ERC-6551 NFT绑定账户提案
- dwong
- 发布于 2023-07-10 21:26
- 阅读 5825
该提案定义了一个系统,为每个ERC-721代币提供了一个智能合约账户。这些与代币绑定的账户允许ERC-721代币拥有资产并与应用程序进行交互,而无需对现有的ERC-721智能合约或基础设施进行更改。
| eip | 标题 | 描述 | 作者 | 讨论链接 | 状态 | type | 分类 | 创建时间 | 依赖 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6551 | 非同质化代币绑定账户 | ERC-721代币所拥有的智能合约账户的接口和注册表 | Jayden Windle (@jaydenwindle)<br> Benny Giang <bg@futureprimitive.xyz> <br> Steve Jang, Druzy Downs (@druzydowns)<br>Raymond Huynh (@huynhr), Alanah Lam <alanah@futureprimitive.xyz><br>Wilkins Chung (@wwhchung) <wilkins@manifold.xyz><br>Paul Sullivan (@sullivph) <paul.sullivan@manifold.xyz> | https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/non-fungible-token-bound-accounts/13030 | 草稿 | Standards Track | ERC | 2023-02-23 | 155, 165, 721, 1167, 1271 |
摘要
该提案定义了一个系统,为每个ERC-721代币提供了一个智能合约账户。这些与代币绑定的账户允许ERC-721代币拥有资产并与应用程序进行交互,而无需对现有的ERC-721智能合约或基础设施进行更改。
动机
ERC-721标准推动了非同质化代币应用的爆发。一些值得注意的应用案例包括可繁殖的猫咪、生成艺术品和流动性仓位。
非同质化代币越来越成为链上身份的一种形式。这是从ERC-721规范中自然而然地延伸出来的——每个非同质化代币都有一个全球唯一的标识符,进一步地,具有独特的身份。
与其他形式的链上身份不同,ERC-721代币无法充当代理人或与其他链上资产关联。这种限制与许多现实世界中的非同质化资产形成鲜明对比。例如:
- 一个角色扮演游戏中的角色,根据他们所采取的行动逐渐积累财产和能力
- 一辆由许多可替代和不可替代的零部件组成的汽车
- 一个由多个可互换资产组成的自动投资组合
- 一张拳击通行会员卡,可以进入一个场所,并记录过去的互动历史
有几个提案试图赋予ERC-721代币拥有资产的能力。这些提案中的每一个都对ERC-721标准进行了扩展。这要求智能合约作者在他们的ERC-721代币合约中包含提案支持。因此,这些提案在很大程度上与先前部署的ERC-721合约不兼容。
该提案赋予每个ERC-721代币与以前部署的ERC-721代币合约保持向后兼容的情况下,完全具备以太坊账户的全部功能。通过使用无需许可的注册表,为每个ERC-721代币部署独特的确定性寻址的智能合约账户。
每个代币绑定账户都由一个单独的ERC-721代币拥有,使得该代币能够与区块链进行交互,记录交易历史,并拥有链上资产。每个代币绑定账户的控制权被委托给ERC-721代币的所有者,使得所有者能够代表其代币发起链上操作。
代币绑定账户与几乎所有支持以太坊账户的现有基础设施兼容,包括链上协议和链下索引器。代币绑定账户可以拥有任何类型的链上资产,并可以扩展以支持未来创建的新资产类型。
规范
本文档中的关键词“必须”、“不得”、“要求”、“应当”、“不应”、“应该”、“不应该”、“建议”、“不建议”、“可能”和“可选”应按照RFC 2119和RFC 8174中的描述进行解释。
概述
本提案中概述的系统有两个主要组成部分:
- 一个无需许可的注册表,用于部署绑定代币账户
- 代币绑定账户实现的标准接口
下图说明了ERC-721代币、ERC-721代币所有者、代币绑定账户和注册表之间的关系:
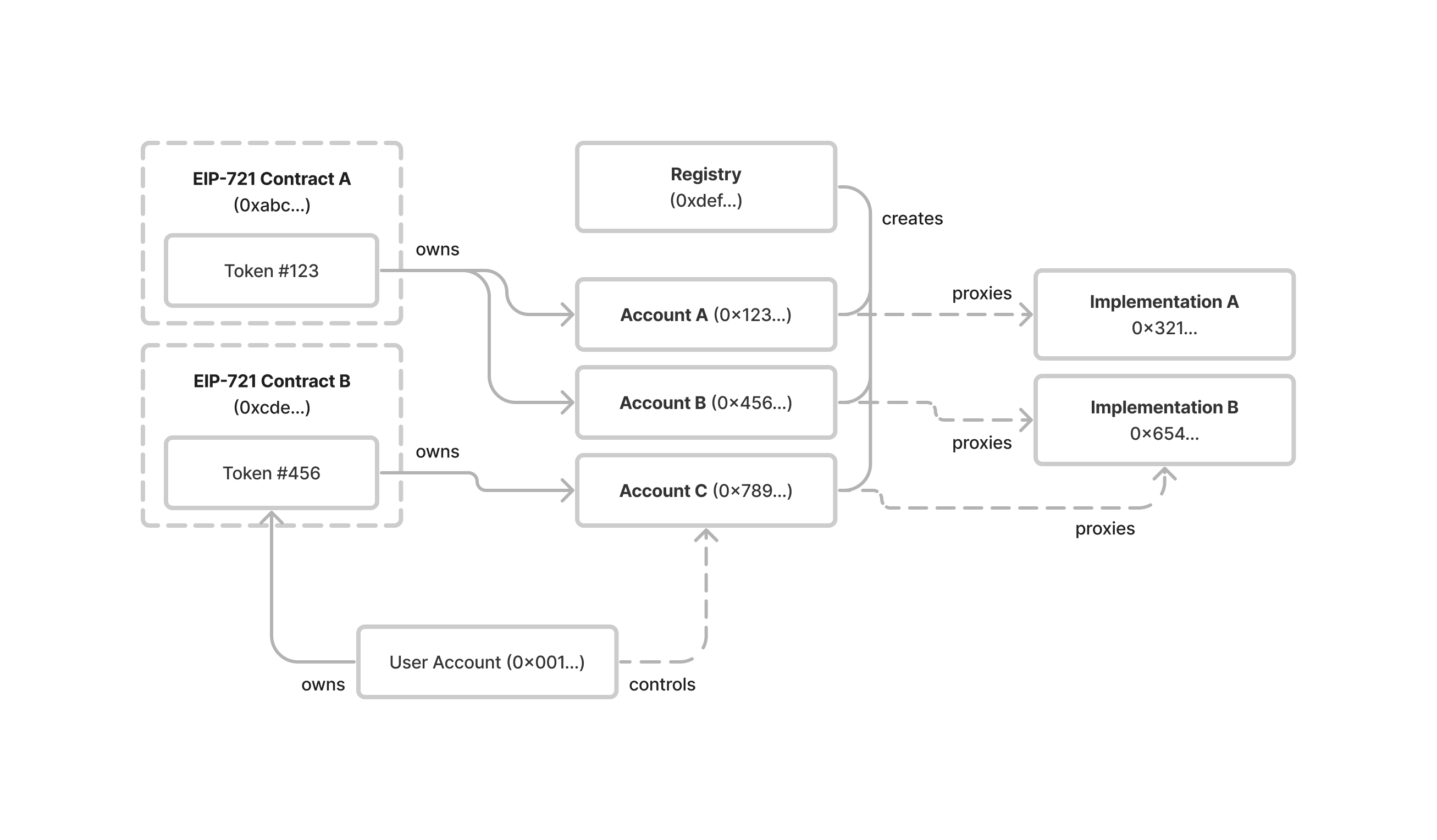
注册
注册表作为希望使用代币绑定账户的项目的单一入口点。它具有两个功能:
createAccount- 给定implementation地址部署一个ERC-721代币绑定账户account- 一个只读函数,根据implementation地址计算ERC-721代币绑定账户地址
注册表应将每个与代币绑定账户部署为一个ERC-1167最小代理,其中不可变的常量数据附加到字节码中。
每个代币绑定账户的部署字节码应具有以下结构:
ERC-1167 Header (10 bytes)
<implementation (address)> (20 bytes)
ERC-1167 Footer (15 bytes)
<salt (uint256)> (32 bytes)
<chainId (uint256)> (32 bytes)
<tokenContract (address)> (32 bytes)
<tokenId (uint256)> (32 bytes)例如,具有实施地址 0xbebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebe 、盐值 0 、链ID 1 、代币合约 0xcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcf 和代币ID 123 的代币绑定账户将具有以下部署的字节码:
363d3d373d3d3d363d73bebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebebe5af43d82803e903d91602b57fd5bf300000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001000000000000000000000000cfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcfcf000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007b每个代币绑定账户代理应该将执行委托给实现了 IERC6551Account 接口的合约。
注册合约是无需许可、不可变且没有所有者的。注册表的完整源代码可以在下面的注册表实现找到。注册表应该在(待定)地址上部署,使用Nick的工厂合约( 0x4e59b44847b379578588920cA78FbF26c0B4956C )和盐 0x6551655165516551655165516551655165516551655165516551655165516551 。
注册表应使用 create2 操作码部署所有绑定代币账户合约,以便每个ERC-721代币的账户地址是确定的。每个ERC-721代币的账户地址应由实现地址、代币合约地址、代币ID、EIP-155链ID和可选盐的唯一组合派生。
注册表应实现以下接口:
interface IERC6551Registry {
/// @dev The registry SHALL emit the AccountCreated event upon successful account creation
event AccountCreated(
address account,
address implementation,
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 salt
);
/// @dev Creates a token bound account for an ERC-721 token.
///
/// If account has already been created, returns the account address without calling create2.
///
/// If initData is not empty and account has not yet been created, calls account with
/// provided initData after creation.
///
/// Emits AccountCreated event.
///
/// @return the address of the account
function createAccount(
address implementation,
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 salt,
bytes calldata initData
) external returns (address);
