死磕以太坊源码分析之挖矿流程
- 链上无名
- 发布于 2021-02-25 09:29
- 阅读 7840
死磕以太坊源码分析之挖矿流程
死磕以太坊源码分析之挖矿流程
https://github.com/blockchainGuide (文章资料在此,给个Star哦)
基本架构
以太坊挖矿的主要流程是由miner包负责的,下面是基本的一个架构:
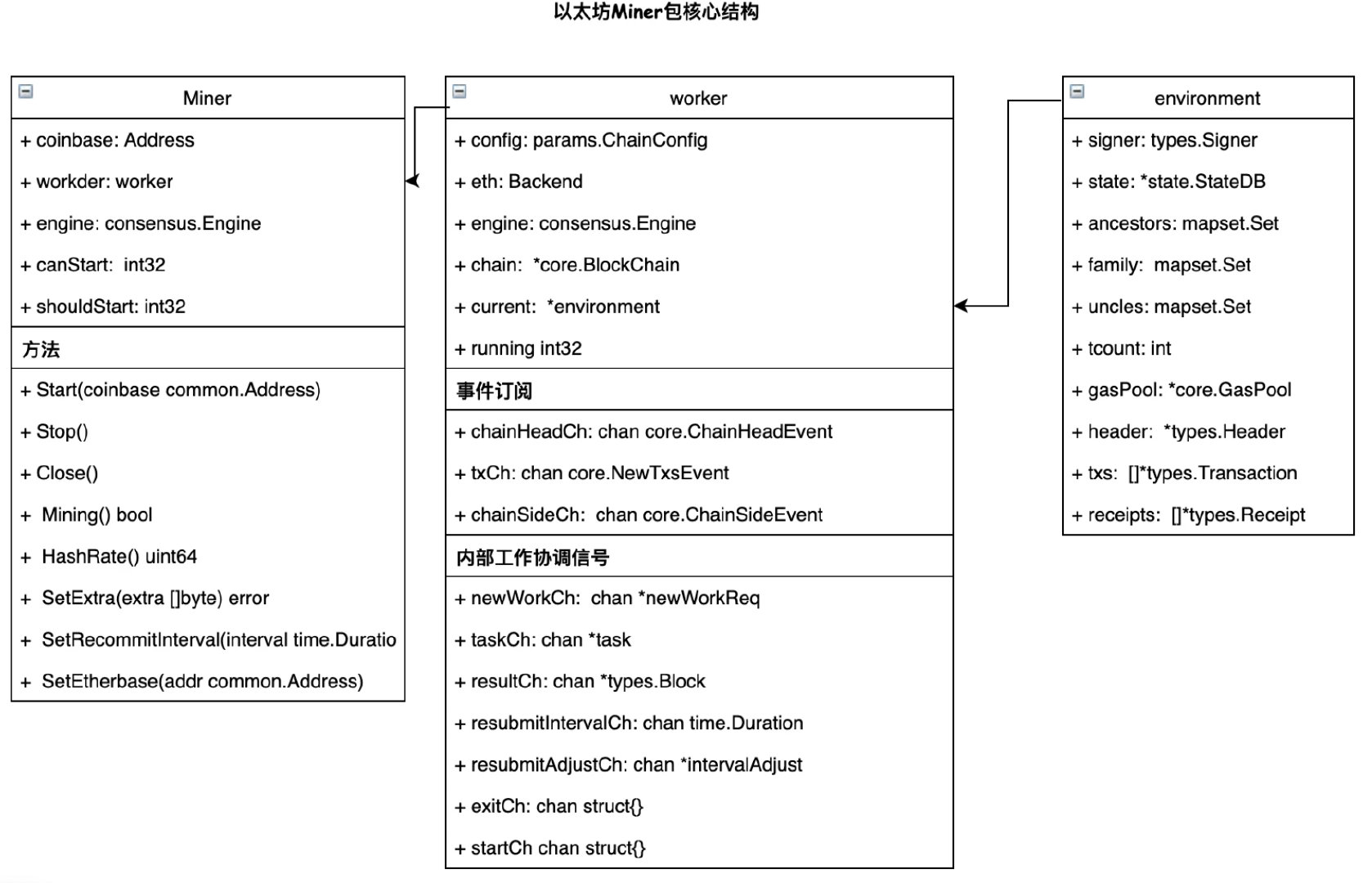
首先外部是通过miner对象进行了操作,miner里面则是实用worker对象来实现挖矿的整体功能。miner决定着是否停止挖矿或者是否可以开始挖矿,同时还可以设置矿工的地址来获取奖励。
真正调度处理挖矿相关细节的则是在worker.go里面,我们先来看一张总体的图。
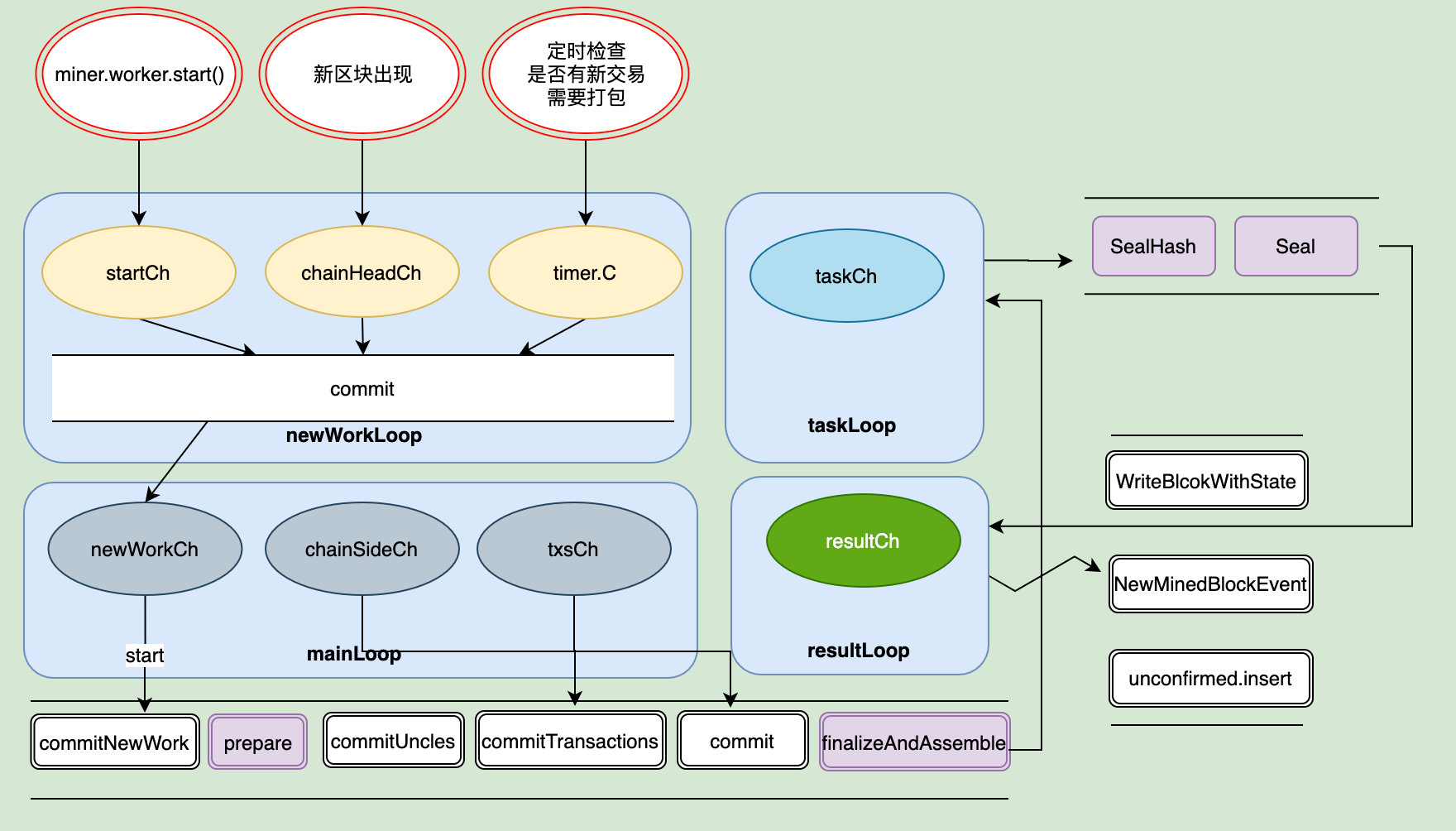
上图我们看到有四个循环,分别通过几个channel负责不同的事:
newWorkLoop
startCh:接收startCh信号,开始挖矿chainHeadCh:表示接收到新区块,需要终止当前的挖矿工作,开始新的挖矿。timer.C:默认每三秒检查一次是否有新交易需要处理。如果有则需要重新开始挖矿。以便将加高的交易优先打包到区块中。
在 newWorkLoop 中还有一个辅助信号,resubmitAdjustCh 和 resubmitIntervalCh。运行外部修改timer计时器的时钟。resubmitAdjustCh是根据历史情况重新计算一个合理的间隔时间。而resubmitIntervalCh则允许外部,实时通过 Miner 实例方法 SetRecommitInterval 修改间隔时间。
mainLoop
newWorkCh:接收生成新的挖矿任务信号chainSideCh:接收区块链中加入了一个新区块作为当前链头的旁支的信号txsCh:接收交易池的Pending中新加入了交易事件的信号
TaskLoop则是提交新的挖矿任务,而resultLoop则是成功出块之后做的一些处理。
启动挖矿
挖矿的参数设置
geth挖矿的参数设置定义在 cmd/utils/flags.go 文件中
| 参数 | 默认值 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| –mine | false | 是否开启自动挖矿 |
| –miner.threads | 0 | 挖矿时可用并行PoW计算的协程(轻量级线程)数。 兼容过时参数 —minerthreads。 |
