solana序列数据
- 想样
- 发布于 2024-11-26 16:25
- 阅读 2397
当我们谈论序列化时,我们指的是数据的序列化和反序列化。序列化在Solana程序和程序账户的生命周期中的几个点上起着作用:将指令数据序列化到客户端上在程序中反序列化指令数据将账户数据序列化到程序中在客户端上反序列化账户数据重要的是,上述操作都应该采用相同的序列化方法。下面的示例演示了
<!--StartFragment-->
当我们谈论序列化时,我们指的是数据的序列化和反序列化。
序列化在Solana程序和程序账户的生命周期中的几个点上起着作用:
- 将指令数据序列化到客户端上
- 在程序中反序列化指令数据
- 将账户数据序列化到程序中
- 在客户端上反序列化账户数据
重要的是,上述操作都应该采用相同的序列化方法。下面的示例演示了使用[Borsh]进行序列化。
本文档的其余部分中的示例摘录自[Solana CLI 程序模板]
设置Borsh序列化
为了使用Borsh进行序列化,需要在Rust程序、Rust客户端、节点和/或Python客户端中设置Borsh库。
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
[package]
name = "cli-program-template"
version = "0.1.5"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
publish = false
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
clap = "2.33.3"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
serde = { version = "1.0.125", features = ["derive"] }
serde_yaml = "0.8.17"
sol-template-shared = {path = "shared"}
solana-clap-utils = "1.8.2"
solana-cli-config = "1.8.2"
solana-client = "1.8.2"
solana-logger = "1.8.2"
solana-remote-wallet = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full"] }
[workspace]
members = [
"program",
"shared",
]
[dev-dependencies]
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
solana-validator = "1.8.2"
solana-streamer = "1.8.2"<!--EndFragment-->
<!--StartFragment-->
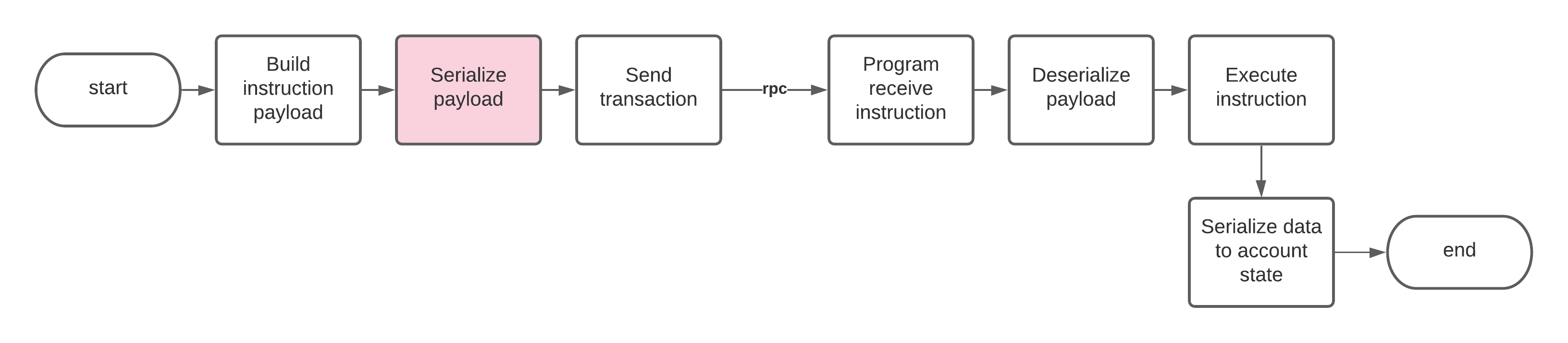
如何序列化客户端上的指令数据
<!--EndFragment-->
 <!--StartFragment-->
<!--StartFragment-->
如果你要将出站指令数据序列化并发送给程序,它必须与程序反序列化入站指令数据的方式保持一致。
在此模板中,指令数据块是一个包含序列化数组的数据块,例如:
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
| Instruction (Variant index) | Serialized Key | Serialized Value |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize (0) | not applicable for instruction | not applicable for instruction |
| Mint (1) | "foo" | "bar" |
| Transfer (2) | "foo" | not applicable for instruction |
| Burn (2) | "foo" | not applicable for instruction |
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
在下面的示例中,我们假设程序拥有的账户已经初始化完成。
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
// Include borsh functionality
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
// Get Solana
import {
Keypair,
Connection,
PublicKey,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
// Our instruction payload vocabulary
class Payload extends Assignable {}
// Borsh needs a schema describing the payload
const payloadSchema = new Map([
[
Payload,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["id", "u8"],
["key", "string"],
["value", "string"],
],
},
],
]);
// Instruction variant indexes
enum InstructionVariant {
InitializeAccount = 0,
MintKeypair,
TransferKeypair,
BurnKeypair,
}
/**
* Mint a key value pair to account
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} progId - Sample Program public key
* @param {PublicKey} account - Target program owned account for Mint
* @param {Keypair} wallet - Wallet for signing and payment
* @param {string} mintKey - The key being minted key
* @param {string} mintValue - The value being minted
* @return {Promise<Keypair>} - Keypair
*/
export async function mintKV(
connection: Connection,
