智能合约语言 Solidity 教程系列3 - 函数类型
- Tiny熊
- 发布于 2017-12-12 15:25
- 阅读 42627
Solidity 教程系列第三篇 - Solidity 函数类型介绍。 Solidity 系列完整的文章列表请查看分类-Solidity。
Solidity 教程系列第三篇 - Solidity 函数类型介绍。 Solidity 系列完整的文章列表请查看分类-Solidity。
写在前面
Solidity 是以太坊智能合约编程语言,阅读本文前,你应该对以太坊、智能合约有所了解,如果你还不了解,建议你先看以太坊是什么
本文前半部分是参考Solidity 官方文档(当前最新版本:0.4.20)进行翻译,后半部分函数可见性( public, external, internal, privite )深度分析(仅针对专栏订阅用户)。
函数类型(Function Types)
函数也是一种类型,且属于值类型。 可以将一个函数赋值给一个函数类型的变量。还可以将一个函数作为参数进行传递。也可以在函数调用中返回一个函数。 函数类型有两类:内部(internal)和外部(external)函数
内部(internal)函数只能在当前合约内被调用(在当前的代码块内,包括内部库函数,和继承的函数中)。 外部(external)函数由地址和函数方法签名两部分组成,可作为外部函数调用的参数,或返回值。
函数类型定义如下:
function (<parameter types>) {internal|external} [pure|constant|view|payable] [returns (<return types>)]如果函数不需要返回,则省去returns (<return types>) 函数类型默认是internal, 因此internal可以省去。但以此相反,合约中函数本身默认是public的, 仅仅是当作类型名使用时默认是internal的。
有两个方式访问函数,一种是直接用函数名f, 一种是this.f, 前者用于内部函数,后者用于外部函数。
如果一个函数变量没有初始化,直接调用它将会产生异常。如果delete了一个函数后调用,也会发生同样的异常。
如果外部函数类型在Solidity的上下文环境以外的地方使用,他们会被视为function类型。它会编码为20字节的函数所在地址,和在它之前的4字节的函数方法签名一起作为bytes24类型。 合约中的public的函数,可以使用internal和external两种方式来调用。 internal访问形式为f, external访问形式为this.f
成员: 属性 selector
public (或 external) 函数有一个特殊的成员selector, 它对应一个ABI 函数选择器。
pragma solidity ^0.4.16;
contract Selector {
function f() public view returns (bytes4) {
return this.f.selector;
}
}下面的代码显示内部(internal)函数类型的使用:
pragma solidity ^0.4.16;
library ArrayUtils {
// internal functions can be used in internal library functions because
// they will be part of the same code context
function map(uint[] memory self, function (uint) pure returns (uint) f)
internal
pure
returns (uint[] memory r)
{
r = new uint[](self.length);
for (uint i = 0; i < self.length; i++) {
r[i] = f(self[i]);
}
}
function reduce(
uint[] memory self,
function (uint, uint) pure returns (uint) f
)
internal
pure
returns (uint r)
{
r = self[0];
for (uint i = 1; i < self.length; i++) {
r = f(r, self[i]);
}
}
function range(uint length) internal pure returns (uint[] memory r) {
r = new uint[](length);
for (uint i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
r[i] = i;
}
}
}
contract Pyramid {
using ArrayUtils for *;
function pyramid(uint l) public pure returns (uint) {
return ArrayUtils.range(l).map(square).reduce(sum);
}
function square(uint x) internal pure returns (uint) {
return x * x;
