Web3系列教程之进阶篇---11. The Graph索引协议
- 李留白
- 发布于 2022-09-08 13:51
- 阅读 6527
TheGraph是区块链的一个去中心化的查询协议和索引服务。它允许开发人员轻松地跟踪各种网络上的智能合约所发出的事件,并编写定制的数据转换脚本,这些脚本是实时运行的。这些数据也通过一个简单的GraphQLAPI提供,然后开发者可以用它来在他们的前端显示东西。
The Graph 是区块链的一个去中心化的查询协议和索引服务。它允许开发人员轻松地跟踪各种网络上的智能合约所发出的事件,并编写定制的数据转换脚本,这些脚本是实时运行的。这些数据也通过一个简单的GraphQL API提供,然后开发者可以用它来在他们的前端显示东西。
先决条件
- 我们将使用yarn,它是一个和npm一样的包管理器。
- 如果你的电脑还没有安装yarn的话,请从这里安装yarn
- 请观看这个40分钟的GraphQL教程
- 如果你不知道axios是什么,请看这个简短的教程
- 你应该已经完成了 Chainlink VRF 的教程
它是如何工作的
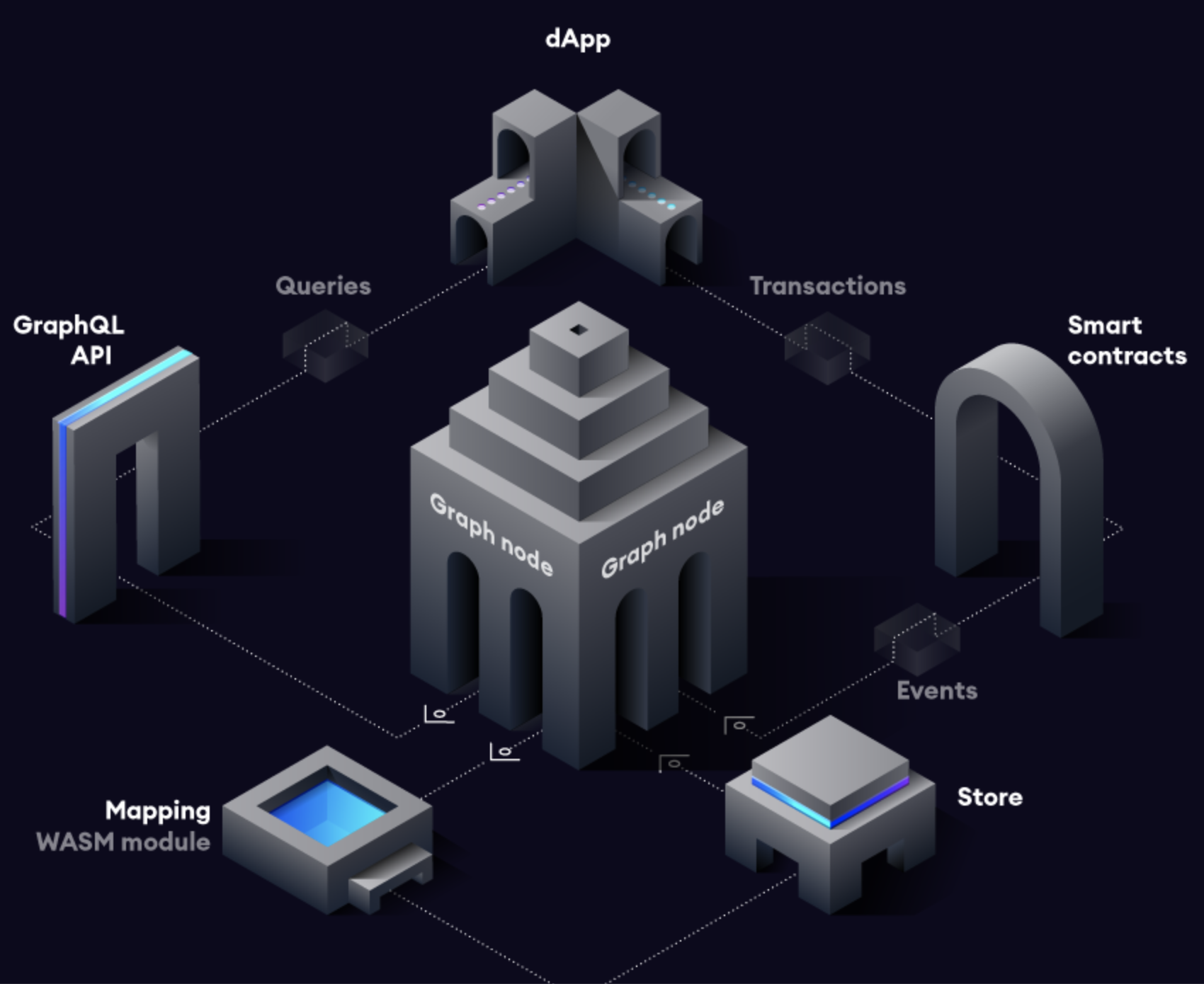
- dApp发送一个交易,之后一些数据被存储在智能合约中。然后这个智能合约发出一个或多个事件。
- Graph的节点不断扫描以太坊的新区块和这些区块可能包含的你的子图的数据。
- 如果节点找到你要找的并在你的子图中定义的事件,它就运行你定义的数据转换脚本(映射)。映射是一个WASM(Web assembly)模块,它响应事件,在图式节点上创建或更新数据
Entities。 - 我们可以使用 GraphQL Endpoint查询Graph的节点,以获得这些数据
构建
- 我们将使用你在
Chainlink VRF教程中创建的名为RandomWinnerGame的文件夹。 - 在你的
RandomWinnerGame文件夹内创建一个abi.json文件(你将需要这个文件来整合你的图)并复制以下内容。 - 请注意,这是你在Chainlink VRF教程中创建的