progId: PublicKey,
account: PublicKey,
wallet: Keypair,
mintKey: string,
mintValue: string
): Promise<string> {
// Construct the payload
const mint = new Payload({
id: InstructionVariant.MintKeypair,
key: mintKey, // 'ts key'
value: mintValue, // 'ts first value'
});
// Serialize the payload
const mintSerBuf = Buffer.from(serialize(payloadSchema, mint));
// console.log(mintSerBuf)
// => <Buffer 01 06 00 00 00 74 73 20 6b 65 79 0e 00 00 00 74 73 20 66 69 72 73 74 20 76 61 6c 75 65>
// let mintPayloadCopy = deserialize(schema, Payload, mintSerBuf)
// console.log(mintPayloadCopy)
// => Payload { id: 1, key: 'ts key', value: 'ts first value' }
// Create Solana Instruction
const instruction = new TransactionInstruction({
data: mintSerBuf,
keys: [
{ pubkey: account, isSigner: false, isWritable: true },
{ pubkey: wallet.publicKey, isSigner: false, isWritable: false },
],
programId: progId,
});
// Send Solana Transaction
const transactionSignature = await sendAndConfirmTransaction(
connection,
new Transaction().add(instruction),
[wallet],
{
commitment: "singleGossip",
preflightCommitment: "singleGossip",
}
);
console.log("Signature = ", transactionSignature);
return transactionSignature;
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
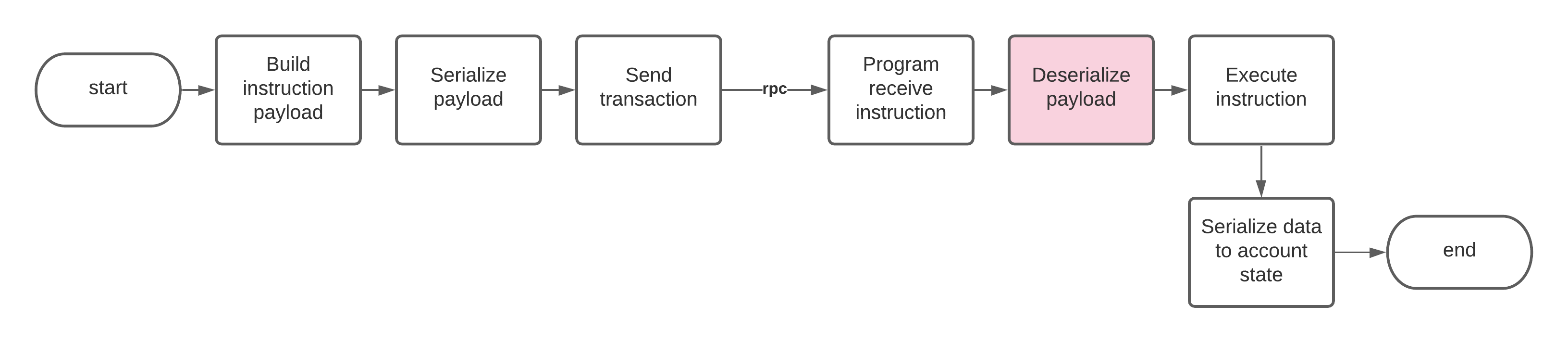
如何在程序中反序列化指令数据
<!--EndFragment-->
 <!--StartFragment-->
<!--StartFragment-->
//! instruction Contains the main ProgramInstruction enum
use {
crate::error::SampleError, borsh::BorshDeserialize, solana_program::program_error::ProgramError,
};
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq)]
/// All custom program instructions
pub enum ProgramInstruction {
InitializeAccount,
MintToAccount { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccounts { key: String },
BurnFromAccount { key: String },
MintToAccountWithFee { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: String },
BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: String },
}
/// Generic Payload Deserialization
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, Debug)]
struct Payload {
variant: u8,
arg1: String,
arg2: String,
}
impl ProgramInstruction {
/// Unpack inbound buffer to associated Instruction
/// The expected format for input is a Borsh serialized vector
pub fn unpack(input: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
let payload = Payload::try_from_slice(input).unwrap();
match payload.variant {
0 => Ok(ProgramInstruction::InitializeAccount),
1 => Ok(Self::MintToAccount {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
2 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccounts { key: payload.arg1 }),
3 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccount { key: payload.arg1 }),
4 => Ok(Self::MintToAccountWithFee {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
5 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
6 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
_ => Err(SampleError::DeserializationFailure.into()),
}
}
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
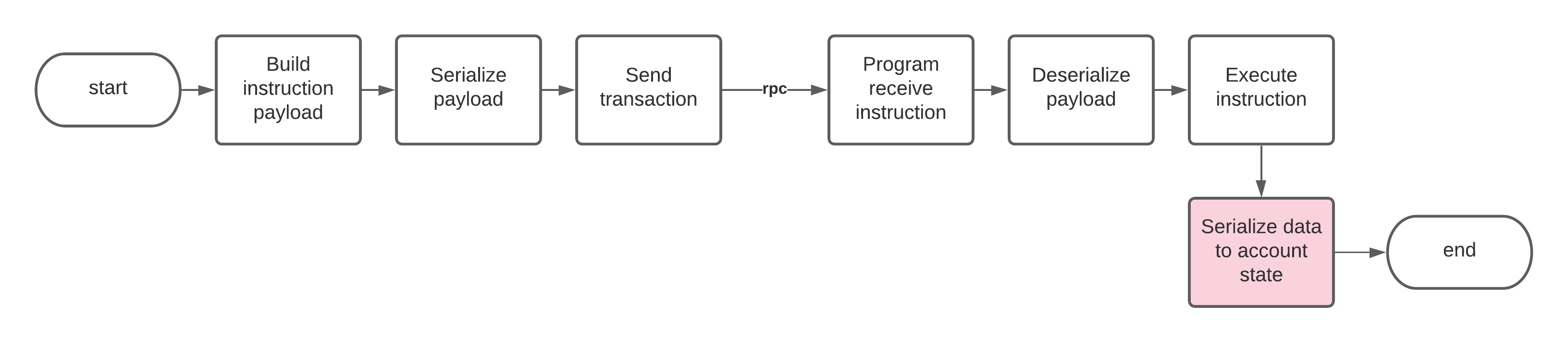
如何在程序中序列化账户数据
<!--EndFragment-->