| –miner.notify | 空 | 挖出新块时用于通知远程服务的任意数量的远程服务地址。 是用 ,分割的多个远程服务器地址。 如:”http://api.miner.com,http://api2.miner.com“ |
| –miner.noverify | false | 是否禁用区块的PoW工作量校验。 |
| –miner.gasprice | 1000000000 wei | 矿工可接受的交易Gas价格, 低于此GasPrice的交易将被拒绝写入交易池和不会被矿工打包到区块。 |
| –miner.gastarget | 8000000 gas | 动态计算新区块燃料上限(gaslimit)的下限值。 兼容过时参数 —targetgaslimit。 |
| –miner.gaslimit | 8000000 gas | 动态技术新区块燃料上限的上限值。 |
| –miner.etherbase | 第一个账户 | 用于接收挖矿奖励的账户地址, 默认是本地钱包中的第一个账户地址。 |
| –miner.extradata | geth版本号 | 允许矿工自定义写入区块头的额外数据。 |
| –miner.recommit | 3s | 重新开始挖掘新区块的时间间隔。 将自动放弃进行中的挖矿后,重新开始一次新区块挖矿。 |
常见的启动挖矿的方式
参数设置挖矿
dgeth --dev --mine
控制台启动挖矿
miner.start(1)
rpc 启动挖矿
这是部署节点使用的方式,一般设置如下:
/geth --datadir "/data0" --nodekeyhex "27aa615f5fa5430845e4e99229def5f23e9525a20640cc49304f40f3b43824dc" --bootnodes $enodeid --mine --debug --metrics --syncmode="full" --gcmode=archive --istanbul.blockperiod 5 --gasprice 0 --port 30303 --rpc --rpcaddr "0.0.0.0" --rpcport 8545 --rpcapi "db,eth,net,web3,personal" --nat any --allow-insecure-unlock
开始源码分析,进入到miner.go的New函数中:
func New(eth Backend, config *Config, chainConfig *params.ChainConfig, mux *event.TypeMux, engine consensus.Engine, isLocalBlock func(block *types.Block) bool) *Miner {