RandomWinnerGame合同的ABI。 - 因此,你的最终文件夹结构应该看起来像这样。
RandomWinnerGame
- hardhat-tutorial
- abi.json-
要创建你的子图,你将需要去The Graph's Hosted Service
-
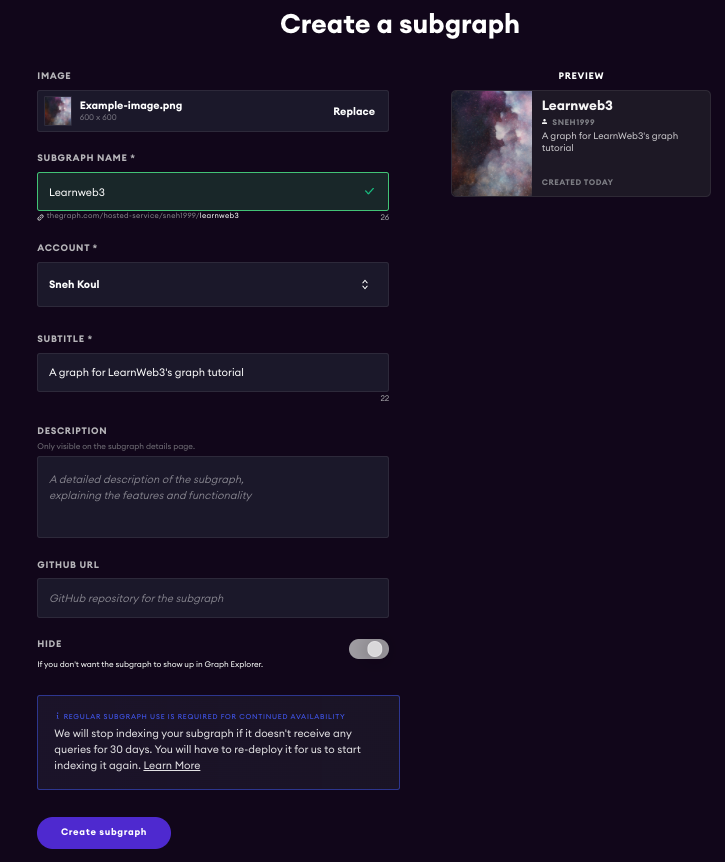
使用您的github登录并访问
My Dashboard标签

- 单击
Add Subgraph,填写信息并创建子图。
- 当你的子图被创建后,它将向你显示
Install、Init和Deploy中的一些命令

- 在你的终端执行这个命令,指向
RandomWinnerGame文件夹。
yarn global add @graphprotocol/graph-cli- 之后执行这个命令,但用你的Github用户名替换
GITHUB_USERNAME,用你在Chainlink VRF教程中部署的RandomWinnerGame合约的地址替换YOUR_RANDOM_WINNER_GAME_CONTRACT_ADDRESS。之后的所有问题都按回车键 :)
graph init --contract-name RandomWinnerGame --product hosted-service GITHUB_USERNAME/Learnweb3 --from-contract YOUR_RANDOM_WINNER_GAME_CONTRACT_ADDRESS --abi ./abi.json --network mumbai graph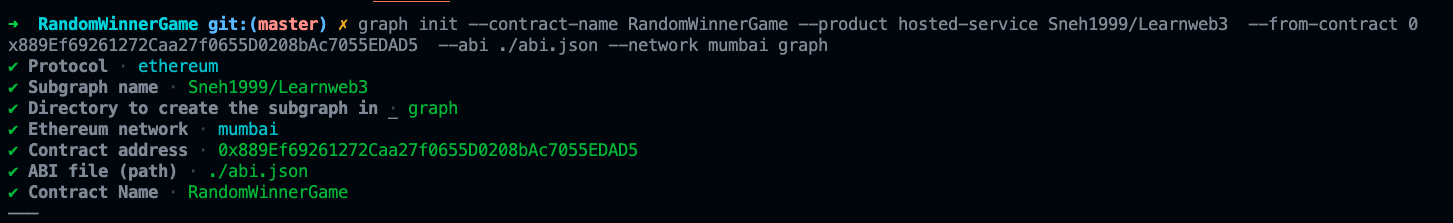
- 对于部署密钥,进入 The Graph's Hosted Service,点击
My Dashboard,复制Access Token并将其粘贴到Deploy Key上。
graph auth
- 现在要执行的最后两条命令是