 <!--StartFragment-->
<!--StartFragment-->
程序账户数据块(来自示例仓库)的布局如下: <!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
| Byte 0 | Bytes 1-4 | Remaining Byte up to 1019 |
|---|---|---|
| Initialized flag | length of serialized BTreeMap | BTreeMap (where key value pairs are stored) |
Pack
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
关于 [Packopen in new window] trait
可以更容易地隐藏账户数据序列化/反序列化的细节,使你的核心程序指令处理代码更简洁。因此,不需要将所有的序列化/反序列化逻辑放在程序处理代码中,而是将这些细节封装在以下三个函数中:
unpack_unchecked- 允许你对账户进行反序列化,而无需检查它是否已被初始化。当实际处理初始化函数(变体索引为0)时,这非常有用。unpack- 调用你的Pack实现的unpack_from_slice函数,并检查账户是否已被初始化。pack- 调用您的Pack实现的pack_into_slice函数。
下面是我们示例程序的Pack trait实现。随后是使用Borsh进行账户数据处理的示例。
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
//! @brief account_state manages account data
use crate::error::SampleError;
use sol_template_shared::ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
use solana_program::{
entrypoint::ProgramResult,
program_error::ProgramError,
program_pack::{IsInitialized, Pack, Sealed},
};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
/// Maintains global accumulator
#[derive(Debug, Default, PartialEq)]
pub struct ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: BTreeMap<String, String>,
}
impl ProgramAccountState {
/// Returns indicator if this account has been initialized
pub fn set_initialized(&mut self) {
self.is_initialized = true;
}
/// Adds a new key/value pair to the account
pub fn add(&mut self, key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(&key) {
true => Err(SampleError::KeyAlreadyExists.into()),
false => {
self.btree_storage.insert(key, value);
Ok(())
}
}
}
/// Removes a key from account and returns the keys value
pub fn remove(&mut self, key: &str) -> Result<String, SampleError> {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(key) {
true => Ok(self.btree_storage.remove(key).unwrap()),
false => Err(SampleError::KeyNotFoundInAccount),
}
}
}
impl Sealed for ProgramAccountState {}
// Pack expects the implementation to satisfy whether the
// account is initialzed.
impl IsInitialized for ProgramAccountState {
fn is_initialized(&self) -> bool {
self.is_initialized
}
}
impl Pack for ProgramAccountState {
const LEN: usize = ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
/// Store 'state' of account to its data area
fn pack_into_slice(&self, dst: &mut [u8]) {
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice(self.is_initialized, &self.btree_storage, dst);
}
/// Retrieve 'state' of account from account data area
fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
match sol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice(src) {
Ok((is_initialized, btree_map)) => Ok(ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized,
btree_storage: btree_map,
}),
Err(_) => Err(ProgramError::InvalidAccountData),
}
}
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
序列化/反序列化
为了完成底层的序列化和反序列化:
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice- 进行序列化的地方sol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice- 进行反序列化的地方