miner := &Miner{
...
}
go miner.update()
return miner
}func (miner *Miner) update() {
switch ev.Data.(type) {
case downloader.StartEvent:
atomic.StoreInt32(&miner.canStart, 0)
if miner.Mining() {
miner.Stop()
atomic.StoreInt32(&miner.shouldStart, 1)
log.Info("Mining aborted due to sync")
}
case downloader.DoneEvent, downloader.FailedEvent:
shouldStart := atomic.LoadInt32(&miner.shouldStart) == 1
atomic.StoreInt32(&miner.canStart, 1)
atomic.StoreInt32(&miner.shouldStart, 0)
if shouldStart {
miner.Start(miner.coinbase)
}
}一开始我们初始化的canStart=1 , 如果Downloader模块正在同步,则canStart=0,并且停止挖矿,如果Downloader模块Done或者Failed,则canStart=1,且同时shouldStart=0,miner将启动。
miner.Start(miner.coinbase)
func (miner *Miner) Start(coinbase common.Address) {
...
miner.worker.start()
}func (w *worker) start() {
...
w.startCh <- struct{}{}
}接下来将会进入到mainLoop中去处理startCh:
①:清除过旧的挖矿任务
clearPending(w.chain.CurrentBlock().NumberU64())②:提交新的挖矿任务
commit := func(noempty bool, s int32) {
...
w.newWorkCh <- &newWorkReq{interrupt: interrupt, noempty: noempty, timestamp: timestamp}
...
