循环套利入门
- 落花
- 发布于 2022-03-26 17:06
- 阅读 9210
概述 DeFi已经发展了有一段时间了,虽然现在在去中心交易所上进行套利已经非常困难了,但是本文仍然要展示一个在Polygon上在单个AMM机制的去中心化交易所上进行循环套利的入门教程,算是...
概述
DeFi已经发展了有一段时间了,虽然现在在去中心交易所上进行套利已经非常困难了,但是本文仍然要展示一个在Polygon上在单个AMM机制的去中心化交易所上进行循环套利的入门教程,算是抛砖引玉了。至于为啥选择在Ploygon上进行程序测试,是因为以太坊实在太贵了,Polygon这个Layer2的网络上交易费用非常便宜。
循环套利的原理
众所周知,每个token在这些swap交易所上就有很多对与其他token兑换的pair,而在AMM机制中,每个pair中两个token的价格取决于在这个pair中两个token的的储备量,那么如果在网络中,有人大量取出某一个pair中其中一个token的储备量,那么就会造成这个pair中这个token的价格在短时间内升高。这个时候就需要套利机器人去平衡这个市场,而套利机器人所做的事情就是从其他地方搬运来对应的token,平衡该pair的价格。
知道为什么存在套利的背景之后,套利机器人下一个需要解决的问题就是如何寻找到失衡的pair,这一过程有很多方法可以参考,在这里就不过程阐述来,本文只介绍一种最简单的寻找失衡pair的方法:循环套利。所谓循环套利就是用一个token作为输入,用同一个token作为输出,然后在输入和输出之间经过多个pair进行交易。在多个pair交易的过程中,可以将不平衡的pair变的平衡,然后平衡过程中产生的利润会给到循环套利的发起者。一个理想的循环套利最终输出的token数量应当大于输入的token数量。
接下来的问题就变成了如何寻找到这样一个循环套利的机会。根据上面的定义,我们实际上是想要寻找一个A->B-...->C->A这样一个交易路径。在这里主要需要解决以下两个问题:
- 在这个循环路径中,需要包含哪些Pair
- 如果找到这样一个路径,我们应该使用多少数量的token A进行交易
这里我就不去进行算法的推导(主要我懒得敲那些公式),只看实现,具体的算法推导,大家可以去参考这个repo。
方法实现
最简单的套利机器人,应该包含链上程序和链下程序两部分。其中链下程序主要是负责寻找循环套利的机会,链上程序主要负责在链下程序寻找到套利机会之后进行交易。
首先看一下一个最简单的链上程序,链上程序由Solidity编写。该链上程序主要函数是printMoney,函数的输入参数如下:
- tokenIn:输入token的address
- amountIn:token的输入金额
- amountOutMin:token的最小输出金额
- path:套利交易的pair路径
- deadline:交易的截止时间
- swapAddress:进行套利的swap地址
printMoney函数主要做的事情,从调用者账户转移token到合约地址上,然后合约调用swap的Router02合约的swapExactTokenForTokens方法传入对应的参数进行循环交易。
pragma solidity ^0.5.7;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import "./IERC20.sol";
import './IUniswapV2Router02.sol';
import './IWeth.sol';
contract MoneyPrinter {
address owner;
constructor() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
modifier onlyOwner() {
require(msg.sender == owner);
_;
}
function setOwner(address _o) onlyOwner external {
owner = _o;
}
function printMoney(
address tokenIn,
uint256 amountIn,
uint256 amountOutMin,
address[] memory path,
uint256 deadline,
address swapAddress
) onlyOwner public {
IUniswapV2Router02 uni = IUniswapV2Router02(swapAddress);
IERC20 erc20 = IERC20(tokenIn);
erc20.transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), amountIn);
erc20.approve(swapAddress, amountIn); // usdt -1 six decimal would fail!