cd graph
yarn deploy你可以回到The Graph's Hosted Service ,点击 My Dashboard,你将能够看到你的图表,因为它现在已经部署了🚀 👀
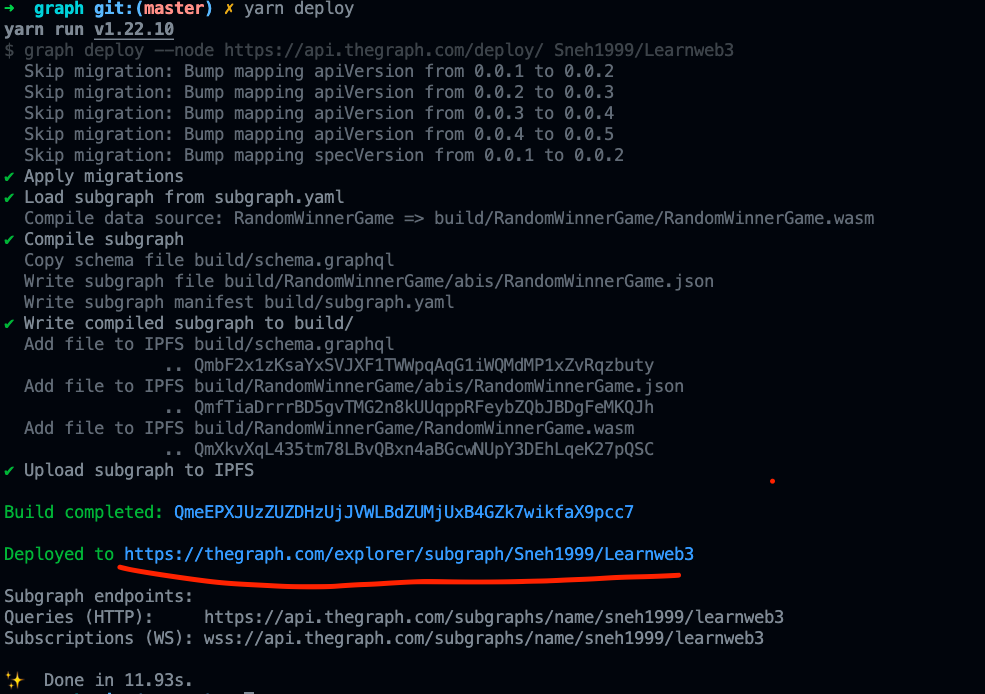
你已经部署了你的第一个图表!!!。
现在,有趣的部分来了,我们将把The Graph提供给我们的默认代码修改为可以帮助我们跟踪合同事件的代码。
让我们开始吧
-
打开
graph文件夹中的subgraph.yaml,在abi: RamdomWinnerGame一行之后添加一个startBlock到yaml文件中。为了获得startBlock,你需要到 Mumbai PolygonScan中搜索你的合同地址,然后你需要复制你的合同所在区块的区块号。 -
开始区块没有默认设置,但因为我们知道我们只需要跟踪合同部署区块的事件,所以我们不需要同步整个区块链,只需要同步合同部署后的部分来跟踪事件。
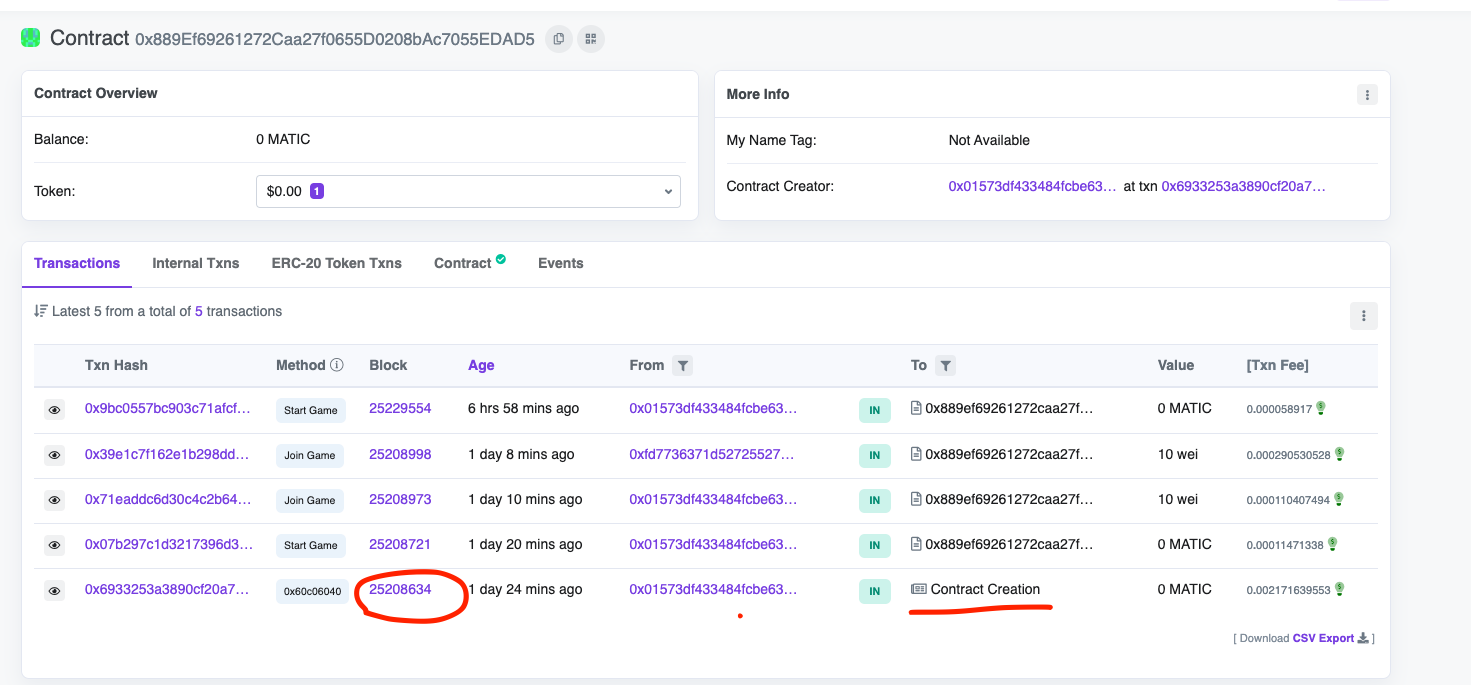
source:
address: "0x889Ef69261272Caa27f0655D0208bAc7055EDAD5"
abi: RandomWinnerGame
startBlock: BLOCK_NUMBER你的最终文件应该是这样的
- 好了,现在是时候创建一些
Entities了。Entities是定义你的数据将如何存储在The Graph's nodes的结构的对象。如果你想阅读更多关于它们的信息,请点击这个链接
我们将需要一个Entity,它可以涵盖我们事件中的所有变量,以便我们可以跟踪所有的变量。打开schema.graphql文件,用以下几行代码替换已有的代码。
type Game @entity {
id: ID!
maxPlayers: Int!
entryFee: BigInt!
winner: Bytes
requestId: Bytes
players: [Bytes!]!
}- 这里的
ID是一个游戏的唯一标识符,将等同于我们在合同中的gameId变量。 maxPlayers将记录这个游戏中允许有多少最大的玩家。entryFee是进入游戏的费用,它是一个BigInt,因为在我们的合同中,entryFee是一个uint256,它是一个BigNumber。winner是游戏中赢家的地址,定义为Bytes,因为地址是一个十六进制的字符串。requestId也是一个十六进制的字符串,因此被定义为Bytesplayers是游戏中玩家的地址列表,由于每个地址都是一个十六进制的字符串,我们将玩家符号化为一个字节数组。- 另外,请注意
!表示必须的变量,我们将maxPlayers、entryFee、player和id标记为必须,因为当Game最初启动时,它将发出GameStarted事件,该事件将发出这三个变量(maxPlayers、entryFee和id),所以没有这三个变量,一个Game实体永远无法被创建,对于player阵列,它将被我们初始化为一个空阵列。 winner和requestId将与GameEnded事件一起出现,players将跟踪每个player address,这是由PlayerJoined事件发出的。
如果你想了解更多的类型,你可以访问这个链接
好了,现在我们已经让the graph知道我们将追踪什么样的数据,以及它将包含什么🥳 🥳 🥳
现在是查询这些数据的时候了🎉
Graph 有一个惊人的功能,给定的Entity可以为你自动生成大块的代码!!。
这不是很神奇吗?让我们使用这个功能。在你的终端指向 the graph目录,执行以下命令
yarn codegen- 在这之后,
The Graph将为你创建大部分的代码,希望你的映射。 - 如果你看一下
src中的mapping.ts,graph 会为你创建一些函数,每个都指向你在合同中创建的一个事件。 - 每次Graph发现与这些函数有关的事件时,这些函数都会被调用。
- 我们将为这些函数添加一些代码,这样我们就可以在事件来临时存储数据。
- 复制以下几行代码到你的
mapping.ts中
import { BigInt } from "@graphprotocol/graph-ts";
import {
PlayerJoined,
GameEnded,
GameStarted,
OwnershipTransferred,
} from "../generated/RandomWinnerGame/RandomWinnerGame";
import { Game } from "../generated/schema";
export function handleGameEnded(event: GameEnded): void {
// Entities can be loaded from the store using a string ID; this ID
// needs to be unique across all entities of the same type
let entity = Game.load(event.params.gameId.toString());
// Entities only exist after they have been saved to the store;
// `null` checks allow to create entities on demand
if (!entity) {
return;
}
// Entity fields can be set based on event parameters
entity.winner = event.params.winner;
entity.requestId = event.params.requestId;
// Entities can be written to the store with `.save()`
entity.save();
}
export function handlePlayerJoined(event: PlayerJoined): void {
// Entities can be loaded from the store using a string ID; this ID
// needs to be unique across all entities of the same type
let entity = Game.load(event.params.gameId.toString());
// Entities only exist after they have been saved to the store;
// `null` checks allow to create entities on demand
if (!entity) {
return;
}
// Entity fields can be set based on event parameters
let newPlayers = entity.players;
newPlayers.push(event.params.player);
entity.players = newPlayers;
// Entities can be written to the store with `.save()`
entity.save();
}
export function handleGameStarted(event: GameStarted): void {
// Entities can be loaded from the store using a string ID; this ID
// needs to be unique across all entities of the same type
let entity = Game.load(event.params.gameId.toString());
// Entities only exist after they have been saved to the store;
// `null` checks allow to create entities on demand
if (!entity) {
entity = new Game(event.params.gameId.toString());
entity.players = [];
}
// Entity fields can be set based on event parameters
entity.maxPlayers = event.params.maxPlayers;
entity.entryFee = event.params.entryFee;
// Entities can be written to the store with `.save()`
entity.save();
}
export function handleOwnershipTransferred(event: OwnershipTransferred): void {}-
让我们了解
handleGameEnded函数中发生了什么- 它接受
GameEnded事件并期望void被返回,这意味着函数没有返回任何内容 - 它从
Graph的数据库中加载一个Game对象,其ID等于Graph检测到的事件中存在的gameId。 - 如果具有给定的实体
id不存在,则从函数返回并且不做任何事情 - 如果存在,则将事件中的获胜者和 requestId 设置到我们的游戏对象中(注意
GameEnded事件有获胜者和 requestId) - 然后将这个更新的游戏对象保存回
Graph's DB - 对于每个游戏,都会有一个独特的
Game对象,该对象将具有独特的gameId
- 它接受
-
现在让我们看看在
handlePlayerJoined中发生了什么。- 它从Graph的数据库中加载一个
Game对象,其ID等于Graph检测到的事件中存在的gameId。 - 如果一个具有给定
ID的实体不存在,则从函数中返回,不做任何事情。 - 为了实际更新玩家的数组,我们需要重新分配包含数组的实体上的属性(即玩家),类似于我们给实体上的其他属性(如maxPlayers)赋值的方法。因此,我们需要创建一个临时数组,其中包含所有现有的entity.player元素,推送到该数组,并重新分配entity.player,使其等于新数组。
- 然后将这个更新的游戏对象保存到
Graph's DB中。
- 它从Graph的数据库中加载一个
-
现在让我们看看
handleGameStarted中发生了什么- 它从Graph的数据库中加载一个
Game对象,其ID等于Graph检测到的事件中存在的gameId。 - 如果一个这样的实体不存在,就创建一个新的,同时初始化玩家数组
- 然后在我们的游戏对象中设置事件中的maxPlayer和entryFee。
- 将这个更新的游戏对象保存到
Graph's DB。
- 它从Graph的数据库中加载一个
现在你可以去你的终端,指向graph文件夹,执行以下命令。
yarn deploy- 部署好The Graph's Hosted Service,点击
My Dashboard,你就可以看到你的图表了。 - 点击你的图表,确保它显示已同步,如果没有,请等待它被同步后再继续。
网站
-
为了开发该网站,我们将使用React 和Next Js.。React是一个用于制作网站的javascript框架,而Next Js是建立在React之上的。
-
首先,你将需要创建一个新的
next应用程序。你的文件夹结构应该是这样的
- RandomWinnerGame
- graph
- hardhat-tutorial
- next-app
- abi.json- 要创建这个
next-app,在终端指向RandomWinnerGame文件夹并输入
npx create-next-app@latest并对所有问题按回车键
- 现在要运行该应用程序,在终端执行这些命令
cd my-app
npm run dev- 现在让我们安装Web3Modal库(https://github.com/Web3Modal/web3modal)。Web3Modal是一个易于使用的库,帮助开发者通过简单的可定制配置在他们的应用程序中添加对多个供应商的支持。默认情况下,Web3Modal库支持注入的提供者,如(Metamask、Dapper、Gnosis Safe、Frame、Web3 Browsers等),你也可以轻松配置该库以支持Portis、Fortmatic、Squarelink、Torus、Authereum、D'CENT Wallet和Arkane。打开终端,指向
my-app目录,执行以下命令
npm install web3modal- 在同一终端中也安装
ethers.js
npm i ethers- 我们还将使用
axios来向the graph,发送请求,所以让我们安装它吧
npm i axios-
在你的公共文件夹中,下载这张图片。确保下载的图像名称为
randomWinner.png。 -
现在去
style文件夹,用以下代码替换Home.modules.css文件的所有内容,这将给你的dapp添加一些样式。 -
.main { min-height: 90vh; display: flex; flex-direction: row; justify-content: center; align-items: center; font-family: "Courier New", Courier, monospace; } .footer { display: flex; padding: 2rem 0; border-top: 1px solid #eaeaea; justify-content: center; align-items: center; } .input { width: 200px; height: 100%; padding: 1%; margin: 2%; box-shadow: 0 0 15px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.06); border-radius: 10px; } .image { width: 70%; height: 50%; margin-left: 20%; } .title { font-size: 2rem; margin: 2rem 1rem; } .description { line-height: 1; margin: 2rem 1rem; font-size: 1.2rem; } .log { line-height: 1rem; margin: 1rem 1rem; font-size: 1rem; } .button { border-radius: 4px; background-color: blue; border: none; color: #ffffff; font-size: 15px; padding: 8px; width: 200px; cursor: pointer; margin: 2rem 1rem; } @media (max-width: 1000px) { .main { width: 100%; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; } } -
现在让我们写一些代码来查询 the graph,,在你的
my-app文件夹内创建一个新的文件夹,并命名为queries。在queries文件夹中创建一个名为index.js的新文件,并粘贴以下几行代码。
export function FETCH_CREATED_GAME() {
return `query {
games(orderBy:id, orderDirection:desc, first: 1) {
id
maxPlayers
entryFee
winner
players
}
}`;
}- 正如你所看到的,我们创建了一个
GraphQL查询,我们说我们想要一个game对象,其中的数据按Id(也就是gameId)降序排列,我们想从这个有序的数据中获得第一个游戏。 - 让我们用一个例子来简化这个问题。假设你有三个游戏对象存储在
The Graph's内。
{
"id": "1",
"maxPlayers": 2,
"entryFee": "10000000000000",
"winner": "0xdb6eaffa95899b53b27086bd784f3bbfd58ff843"
},
{
"id": "2",
"maxPlayers": 2,
"entryFee": "10000000000000",
"winner": "0x01573df433484fcbe6325a0c6e051dc62ab107d1"
},
{
"id": "3",
"maxPlayers": 2,
"entryFee": "100000000000000",
"winner": "0x01573df433484fcbe6325a0c6e051dc62ab107d1"
},
{
"id": "4",
"maxPlayers": 2,
"entryFee": "10",
"winner": null
}-
现在你希望每次都是最新的游戏。为了得到最新的游戏,你首先要按id排序,然后把这些数据按降序排列,这样gameId 4就可以排在最前面(它将是当前的游戏),然后我们说
first:1,因为我们只想要gameId 4对象,我们不关心旧游戏。 -
你实际上可以看到这个查询在
the graph'的托管服务上工作。让我们试着这样做。 -
我已经部署了一个graph,让我们看看graph,并使用查询来查询它,进入这个链接
-
用我们的查询替换示例查询,并点击紫色的播放按钮
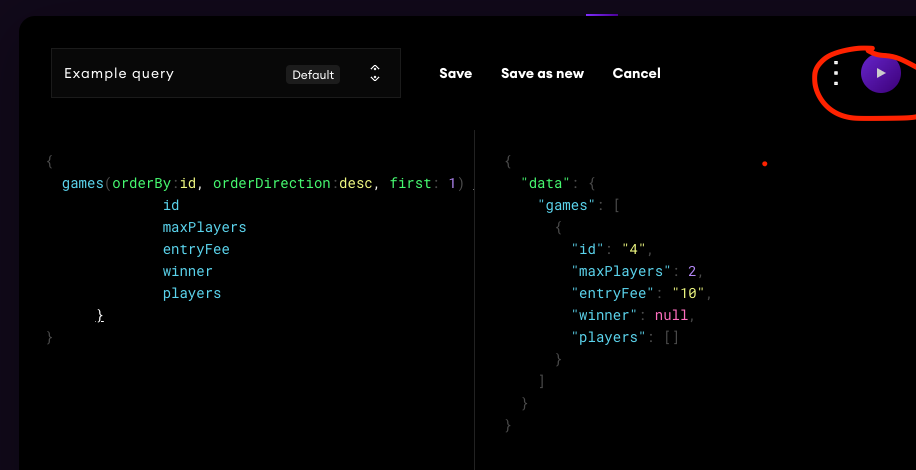
-
你可以看到我的graph 出现了一些数据,游戏的ID是4。
-
简单吧?是的,确实如此 😎
-
你可以通过
My dashboard进入你的图表,做同样的事情🚀,这将很有趣。 -
让我们继续...