}
function sum(uint x, uint y) internal pure returns (uint) {
return x + y;
}
}下面的代码显示外部(external)函数类型的使用:
pragma solidity ^0.4.11;
contract Oracle {
struct Request {
bytes data;
function(bytes memory) external callback;
}
Request[] requests;
event NewRequest(uint);
function query(bytes data, function(bytes memory) external callback) public {
requests.push(Request(data, callback));
NewRequest(requests.length - 1);
}
function reply(uint requestID, bytes response) public {
// Here goes the check that the reply comes from a trusted source
requests[requestID].callback(response);
}
}
contract OracleUser {
Oracle constant oracle = Oracle(0x1234567); // known contract
function buySomething() {
oracle.query("USD", this.oracleResponse);
}
function oracleResponse(bytes response) public {
require(msg.sender == address(oracle));
// Use the data
}
}
函数可见性分析
- public - 任意访问
- private - 仅当前合约内
- internal - 仅当前合约及所继承的合约
- external - 仅外部访问(在内部也只能用外部访问方式访问)
public 还是 external 最佳实践
请订阅区块链技术查看。
参考文档
深入浅出区块链 - 打造高质量区块链技术博客,学区块链都来这里,关注知乎、微博 掌握区块链技术动态。 我的知识星球为各位解答区块链技术问题,欢迎加入讨论。
先上一个例子看 public 与 external 不同,代码如下:
pragma solidity^0.4.18;
contract Test {
uint[10] x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
function test(uint[10] a) public returns (uint){
return a[9]*2;
}
function test2(uint[10] a) external returns (uint){
return a[9]*2;
}
function calltest() {
test(x);
}
function calltest2() {
this.test2(x);
//test2(x); //不能在内部调用一个外部函数,会报编译错误。
}
}打开Remix - Solidity IDE,帖入代码,创建合约。
然后,我们分别调用 test 及 test2 ,对比执行花费的 gas。
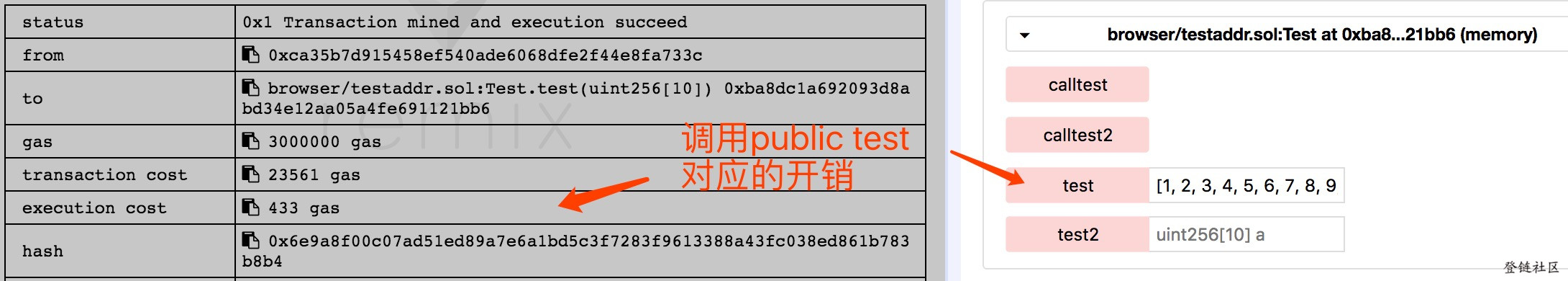
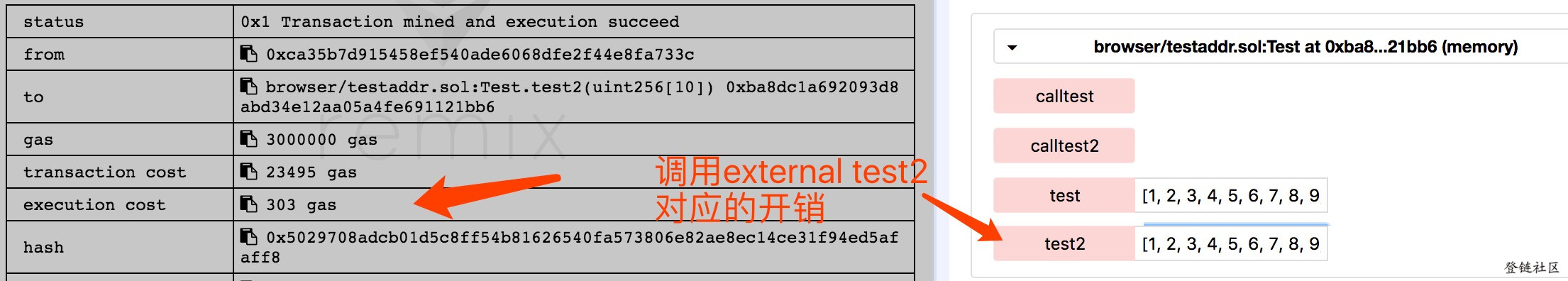 可以看到调用pubic函数花销更大,这是为什么呢?
可以看到调用pubic函数花销更大,这是为什么呢?
当使用public 函数时,Solidity会立即复制数组参数数据到内存, 而external函数则是从calldata读取,而分配内存开销比直接从calldata读取要大的多。 那为什么public函数要复制数组参数数据到内存呢?是因为public函数可能会被内部调用,而内部调用数组的参数是当做指向一块内存的指针。 对于external函数不允许内部调用,它直接从calldata读取数据,省去了复制的过程。
所以,如果确认一个函数仅仅在外部访问,请用external。
同样,我们接着对比calltest()及calltest2(),这里不截图了,大家自己运行对比一下,可以发现:calltest2的开销比calltest的开销大很多,这是因为通过this.f()模式调用,会有一个大开销的CALL调用,并且它传参的方式也比内部传递开销更大。
因此,当需要内部调用的时候,请用public。
-->
- Solidity多重角色:让你的合约权限像俄罗斯套娃一样层层嵌套 318 浏览
- CrossFi Visa 卡的加密支付安全吗? 314 浏览
- 释放 700 万亿美元:智能合约衍生品如何重新定义全球金融 447 浏览
- 在 Wake 调试 EIP-712 类型字符串和哈希 167 浏览
- 无代码Polygon开发:人工智能正在改变智能合约的创建方式⚙️ 115 浏览
- AI 是新的开发者:轻松创建 Polygon 智能合约 🤖✨ 128 浏览