请关注 在下面的示例中,我们在BTREE_LENGTH的数据布局中的BTREE_STORAGE之前有一个u32(4字节)的分区。这是因为在反序列化过程中,borsh会检查您正在反序列化的切片的长度是否与它实际读取的数据量一致,然后才进行对象的重组。下面演示的方法首先读取BTREE_LENGTH,以获取要从BTREE_STORAGE指针中slice的大小。
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
solana_program::program_memory::sol_memcpy,
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
/// Initialization flag size for account state
pub const INITIALIZED_BYTES: usize = 1;
/// Storage for the serialized size of the BTreeMap control
pub const BTREE_LENGTH: usize = 4;
/// Storage for the serialized BTreeMap container
pub const BTREE_STORAGE: usize = 1019;
/// Sum of all account state lengths
pub const ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE: usize = INITIALIZED_BYTES + BTREE_LENGTH + BTREE_STORAGE;
/// Packs the initialized flag and data content into destination slice
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn pack_into_slice(
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: &BTreeMap<String, String>,
dst: &mut [u8],
) {
let dst = array_mut_ref![dst, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_dst, data_len_dst, data_dst) =
mut_array_refs![dst, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
// Set the initialized flag
is_initialized_dst[0] = is_initialized as u8;
// Store the core data length and serialized content
let keyval_store_data = btree_storage.try_to_vec().unwrap();
let data_len = keyval_store_data.len();
if data_len < BTREE_STORAGE {
data_len_dst[..].copy_from_slice(&(data_len as u32).to_le_bytes());
sol_memcpy(data_dst, &keyval_store_data, data_len);
} else {
panic!();
}
}
/// Unpacks the data from slice and return the initialized flag and data content
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
用法
以下将所有内容整合在一起,并演示了程序与ProgramAccountState的交互,其中ProgramAccountState封装了初始化标志以及底层的BTreeMap用于存储键值对。
首先,当我们想要初始化一个全新的账户时:
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
/// Initialize a new program account, which is the first in AccountInfo array
fn initialize_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo]) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Initialize account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Here we use unpack_unchecked as we have yet to initialize
// Had we tried to use unpack it would fail because, well, chicken and egg
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack_unchecked(&account_data)?;
// We double check that we haven't already initialized this accounts data
// more than once. If we are good, we set the initialized flag
if account_state.is_initialized() {
return Err(SampleError::AlreadyInitializedState.into());
} else {
account_state.set_initialized();
}
// Finally, we store back to the accounts space
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data).unwrap();
Ok(())
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
现在,我们可以执行其他指令,下面的示例演示了从客户端发送指令来创建一个新的键值对:
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
/// Mint a key/pair to the programs account, which is the first in accounts
fn mint_keypair_to_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo], key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Mint to account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Unpacking an uninitialized account state will fail
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack(&account_data)?;
// Add the key value pair to the underlying BTreeMap
account_state.add(key, value)?;
// Finally, serialize back to the accounts data
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data)?;
Ok(())
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
如何在客户端中反序列化账户数据
客户端可以调用Solana来获取程序所拥有的账户,其中序列化的数据块是返回结果的一部分。进行反序列化需要了解数据块的布局。
账户数据的布局在[这里]已经被描述了。
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import {
Keypair,
AccountMeta,
Connection,
LAMPORTS_PER_SOL,
PublicKey,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
export class AccoundData extends Assignable {}
const dataSchema = new Map([
[
AccoundData,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["initialized", "u8"],
["tree_length", "u32"],
["map", { kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" }],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Fetch program account data
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} account - Public key for account whose data we want
* @return {Promise<AccoundData>} - Keypair
*/
export async function getAccountData(
connection: Connection,
account: PublicKey
): Promise<AccoundData> {
let nameAccount = await connection.getAccountInfo(account, "processed");
return deserializeUnchecked(dataSchema, AccoundData, nameAccount.data);
}<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
Solana TS/JS 常用映射
[Borsh Specification]中包含了大多数基本和复合数据类型的映射关系。
在TS/JS和Python中,关键是创建一个具有适当定义的Borsh模式,以便序列化和反序列化可以生成或遍历相应的输入。
首先,我们将演示在Typescript中对基本类型(数字、字符串)和复合类型(固定大小数组、Map)进行序列化,然后在Python中进行序列化,最后在Rust中进行等效的反序列化操作:
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { expect } from "chai";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* Primitive extends the Struct type from Solana Library
* for convenience of dynamic property setting
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
*/
class Primitive extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
}
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry() {
// Emulate BTreeMap
let map = new Map();
map.set("cookbook", "recipe");
map.set("recipe", "ingredient");
// Setup a Primitive for all basic and a few
// compound types
const value = new Primitive({
U8: 255,
U16: 65535,
U32: 4294967295,
FIXED_STRING_ARRAY: ["hello", "world"],
FIXED_U8_ARRAY: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
MAP_STRING_STRING: map,
});
// Define our schema
const schema = new Map([
[
Primitive,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["U8", "u8"],
["U16", "u16"],
["U32", "u32"],
["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY", ["string", 2]],
["FIXED_U8_ARRAY", ["u8", 5]],
[
"MAP_STRING_STRING",
{ kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" },
],
],
},
],
]);
console.log("Value = ", value);
// Serialize then deserialize
const dser = Buffer.from(serialize(schema, value));
console.log(dser);
const newValue = deserialize(schema, Primitive, dser);
// Viola!
