简单的 Golang HTTP 服务器
- mobinshaterian
- 发布于 2025-08-11 23:37
- 阅读 1494
本文介绍了如何使用 Go 语言构建一个简单的 HTTP 服务器,采用了三层架构:路由器、控制器和数据库。文章从初始化 Go 模块、设置 GitHub 仓库开始,逐步介绍了使用 net/http 包构建基本服务器、添加平滑关机处理、编写单元测试,以及集成 Gin 框架以实现更好的路由和中间件支持的过程。
在本文中,我将引导你完成使用结构化的三层架构(router、controllers 和 database)在 Golang 中构建一个简单的 HTTP server 的过程。我的目标是创建一个干净且可维护的项目,同时在 Go 中应用关键的设计模式。我首先初始化一个 Go module 并设置一个 GitHub 仓库来分享我的代码。然后,我使用 Go 的 net/http 包实现了一个基本的 server,添加了优雅关闭处理,并编写了单元测试来验证 server 的行为。为了使项目更加健壮,我后来集成了 Gin 框架,以获得更好的路由和中间件支持。无论你是刚开始使用 Go 还是希望改进你的架构,我都希望本指南能帮助你充满信心地进行构建。
加速你的学习。提升你的职业生涯。
加入 270 万+ 开发者的行列,他们在 Meta、Airbnb、Netflix 和 Google 等公司磨练技能——全部使用一个平台。
通过实践而非仅仅观看来学习。构建真实世界的项目,掌握热门技能,并更快地晋升。
注意: Educative.io 是一个推广帖子,包含一个 affiliate link。

构建一个 Go 项目
只需运行该命令,你就可以创建一个 Go module 文件并启动一个项目。
go mod init go-simplego.mod 文件将如下所示:
module go-simple
go 1.23.2创建一个 Git 仓库
由于我想与他人分享我的代码,我可以使用 Git 仓库。为此,我应该在 GitHub 上创建一个仓库并提交项目的初始版本。
echo "# go-simple" >> README.md
git init
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M main
git remote add origin git@github.com:mobintmu/go-simple.git
git push -u origin main仓库 GitHub 地址
这个仓库将包含并分享我的所有代码。
https://github.com/mobintmu/go-simple构建一个 Golang HTTP server
在第一步中,我创建了一个文件夹结构,其中 main.go 文件位于 cmd/web 中。此文件初始化应用程序的新实例并启动 HTTP server。由于该 server 在单独的 goroutine 中运行,因此我实现了一个 channel 以接收程序应终止的信号,从而确保正确的同步和优雅关闭。
package main
import (
application "go-simple/cmd/web/app"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
app := application.New()
app.StartServer()
// Wait for interrupt signal to gracefully shut down
// 等待中断信号以优雅地关闭
sig := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(sig, os.Interrupt, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-sig // Blocks until signal is received
// 阻塞直到收到信号
}该应用程序文件设置了一个基本的 HTTP server,该 server 通过 HTTP 协议处理 4000 端口上的传入请求。
这段 Go 代码使用标准的 net/http 包定义了一个简单的 Web 应用程序。它首先创建一个 Application 结构体,该结构体保存 server 端口,以及一个 New() 函数,该函数通过检查 PORT 环境变量来初始化 app(如果未设置,则使用默认值 :4000)。端口的格式设置为包含冒号(如果缺少),以确保其对于 server 使用是有效的。
StartServer 方法设置了一个基本的 HTTP router(ServeMux),该 router 将传入的请求路由到适当的处理程序——在本例中,只有根路径 / 由 helloHandler 处理。它在单独的 goroutine 中启动 server,因此它在后台运行,记录启动消息和任何错误。helloHandler 函数以纯文本形式响应 "Hello World" 的 GET 请求,并为任何其他 HTTP 方法返回 405 错误。
package application
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
)
type Application struct {
Port string
}
const defaultPort = ":4000"
func New() *Application {
port := os.Getenv("PORT")
if port == "" {
port = defaultPort
} else if port[0] != ':' {
port = ":" + port
}
return &Application{Port: port}
}
func (app *Application) StartServer() {
// router
// 路由
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", helloHandler)
//start the server
//启动服务器
go func() {
log.Printf("Starting server at port %s", app.Port)
err := http.ListenAndServe(app.Port, mux)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}()
}
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method != http.MethodGet {
http.Error(w, http.StatusText(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed), http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
return
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/plain; charset=utf-8")
fmt.Fprint(w, "Hello World")
}为了测试该函数,有必要在 test 文件夹中创建一个测试文件。首先,设置一个简单的 server,然后向该 endpoint 发送一个 HTTP 请求以验证其行为。