uni.swapExactTokensForTokens(amountIn, amountOutMin, path, msg.sender, deadline);
}
function() external payable {}
}链上程序还是比较简单的,要部署一个链上程序的原因,主要是希望循环交易能够在一个区块中完成。
接下来看一下链下程序,链下程序由python实现,首先是链下程序的核心,在Swap的pair中寻找套利的路径以及输入token的最优数量。该函数的输入如下:
- pairs:交易所的pairs对
- tokenIn:从什么token开始计算
- tokenOut:到什么token结束
- maxHops:最大交易深度
- currentPairs:当前的pair对路径
- path:交易的token路径
- bestTrades:最佳的套利交易对
- count:最佳的套利交易对数量
def findArb(pairs, tokenIn, tokenOut, maxHops, currentPairs, path, bestTrades, count=5):
for i in range(len(pairs)):
newPath = path.copy()
pair = pairs[i]
if not pair['token0']['address'] == tokenIn['address'] and not pair['token1']['address'] == tokenIn['address']:
continue
if pair['reserve0']/pow(10, pair['token0']['decimal']) < 1 or pair['reserve1']/pow(10, pair['token1']['decimal']) < 1:
continue
if tokenIn['address'] == pair['token0']['address']:
tempOut = pair['token1']
else:
tempOut = pair['token0']
newPath.append(tempOut)
if tempOut['address'] == tokenOut['address'] and len(path) > 2:
Ea, Eb = getEaEb(tokenOut, currentPairs + [pair])
newTrade = { 'route': currentPairs + [pair], 'path': newPath, 'Ea': Ea, 'Eb': Eb }
if Ea and Eb and Ea < Eb:
newTrade['optimalAmount'] = getOptimalAmount(Ea, Eb)
if newTrade['optimalAmount'] > 0:
newTrade['outputAmount'] = getAmountOut(newTrade['optimalAmount'], Ea, Eb)
newTrade['profit'] = newTrade['outputAmount']-newTrade['optimalAmount']
newTrade['p'] = int(newTrade['profit'])/pow(10, tokenOut['decimal'])
else:
continue
bestTrades = sortTrades(bestTrades, newTrade)
bestTrades.reverse()
bestTrades = bestTrades[:count]
elif maxHops > 1 and len(pairs) > 1:
pairsExcludingThisPair = pairs[:i] + pairs[i+1:]
bestTrades = findArb(pairsExcludingThisPair, tempOut, tokenOut, maxHops-1, currentPairs + [pair], newPath, bestTrades, count)
return bestTrades上面我们已经实现如何寻找一个套利机会,那么在寻找一个套利机会之后,下一步应该考虑如何调用链上程序进行交易。在python中主要使用web3py与链上合约进行交互。交互的流程也非常简单,首先构建交易信息,然后使用自己的私钥对交易进行加密,最后发送交易。
def printMoney(amountIn, p, gasPrice):
deadline = int(time.time()) + 600
# 调用合约交易
tx = printer.functions.printMoney(startToken['address'], amountIn, amountIn, p, deadline, swap_addr).buildTransaction({
'from': address,
'value': 0,
'gasPrice': gasPrice,
'gas': 30000000,
"nonce": web3.eth.getTransactionCount(address),