-
通过
Graph已经提供的UI进行操作是很好的,但是要在我们的前端使用这个,我们需要写一个axios post request,这样我们就可以从 the graph中获得这些数据。 -
创建一个名为
utils的新文件夹,并在该文件夹中创建一个名为index.js的新文件。在index.js文件中复制以下几行代码。
import axios from "axios";
export async function subgraphQuery(query) {
try {
// Replace YOUR-SUBGRAPH-URL with the url of your subgraph
const SUBGRAPH_URL = "YOUR-SUBGRAPH-URL";
const response = await axios.post(SUBGRAPH_URL, {
query,
});
if (response.data.errors) {
console.error(response.data.errors);
throw new Error(`Error making subgraph query ${response.data.errors}`);
}
return response.data.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
throw new Error(`Could not query the subgraph ${error.message}`);
}
}- 让我们试着理解这个函数中发生了什么
- 它需要一个SUBGRAPH_URL,你需要将 "YOUR-SUBGRAPH-URL "替换为你的子图的URL,你可以通过进入图的hosted service ,点击
My dashboard,然后点击你的图来获得。复制Queries(HTTP)下的网址
- 它需要一个SUBGRAPH_URL,你需要将 "YOUR-SUBGRAPH-URL "替换为你的子图的URL,你可以通过进入图的hosted service ,点击
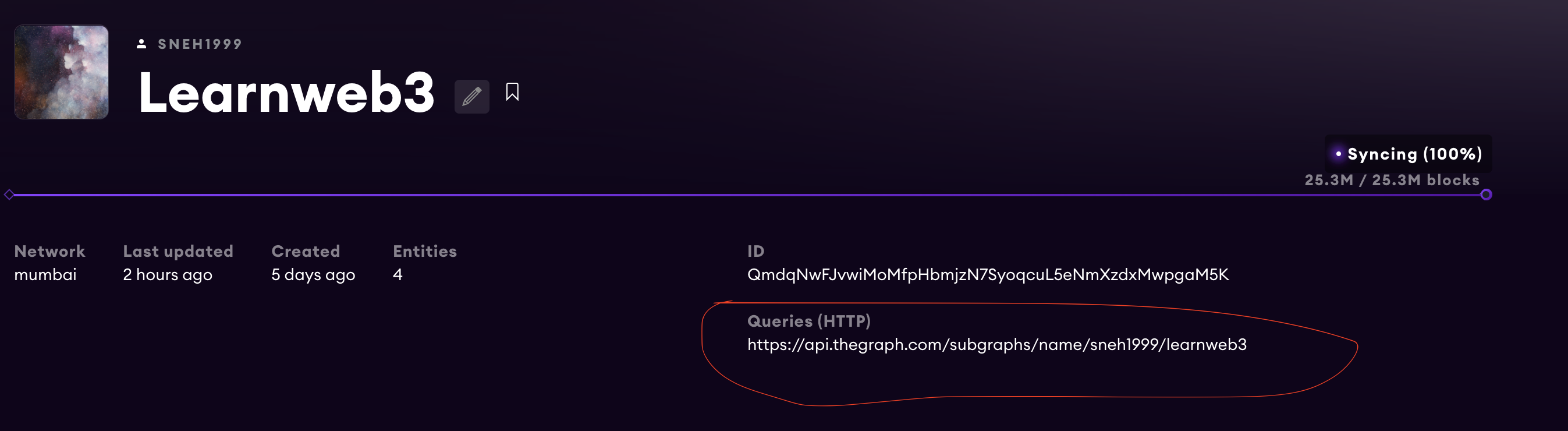
然后它用我们用axios post request创建的查询来调用这个网址
然后,它处理任何错误,如果没有错误,则发回答复。
- 现在打开page文件夹下的index.js文件,粘贴以下代码,代码的解释可以在评论中找到。
import { BigNumber, Contract, ethers, providers, utils } from "ethers";
import Head from "next/head";
import React, { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import Web3Modal from "web3modal";
import { abi, RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS } from "../constants";
import { FETCH_CREATED_GAME } from "../queries";
import styles from "../styles/Home.module.css";
import { subgraphQuery } from "../utils";
export default function Home() {
const zero = BigNumber.from("0");
// walletConnected keep track of whether the user's wallet is connected or not
const [walletConnected, setWalletConnected] = useState(false);
// loading is set to true when we are waiting for a transaction to get mined
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
// boolean to keep track of whether the current connected account is owner or not
const [isOwner, setIsOwner] = useState(false);
// entryFee is the ether required to enter a game
const [entryFee, setEntryFee] = useState(zero);
// maxPlayers is the max number of players that can play the game
const [maxPlayers, setMaxPlayers] = useState(0);
// Checks if a game started or not
const [gameStarted, setGameStarted] = useState(false);
// Players that joined the game
const [players, setPlayers] = useState([]);
// Winner of the game
const [winner, setWinner] = useState();
// Keep a track of all the logs for a given game
const [logs, setLogs] = useState([]);
// Create a reference to the Web3 Modal (used for connecting to Metamask) which persists as long as the page is open
const web3ModalRef = useRef();
// This is used to force react to re render the page when we want to
// in our case we will use force update to show new logs
const forceUpdate = React.useReducer(() => ({}), {})[1];
/*
connectWallet: Connects the MetaMask wallet
*/
const connectWallet = async () => {
try {
// Get the provider from web3Modal, which in our case is MetaMask
// When used for the first time, it prompts the user to connect their wallet
await getProviderOrSigner();
setWalletConnected(true);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
};
/**
* Returns a Provider or Signer object representing the Ethereum RPC with or without the
* signing capabilities of metamask attached
*
* A `Provider` is needed to interact with the blockchain - reading transactions, reading balances, reading state, etc.
*
* A `Signer` is a special type of Provider used in case a `write` transaction needs to be made to the blockchain, which involves the connected account
* needing to make a digital signature to authorize the transaction being sent. Metamask exposes a Signer API to allow your website to
* request signatures from the user using Signer functions.