/// @dev Returns the computed address of a token bound account
///
/// @return The computed address of the account
function account(
address implementation,
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 salt
) external view returns (address);
}账户接口
所有代币绑定账户应通过注册表创建。
所有代币绑定账户的实现都必须实现ERC-165接口检测。
所有代币绑定账户的实现都必须实现ERC-1271签名验证。
所有代币绑定账户的实现都必须实现以下接口:
/// @dev the ERC-165 identifier for this interface is `0x400a0398`
interface IERC6551Account {
/// @dev Token bound accounts MUST implement a `receive` function.
///
/// Token bound accounts MAY perform arbitrary logic to restrict conditions
/// under which Ether can be received.
receive() external payable;
/// @dev Executes `call` on address `to`, with value `value` and calldata
/// `data`.
///
/// MUST revert and bubble up errors if call fails.
///
/// By default, token bound accounts MUST allow the owner of the ERC-721 token
/// which owns the account to execute arbitrary calls using `executeCall`.
///
/// Token bound accounts MAY implement additional authorization mechanisms
/// which limit the ability of the ERC-721 token holder to execute calls.
///
/// Token bound accounts MAY implement additional execution functions which
/// grant execution permissions to other non-owner accounts.
///
/// @return The result of the call
function executeCall(
address to,
uint256 value,
bytes calldata data
) external payable returns (bytes memory);
/// @dev Returns identifier of the ERC-721 token which owns the
/// account
///
/// The return value of this function MUST be constant - it MUST NOT change
/// over time.
///
/// @return chainId The EIP-155 ID of the chain the ERC-721 token exists on
/// @return tokenContract The contract address of the ERC-721 token
/// @return tokenId The ID of the ERC-721 token
function token()
external
view
returns (
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId
);
/// @dev Returns the owner of the ERC-721 token which controls the account
/// if the token exists.