package test
import (
"io"
"net/http"
"testing"
"time"
application "go-simple/cmd/web/app"
)
func startTestServer() {
a := application.New()
a.StartServer()
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond) // Give server time to start
// 给服务器启动时间
}
func TestHelloWorldEndpoint(t *testing.T) {
startTestServer()
resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:4000/")
if err != nil {
t.Fatalf("Failed to send GET request: %v", err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
t.Errorf("Expected status 200 OK, got %d", resp.StatusCode)
}
body, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
t.Fatalf("Failed to read response body: %v", err)
}
expected := "Hello World"
if string(body) != expected {
t.Errorf("Expected body '%s', got '%s'", expected, string(body))
}
}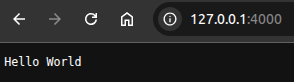
运行 Golang 项目:
go run cmd/web/main.go此部分的 GitHub 代码
feat: server http in golang · mobintmu/go-simple@1a3e1d4
Gin Router
在下一步中,我将集成 Gin router 以在我的 Go 项目中处理路由。
GitHub - gin-gonic/gin: Gin is a HTTP web framework written in Go (Golang). It features a…
在你的终端中运行此命令:
go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin在 app.go 文件中添加一个 gin router
package application
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type Application struct {
Port string
Router *gin.Engine
}
const defaultPort = ":4000"
func New() *Application {
// Set release mode
// 设置发布模式
gin.SetMode(gin.DebugMode)
// Use New() for full control, or Default() if you're okay with built-ins
// 使用 New() 进行完全控制,如果可以接受内置函数,则使用 Default()
router := gin.New()
// Add middleware explicitly
// 显式添加中间件
router.Use(gin.Logger())
router.Use(gin.Recovery())
port := os.Getenv("PORT")
if port == "" {
port = defaultPort
}
return &Application{Port: port, Router: router}
}
func (app *Application) StartServer() {
//start the server
//启动服务器
go func() {
log.Printf("Starting Gin server at port %s", app.Port)
err := app.Router.Run(app.Port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}()
}
func (a *Application) Routes() {
a.Router.GET("/", helloHandler)
}
func helloHandler(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "hello world",
})
}GitHub 上的当前提交
add: gin router · mobintmu/go-simple@913ef7d
🧩 结论:
构建这个简单的 Golang HTTP server 是一个很好的练习,可以应用清晰的架构并探索标准的 net/http 包和更强大的 Gin 框架。从头开始——设置 module,构建项目,编写测试,最后集成 Gin——帮助我了解如何在保持模块化和可维护性的同时扩展 Go 应用程序。在 GitHub 上分享代码不仅使其他人更容易学习或为项目做出贡献,而且还让我有责任编写干净、文档完善的代码。我很高兴继续扩展这个项目,我希望它可以作为任何使用 Go 深入研究 Web 开发的人的有用起点。
感谢你成为社区的一员
在你离开之前:

👉 请务必鼓掌并关注作者️👏 ️️
👉 关注我们:X** ](https://medium.com/codetodeploy)
👉 关注我们的出版物, CodeToDeploy,以获取每日见解:** ](https://www.educative.io/unlimited?aff=xkRD) 帮助你成长更快——没有虚张声势,只有真正的进步。
用户使用此链接可额外享受 10% 的折扣。
👉 立即开始你的职业升级 在 Educative.io
注意: Educative.io 是一个推广帖子,包含一个 affiliate link。
- 原文链接: medium.com/codetodeploy/...
- 登链社区 AI 助手,为大家转译优秀英文文章,如有翻译不通的地方,还请包涵~
- 每个开发者都应该知道的Go高级技巧 (Go并发性能和最佳实践) 469 浏览
- 用 go-panikint 检测 Go 中静默的算术错误 668 浏览
- 使用 Go 构建区块链 API - 从 JSON-RPC 到 GraphQL 1019 浏览
- Go以太坊内部:Golang如何驱动以太坊节点层 526 浏览
- Monad上的Prop AMM - 一种机制完善的、最佳原子执行路由 2535 浏览
- Golang Gin 中间件与监控服务健康控制器 1644 浏览
- 使用 Go 语言中的Token桶算法构建速率限制器 1600 浏览
- 性能飞跃:ZeroDev为关键任务型Web3规模化应用解锁Go原生账户抽象 1835 浏览
- 互联网是什么? 1843 浏览
- 使用Yellowstone gRPC Geyser插件(Go)监控Solana流动性池 2657 浏览
- 中间件指南链接:构建 AVS 合约快速入门指南 872 浏览