*
* @param {*} needSigner - True if you need the signer, default false otherwise
*/
const getProviderOrSigner = async (needSigner = false) => {
// Connect to Metamask
// Since we store `web3Modal` as a reference, we need to access the `current` value to get access to the underlying object
const provider = await web3ModalRef.current.connect();
const web3Provider = new providers.Web3Provider(provider);
// If user is not connected to the Mumbai network, let them know and throw an error
const { chainId } = await web3Provider.getNetwork();
if (chainId !== 80001) {
window.alert("Change the network to Mumbai");
throw new Error("Change network to Mumbai");
}
if (needSigner) {
const signer = web3Provider.getSigner();
return signer;
}
return web3Provider;
};
/**
* startGame: Is called by the owner to start the game
*/
const startGame = async () => {
try {
// Get the signer from web3Modal, which in our case is MetaMask
// No need for the Signer here, as we are only reading state from the blockchain
const signer = await getProviderOrSigner(true);
// We connect to the Contract using a signer because we want the owner to
// sign the transaction
const randomGameNFTContract = new Contract(
RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
signer
);
setLoading(true);
// call the startGame function from the contract
const tx = await randomGameNFTContract.startGame(maxPlayers, entryFee);
await tx.wait();
setLoading(false);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
setLoading(false);
}
};
/**
* startGame: Is called by a player to join the game
*/
const joinGame = async () => {
try {
// Get the signer from web3Modal, which in our case is MetaMask
// No need for the Signer here, as we are only reading state from the blockchain
const signer = await getProviderOrSigner(true);
// We connect to the Contract using a signer because we want the owner to
// sign the transaction
const randomGameNFTContract = new Contract(
RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
signer
);
setLoading(true);
// call the startGame function from the contract
const tx = await randomGameNFTContract.joinGame({
value: entryFee,
});
await tx.wait();
setLoading(false);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
setLoading(false);
}
};
/**
* checkIfGameStarted checks if the game has started or not and intializes the logs
* for the game
*/
const checkIfGameStarted = async () => {
try {
// Get the provider from web3Modal, which in our case is MetaMask
// No need for the Signer here, as we are only reading state from the blockchain
const provider = await getProviderOrSigner();
// We connect to the Contract using a Provider, so we will only
// have read-only access to the Contract
const randomGameNFTContract = new Contract(
RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
provider
);
// read the gameStarted boolean from the contract
const _gameStarted = await randomGameNFTContract.gameStarted();
const _gameArray = await subgraphQuery(FETCH_CREATED_GAME());
const _game = _gameArray.games[0];
let _logs = [];
// Initialize the logs array and query the graph for current gameID
if (_gameStarted) {
_logs = [`Game has started with ID: ${_game.id}`];
if (_game.players && _game.players.length > 0) {
_logs.push(
`${_game.players.length} / ${_game.maxPlayers} already joined 👀 `
);
_game.players.forEach((player) => {
_logs.push(`${player} joined 🏃♂️`);
});
}
setEntryFee(BigNumber.from(_game.entryFee));
setMaxPlayers(_game.maxPlayers);
} else if (!gameStarted && _game.winner) {
_logs = [
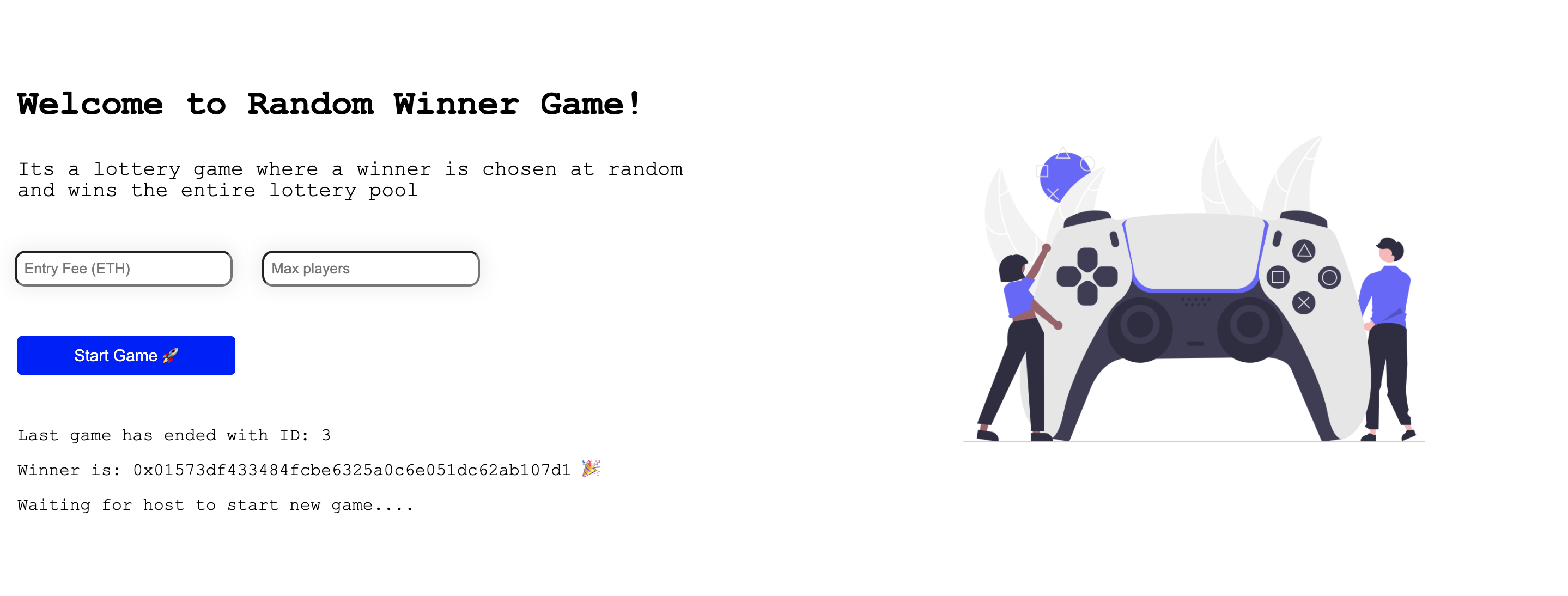
`Last game has ended with ID: ${_game.id}`,
`Winner is: ${_game.winner} 🎉 `,
`Waiting for host to start new game....`,
];
setWinner(_game.winner);
}
setLogs(_logs);
setPlayers(_game.players);
setGameStarted(_gameStarted);
forceUpdate();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
/**
* getOwner: calls the contract to retrieve the owner
*/
const getOwner = async () => {
try {
// Get the provider from web3Modal, which in our case is MetaMask
// No need for the Signer here, as we are only reading state from the blockchain
const provider = await getProviderOrSigner();
// We connect to the Contract using a Provider, so we will only
// have read-only access to the Contract
const randomGameNFTContract = new Contract(
RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS,
abi,
provider
);
// call the owner function from the contract
const _owner = await randomGameNFTContract.owner();
// We will get the signer now to extract the address of the currently connected MetaMask account