///
/// This is value is obtained by calling `ownerOf` on the ERC-721 contract.
///
/// @return Address of the owner of the ERC-721 token which owns the account
function owner() external view returns (address);
/// @dev Returns a nonce value that is updated on every successful transaction
///
/// @return The current account nonce
function nonce() external view returns (uint256);
}原理阐述
反事实帐户地址
通过指定一个规范的账户注册表,希望支持这个提案的应用程序可以在部署该账户的合约之前,使用特定的实现来计算给定代币绑定账户的地址。这样可以安全地将资产发送给代币的所有者,而无需知道所有者的地址。规范的注册表还允许客户端应用程序从单个入口点查询代币所拥有的资产。
账户模糊不清
上述提议的规范允许ERC-721代币拥有多个绑定账户,每个实施地址一个。在制定这个提案的过程中,考虑了替代架构,该架构将为每个ERC-721代币分配一个单一代币绑定账户,使每个代币绑定账户地址成为一个明确的标识符。
然而,这些替代方案存在一些权衡。
首先,由于智能合约的无需许可性质,无法强制限制每个ERC-721代币只能绑定一个代币账户。任何希望在每个ERC-721代币上使用多个代币账户的人都可以通过部署额外的注册合约来实现。
其次,将每个ERC-721代币限制为一个与之绑定的账户将需要在该提案中包含一个静态、可信赖的账户实现。这个实现将不可避免地对代币绑定账户的能力施加特定的限制。鉴于该提案所能实现的未开发用例数量以及多样化账户实施对非同质化代币生态系统所带来的益处,作者认为在该提案中定义一个规范且受限的实施是过早的。
最后,这个提案旨在赋予ERC-721代币在链上充当代理的能力。在当前的实践中,链上代理通常会利用多个账户。一个常见的例子是个人使用一个“热”账户进行日常使用,而使用一个“冷”账户来存储贵重物品。如果链上代理通常使用多个账户,那么ERC-721代币应该具备相同的能力。
代理实现
ERC-1167最小代理在现有基础设施中得到了很好的支持,并且是一种常见的智能合约模式。该提案使用自定义的ERC-1167代理实现来部署每个代币绑定账户,该代理存储了盐值、实现地址、链ID、代币合约地址和代币ID,这些信息以ABI编码的常量数据附加到合约字节码中。这样可以让代币绑定账户的实现轻松查询这些数据,同时确保数据保持不变。采用这种方法是为了最大限度地兼容现有基础设施,同时在创建自定义代币绑定账户实现时给智能合约开发人员提供充分的灵活性。
EIP-155 支持
该提案使用EIP-155链ID来识别ERC-721代币,同时包括其合约地址和代币ID。在单个以太坊链上,ERC-721代币标识符是全球唯一的,但在多个以太坊链上可能不唯一。使用链ID来唯一标识ERC-721代币,允许希望实施此提案的智能合约作者可选择支持多链代币绑定账户。
向后兼容
该提案旨在与现有的非同质化代币合约实现最大程度的向后兼容。因此,它不扩展ERC-721标准。
此外,该提案不要求注册表在创建账户之前执行 ERC-165 接口检查以确保与 ERC-721 的兼容性。这是有意设计的,以便最大限度地与早于ERC-721标准的非同质化代币合约(如Cryptokitties)保持向后兼容性。实施此提案的智能合约作者可以选择强制执行ERC-721的接口检测。
不实现 ownerOf 方法的非同质化代币合约(如Cryptopunks)与本提案不兼容。本提案中概述的系统可以通过进行轻微修改来支持此类收藏品,但这超出了本提案的范围。
参考实现
账户实施示例
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import "openzeppelin-contracts/utils/introspection/IERC165.sol";
import "openzeppelin-contracts/token/ERC721/IERC721.sol";
import "openzeppelin-contracts/interfaces/IERC1271.sol";
import "openzeppelin-contracts/utils/cryptography/SignatureChecker.sol";
import "sstore2/utils/Bytecode.sol";
contract ExampleERC6551Account is IERC165, IERC1271, IERC6551Account {
receive() external payable {}
function executeCall(
address to,
uint256 value,
bytes calldata data
) external payable returns (bytes memory result) {
require(msg.sender == owner(), "Not token owner");
bool success;
(success, result) = to.call{value: value}(data);
if (!success) {
assembly {
revert(add(result, 32), mload(result))
}
}
}
function token()
external
view
returns (
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId
)
{
uint256 length = address(this).code.length
return
abi.decode(
Bytecode.codeAt(address(this), length - 0x60, length),