console.log("New value = ", newValue);
console.log("Fixed string array = ", newValue["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Fixed u8 array = ", newValue["FIXED_U8_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Map = ", newValue["MAP_STRING_STRING"]);
}
entry();<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
高级构造
我们在之前的示例中展示了如何创建简单的负载(Payloads)。有时,Solana会使用某些特殊类型。本节将演示如何正确映射TS/JS和Rust之间的类型,以处理这些情况。 <!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
COption
<!--EndFragment--> <!--StartFragment-->
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* COption is meant to mirror the
* `solana_program::options::COption`
*
* This type stores a u32 flag (0 | 1) indicating
* the presence or not of a underlying PublicKey
*
* Similar to a Rust Option
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
* @implements {encode}
*/
class COption extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
/**
* Creates a COption from a PublicKey
* @param {PublicKey?} akey
* @returns {COption} COption
*/
static fromPublicKey(akey?: PublicKey): COption {
if (akey == undefined) {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 0,
pubKeyBuffer: new Uint8Array(32),
});
} else {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 1,
pubKeyBuffer: akey.toBytes(),
});
}
}
/**
* @returns {Buffer} Serialized COption (this)
*/
encode(): Buffer {
return Buffer.from(serialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this));
}
/**
* Safe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decode(data): COption {
return deserialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
/**
* Unsafe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decodeUnchecked(data): COption {
return deserializeUnchecked(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
}
/**
* Defines the layout of the COption object
* for serializing/deserializing
* @type {Map}
*/
const COPTIONSCHEMA = new Map([
[
COption,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["noneOrSome", "u32"],
["pubKeyBuffer", [32]],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry(indata?: PublicKey) {
// If we get a PublicKey
if (indata) {
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey(indata);
console.log("Testing COption with " + indata.toBase58());
// Serialize it
let copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log("copt_ser ", copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone);
// Validate contains PublicKey
if (tdone["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
console.log("pubkey: " + new PublicKey(tdone["pubKeyBuffer"]).toBase58());
}
/*
Output:
Testing COption with A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
copt_ser Buffer(36) [1, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186, 109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 1064, length: 36]
COption {noneOrSome: 1, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32)}
pubkey: A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
*/
} else {
console.log("Testing COption with null");
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey();
// Serialize it
const copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log(copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone1 = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone1);
// Validate does NOT contains PublicKey
if (tdone1["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
throw Error("Expected no public key");
} else console.log("pubkey: null");
/*
Output:
Testing COption with null
Buffer(36)[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 2272, length: 36]
COption { noneOrSome: 0, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32) }
pubkey: null
*/
}
}
// Test with PublicKey
entry(new PublicKey("A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU"));
console.log("");
// Test without PublicKey
entry();<!--EndFragment-->
- 2026 年六大 Solana 智能合约审计公司 47 浏览
- Orca Whirlpools 对比 Uniswap V3 — ImmuneBytes 72 浏览
- Solana 对比 Near 区块链 – ImmuneBytes 70 浏览
- 原生Solana:程序入口与执行 241 浏览
- 原生 Solana :读取账户数据 236 浏览
- Solana 系统调用:sBPF 汇编中的日志记录 234 浏览
- 指令处理器和运行时设置 220 浏览
- Solana 程序执行与输入序列化 225 浏览
- 跟踪 sBPF 指令执行和计算成本 237 浏览
- 原生 Solana: 函数分发 245 浏览
- 使用 sBPF 汇编读取 Solana 指令输入 226 浏览
- Solana 程序代码结构 158 浏览