const signer = await getProviderOrSigner(true);
// Get the address associated to the signer which is connected to MetaMask
const address = await signer.getAddress();
if (address.toLowerCase() === _owner.toLowerCase()) {
setIsOwner(true);
}
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.message);
}
};
// useEffects are used to react to changes in state of the website
// The array at the end of function call represents what state changes will trigger this effect
// In this case, whenever the value of `walletConnected` changes - this effect will be called
useEffect(() => {
// if wallet is not connected, create a new instance of Web3Modal and connect the MetaMask wallet
if (!walletConnected) {
// Assign the Web3Modal class to the reference object by setting it's `current` value
// The `current` value is persisted throughout as long as this page is open
web3ModalRef.current = new Web3Modal({
network: "mumbai",
providerOptions: {},
disableInjectedProvider: false,
});
connectWallet();
getOwner();
checkIfGameStarted();
setInterval(() => {
checkIfGameStarted();
}, 2000);
}
}, [walletConnected]);
/*
renderButton: Returns a button based on the state of the dapp
*/
const renderButton = () => {
// If wallet is not connected, return a button which allows them to connect their wllet
if (!walletConnected) {
return (
<button onClick={connectWallet} className={styles.button}>
Connect your wallet
</button>
);
}
// If we are currently waiting for something, return a loading button
if (loading) {
return <button className={styles.button}>Loading...</button>;
}
// Render when the game has started
if (gameStarted) {
if (players.length === maxPlayers) {
return (
<button className={styles.button} disabled>
Choosing winner...
</button>
);
}
return (
<div>
<button className={styles.button} onClick={joinGame}>
Join Game 🚀
</button>
</div>
);
}
// Start the game
if (isOwner && !gameStarted) {
return (
<div>
<input
type="number"
className={styles.input}
onChange={(e) => {
// The user will enter the value in ether, we will need to convert
// it to WEI using parseEther
setEntryFee(
e.target.value >= 0
? utils.parseEther(e.target.value.toString())
: zero
);
}}
placeholder="Entry Fee (ETH)"
/>
<input
type="number"
className={styles.input}
onChange={(e) => {
// The user will enter the value in ether, we will need to convert
// it to WEI using parseEther
setMaxPlayers(e.target.value ?? 0);
}}
placeholder="Max players"
/>
<button className={styles.button} onClick={startGame}>
Start Game 🚀
</button>
</div>
);
}
};
return (
<div>
<Head>
<title>LW3Punks</title>
<meta name="description" content="LW3Punks-Dapp" />
<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.ico" />
</Head>
<div className={styles.main}>
<div>
<h1 className={styles.title}>Welcome to Random Winner Game!</h1>
<div className={styles.description}>
Its a lottery game where a winner is chosen at random and wins the
entire lottery pool
</div>
{renderButton()}
{logs &&
logs.map((log, index) => (
<div className={styles.log} key={index}>
{log}
</div>
))}
</div>
<div>
<img className={styles.image} src="./randomWinner.png" />
</div>
</div>
<footer className={styles.footer}>
Made with ❤ by Your Name
</footer>
</div>
);
}-
现在在my-app文件夹下创建一个新的文件夹,并将其命名为
constants。 -
在
constants文件夹中创建一个index.js文件,并粘贴以下代码。- 替换
"address of your RandomWinnerGame contract"与您部署和保存到您的记事本的RandomWinnerGame合同的地址。 - 替换
---your abi---为你的RandomWinnerGame合同的ABI。为了得到你的合同的ABI,去你的hardhat-tutorial/artifacts/contracts/RandomWinnerGame.sol文件夹,从RandomWinnerGame.json文件得到"abi"键下的数组标记。
- 替换
export const abi =---your abi---
export const RANDOM_GAME_NFT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS = "address of your RandomWinnerGame contract"- 现在,在你的终端,也就是指向
my-app文件夹,执行
npm run dev- 你的RandomWinnerGame dapp现在应该没有错误地工作了 🚀
- 玩游戏玩得开心
推送到github
在继续之前,请确保你已经将所有的代码推送到github :)
部署你的dApp
现在我们将部署你的DApp,这样大家就可以看到你的网站,你也可以和所有LearnWeb3 DAO的朋友分享。
-
到https://vercel.com/,用你的GitHub登录。
-
然后点击
New Project按钮,然后选择你的RandomWinnerGame 仓库。 -
在配置你的新项目时,Vercel将允许你自定义你的
Root Directory -
点击
Root Directory旁边的Edit,并将其设置为my-app -
选择框架为
Next.js -
点击部署

-
现在,你可以通过进入你的仪表板,选择你的项目,并从那里复制
domain来查看你部署的网站! -
与大家分享这个域名,让大家一起玩游戏 🚀🚀🚀
原文: https://www.learnweb3.io/tracks/junior/the-graph-protocol

- 期待 POAP 的新篇章 55 浏览
- 以太坊:区块链的根本价值与应用 89 浏览
- 生产级的全同步可组合性现已上线 41 浏览
- 加密货币是AI代理的银行 138 浏览
- 34 个资源:探索、构建和部署基于 ERC-8004 的信任最小化 AI 代理 194 浏览
- 以太坊:应用层开放思维,不弃核心原则 240 浏览
- 理解区块级访问列表 335 浏览
- 以太坊 2029 Strawmap 傻瓜指南 312 浏览
- 以太坊:构建去极权化的数字庇护所 342 浏览
- Orca Whirlpools 对比 Uniswap V3 — ImmuneBytes 221 浏览
- 跨区块链的可升级性模式分析 – ImmuneBytes 249 浏览
- Solana 对比 Near 区块链 – ImmuneBytes 255 浏览