}生成新的挖矿任务
根据newWorkCh生成新的挖矿任务,进入到CommitNewWork中:
①:组装header
header := &types.Header{ //组装header
ParentHash: parent.Hash(),
Number: num.Add(num, common.Big1), //num+1
GasLimit: core.CalcGasLimit(parent, w.config.GasFloor, w.config.GasCeil),
Extra: w.extra,
Time: uint64(timestamp),
}②:根据共识引擎吃初始化header的共识字段
w.engine.Prepare(w.chain, header); ③:为当前挖矿新任务创建环境
w.makeCurrent(parent, header)④:添加叔块
叔块集分本地矿工打包区块和其他挖矿打包的区块。优先选择自己挖出的区块。选择时,将先删除太旧的区块,只从最近的7(staleThreshold)个高度中选择,最多选择两个叔块放入新区块中.在真正添加叔块的同时会进行校验,包括如下:
- 叔块存在报错
- 添加的uncle是父块的兄弟报错
- 叔块的父块未知报错
commitUncles(w.localUncles)
commitUncles(w.remoteUncles)⑤:如果noempty为false,则提交空块,不填充交易进入到区块中,表示提前挖矿
if !noempty {
w.commit(uncles, nil, false, tstart)
}⑥:填充交易到新区块中
6.1 从交易池中获取交易,并把交易分为本地交易和远程交易,本地交易优先,先将本地交易提交,再将外部交易提交。
localTxs, remoteTxs := make(map[common.Address]types.Transactions), pending
for _, account := range w.eth.TxPool().Locals() {
if txs := remoteTxs[account]; len(txs) > 0 {
delete(remoteTxs, account)
localTxs[account] = txs
}
}if len(localTxs) > 0 {
txs := types.NewTransactionsByPriceAndNonce(w.current.signer, localTxs)
if w.commitTransactions(txs, w.coinbase, interrupt) {
return
}
}
if len(remoteTxs) > 0 {
...
}6.2提交交易
- 首先校验有没有可用的
Gas - 如果碰到以下情况要进行交易执行的中断
- 新的头块事件到达,中断信号为 1 (整个任务会被丢弃)
worker开启或者重启,中断信号为 1 (整个任务会被丢弃)worker重新创建挖矿任务根据新的交易,中断信号为 2 (任务还是会被送入到共识引擎)
6.3开始执行交易
logs, err := w.commitTransaction(tx, coinbase)6.4执行交易获取收据
receipt, err := core.ApplyTransaction(w.chainConfig, w.chain, &coinbase, w.current.gasPool, w.current.state, w.current.header, tx, &w.current.header.GasUsed, *w.chain.GetVMConfig())如果执行出错,直接回退上一个快照
if err != nil {
w.current.state.RevertToSnapshot(snap)
return nil, err
}出错的原因大概有以下几个:
- 超出当前块的
gas limit Nonce太低Nonce太高
执行成功的话讲交易和收据存入到w.current中。
⑦:执行交易的状态更改,并组装成最终块
w.commit(uncles, w.fullTaskHook, true, tstart)执行交易的状态更改,并组装成最终块是由下面的共识引擎所完成的事情:
block, err := w.engine.FinalizeAndAssemble(w.chain, w.current.header, s, w.current.txs, uncles, w.current.receipts)底层会调用 state.IntermediateRoot执行状态更改。组装成最终块意味着到这打包任务完成。接着就是要提交新的挖矿任务。
提交新的挖矿任务
①:获取sealHash(挖矿前的区块哈希),重复提交则跳过
sealHash := w.engine.SealHash(task.block.Header()) // 返回挖矿前的块的哈希
if sealHash == prev {
continue
}②:生成新的挖矿请求,结果返回到reultCh或者StopCh中
w.engine.Seal(w.chain, task.block, w.resultCh, stopCh);挖矿的结果会返回到resultCh中或者stopCh中,resultCh有数据成功出块,stopCh不为空,则中断挖矿线程。
成功出块
resultCh有区块数据,则成功挖出了块,到最后的成功出块我们还需要进行相应的验证判断。
①:块为空或者链上已经有块或者pendingTasks不存在相关的sealhash,跳过处理
if block == nil {}
if w.chain.HasBlock(block.Hash(), block.NumberU64()) {}
task, exist := w.pendingTasks[sealhash] if !exist {}②:更新receipts
for i, receipt := range task.receipts {
receipt.BlockHash = hash
...
}③:提交块和状态到数据库
_, err := w.chain.WriteBlockWithState(block, receipts, logs, task.state, true) // 互斥④:广播区块并宣布链插入事件
w.mux.Post(core.NewMinedBlockEvent{Block: block})⑤:等待规范确认本地挖出的块
新区块并非立即稳定,暂时存入到未确认区块集中。
w.unconfirmed.Insert(block.NumberU64(), block.Hash())总结&参考
整个挖矿流程还是比较的简单,通过 4 个Loop互相工作,从开启挖矿到生成新的挖矿任务到提交新的挖矿任务到最后的成功出块,这里面的共识处理细节不会提到,接下来的文章会说到。
https://github.com/blockchainGuide
https://learnblockchain.cn/books/geth/part2/mine/design.html
- Hegotá Headliner 提案:FOCIL,EIP-7805 - 魔法师 / 原始汤 162 浏览
- 引擎 API -- EIP-7805 127 浏览
- 超越博物馆的艺术:当网络成为媒介 214 浏览
- 以太坊代理:一个为代理在以太坊中自主运行而设计的Typescript SDK 300 浏览
- REVM源码阅读-Frame(1) 354 浏览
- 以太坊 - Commit Boost 447 浏览