})
try:
# 估算gas消耗
gasEstimate = web3.eth.estimateGas(tx)
print('estimate gas cost:', gasEstimate*gasPrice/1e18)
signed_tx = web3.eth.account.sign_transaction(tx, private_key='私钥')
txhash = web3.eth.sendRawTransaction(signed_tx.rawTransaction)
print(txhash.hex())
return txhash
except Exception as e:
print('gas estimate err:', e)
return None
def doTrade(trade):
p = [t['address'] for t in trade['path']]
amountIn = int(trade['optimalAmount'])
balance = getBalance(startToken['address'], address)
if amountIn > balance:
print("没钱啦")
return None
amountsOut = [int(trade['outputAmount'])]
if amountsOut[-1] > amountIn:
gasPrice = int(gasnow()['fastest']*1.2) * 1000000000
txhash = printMoney(amountIn, p, gasPrice, amountsOut[-1]-amountIn)
return txhash
return None最后看一下链下程序的主流程,主流程首先读取swap上的pair对,然后更新这些pair的储备量,然后调用寻找套利的算法,找到最优的交易路径,如果满足条件,调用链上程序进行交易。
def main():
allPairs = json.load(open('files/matic_sushiswap_pairs_filteres.json'))
while True:
try:
start = time.time()
pairs = get_reserves_batch_mt(allPairs)
end = time.time()
print('update cost:', end - start, 's')
# 寻找套现交易
trades = findArb(pairs, tokenIn, tokenOut, maxHops, currentPairs, path, bestTrades)
end1 = time.time()
print('dfs cost:', end1 - end, 's, update+dfs cost:', end1 - start, 's')
# 获取start token的余额
if len(trades) == 0:
continue
trade = trades[0]
# 如果最终获利大于最小获利,进行套利
if trade and int(trade['profit'])/pow(10, startToken['decimal']) >= minProfit:
tx = doTrade(trade)
print('tx:', tx)
except Exception as e:
print(e)篇幅原因,还有很多主流程之外的代码没有涉及到,如果大家感兴趣,可以去这个repo去看。
最后看一下程序的效果,因为这些swap都会收取一定比例的手续费,目前在现在的程序中没有考虑手续费,同时目前链上的套利机器人已经非常多了,所以目前的程序不太可能寻找的到合适的套利机会。
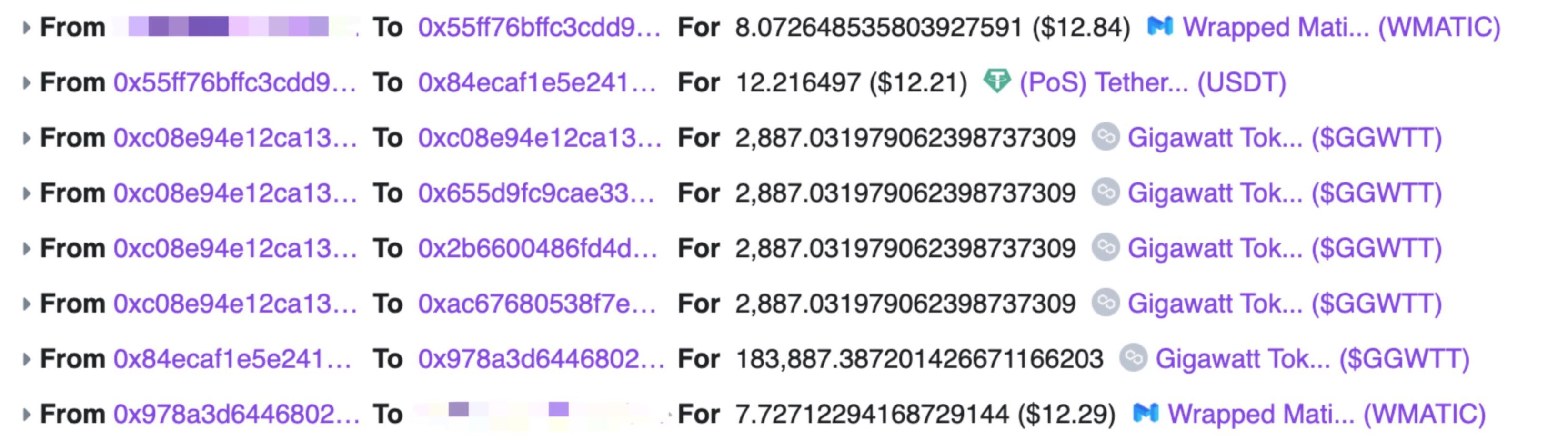
可能的改进方向
目前的套利机器人的运行机制非常简单,如果需要改进的话,我觉得原则有三个faster、faster、faster,只有比别人更快的更新pair储备量、更快获取到套利机会、更快的进行交易,最终才能够做到盈利。个人觉得可以从以下几个方向进行改进:
- 效率更好的套利路径寻找算法,目前使用的是DFS,这个DFS算法优化的空间还是有很大
- 遍历的pair选择,一个swap上面有超过几万个pair,但实际上使用频率最高的只有即少的一部分,所以为了更快的DFS,所以应该对这些pair进行筛选
- 更快的更新储备量,目前是通过调用所有pair合约的getReserve方法,实际上这个过程完全没有必要,因为只有交易才会产生套利机会,而大部分的pair的交易频率很低,所有完全没有必要进行全量更新,比如:可以通过监听pair合约的Sync事件,或者想要更快,可以监听那些还在pedding的交易,提前获取储备量的变化,提前进行计算。
- 目前这个套利机器人只是运行在单个swap上,未来还是可以引入更多swap,在多个swap之间寻找套利机会。
总结
虽然这个程序不太能盈利,但是目前在链上还是有一些能够稳定盈利的套利机器人,本文也是抛砖引玉,所以大家如果感兴趣,还是可以happy hacking~争取早点研发出稳定套利的机器人。
- 学分: 6
- 标签:

