#[test]
fun test_sword_transactions() {
use sui::test_scenario;
// 创建测试地址,表示两个用户
let initial_owner = @0xCAFE; // 初始所有者地址
let final_owner = @0xFACE; // 最终所有者地址
// 第一次交易,由初始所有者执行,创建一把sword剑
let mut scenario = test_scenario::begin(initial_owner);
{
// 创建一把剑并转移给初始所有者
// 创建一个魔力为 42,力量为 7 的剑
let sword = sword_create(42, 7, scenario.ctx());
// 转移剑给初始所有者
transfer::public_transfer(sword, initial_owner);
};
// 第二次交易,由初始所有者执行
// 切换到初始所有者的下一步交易
scenario.next_tx(initial_owner);
{
// 从发送者处提取剑
let sword = scenario.take_from_sender<Sword>();
// 转移剑给最终所有者
transfer::public_transfer(sword, final_owner);
};
// 第三次交易,由最终所有者执行
// 切换到最终所有者的下一步交易
scenario.next_tx(final_owner);
{
// 从最终所有者处提取剑
let sword = scenario.take_from_sender<Sword>();
// 验证剑的属性是否正确
// 检查剑的魔力值和力量值
assert!(sword.magic() == 42 && sword.strength() == 7, 1);
// 将剑归还到对象池(不能简单地丢弃)
scenario.return_to_sender(sword);
};
// 结束当前测试场景
scenario.end();
}
3.2 测试模块初始化和 Forge 对象的创建与管理
#[test]
fun test_module_init() {
use sui::test_scenario;
// 创建测试地址,表示管理员和初始所有者
let admin = @0xAD; // 管理员地址
let initial_owner = @0xCAFE; // 初始所有者地址
// 第一次交易,模拟模块初始化
let mut scenario = test_scenario::begin(admin);
{
// 执行模块初始化
init(scenario.ctx());
};
// 第二次交易,检查是否创建了 forge,并且初始值为0
// 切换到管理员的下一步交易
scenario.next_tx(admin);
{
// 从发送者提取 Forge 对象
let forge = scenario.take_from_sender<Forge>();
// 验证创建的剑数是否为0
// 验证初始时 forge 的 swords_created 字段是否为0
assert!(forge.swords_created() == 0, 1);
// 将 Forge 对象归还到对象池
scenario.return_to_sender(forge);
};
// 第三次交易,由管理员执行,创建一把剑
// 切换到管理员的下一步交易
scenario.next_tx(admin);
{
let mut forge = scenario.take_from_sender<Forge>();
// 创建一把剑并转移给初始所有者
// 创建一个魔力为 42,力量为 7 的剑
let sword = forge.new_sword(42, 7, scenario.ctx());
// 转移剑给初始所有者
transfer::public_transfer(sword, initial_owner);
// 将 forge 对象归还
scenario.return_to_sender(forge);
};
// 结束测试场景
scenario.end();
}总结
熟练掌握 debug 和 test_scenario 这两个工具包,开发者在 Move 开发中遇到问题时,便能够高效地进行调试与模拟测试,极大提升开发效率与代码质量。
参考文档
Debugging <!--StartFragment-->
关注《HOH水分子》公众号,我们将持续分享和制作变成语言教程,让大家对编程产生化学反应。

<!--EndFragment-->
点赞 0
收藏 0
分享
本文参与登链社区写作激励计划 ,好文好收益,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入。
- Sui Move安全研讨会总结与材料 357 浏览
- Move语言安全吗?Typus权限验证漏洞 3095 浏览
- EVM和SVM开发者的Sui Move指南:第一部分 - 心理模型 991 浏览
- go语言入门move ctf 2935 浏览
- Move智能合约初体验 - 第1部分 2630 浏览
- 随笔小记—Move篇(1) 2185 浏览
- 探索 Web3 新星:Sui 的 Object 架构与 Move 语言实践 2397 浏览
- Web3 实践:Sui 区块链交易全流程解析与实战指南 4502 浏览
- 六、Move Patterns 3053 浏览
- Web3 新玩法:用 Sui Move 打造 NFT 抽奖游戏 3362 浏览
- Web3新玩法:Sui区块链NFT创建与部署实战 2767 浏览
- 有关于kiosk的学习笔记(sui move) 2488 浏览
0 条评论
请先 登录 后评论