(uint256, address, uint256)
);
}
function owner() public view returns (address) {
(uint256 chainId, address tokenContract, uint256 tokenId) = this
.token();
if (chainId != block.chainid) return address(0);
return IERC721(tokenContract).ownerOf(tokenId);
}
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public pure returns (bool) {
return (interfaceId == type(IERC165).interfaceId ||
interfaceId == type(IERC6551Account).interfaceId);
}
function isValidSignature(bytes32 hash, bytes memory signature)
external
view
returns (bytes4 magicValue)
{
bool isValid = SignatureChecker.isValidSignatureNow(
owner(),
hash,
signature
);
if (isValid) {
return IERC1271.isValidSignature.selector;
}
return "";
}
}注册表实现
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import "openzeppelin-contracts/utils/Create2.sol";
contract ERC6551Registry is IERC6551Registry {
error InitializationFailed();
function createAccount(
address implementation,
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 salt,
bytes calldata initData
) external returns (address) {
bytes memory code = _creationCode(implementation, chainId, tokenContract, tokenId, salt);
address _account = Create2.computeAddress(
bytes32(salt),
keccak256(code)
);
if (_account.code.length != 0) return _account;
_account = Create2.deploy(0, bytes32(salt), code);
if (initData.length != 0) {
(bool success, ) = _account.call(initData);
if (!success) revert InitializationFailed();
}
emit AccountCreated(
_account,
implementation,
chainId,
tokenContract,
tokenId,
salt
);
return _account;
}
function account(
address implementation,
uint256 chainId,
address tokenContract,
uint256 tokenId,
uint256 salt
) external view returns (address) {
bytes32 bytecodeHash = keccak256(
_creationCode(implementation, chainId, tokenContract, tokenId, salt)
);
return Create2.computeAddress(bytes32(salt), bytecodeHash);
}
function _creationCode(
address implementation_,
uint256 chainId_,
address tokenContract_,
uint256 tokenId_,
uint256 salt_
) internal pure returns (bytes memory) {
return
abi.encodePacked(
hex"3d60ad80600a3d3981f3363d3d373d3d3d363d73",
implementation_,
hex"5af43d82803e903d91602b57fd5bf3",
abi.encode(salt_, chainId_, tokenContract_, tokenId_)
);
}
}安全考虑
防止欺诈
为了实现无需信任的代币绑定账户销售,去中心化市场将需要采取措施来防范恶意账户所有者的欺诈行为。
考虑以下可能的骗局:
- Alice拥有一个ERC-721代币X,该代币拥有绑定账户Y
- Alice将10ETH存入Y账户
- Bob提议通过一个去中心化市场以11ETH购买代币X,假设他将收到存放在账户Y中的10ETH和代币
- Alice从绑定账户中提取了10ETH,并立即接受了Bob的报价
- Bob收到了代币X,但账户Y是空的
为了减轻恶意账户所有者的欺诈行为,去中心化市场应在市场层面上实施对此类欺诈的保护措施。实施此EIP的合约也可以对欺诈行为实施一定的保护措施。
以下是一些应考虑的缓解策略:
- 将当前代币绑定账户的nonce附加到市场订单上。如果账户的nonce自订单下达以来发生了变化,请视为该报价无效。此功能需要在市场层面上得到支持。
- 在完成订单时,附上一份资产承诺清单,这些资产预计会保留在代币绑定账户中。如果自订单下达以来,任何已承诺的资产已从账户中移除,请视为该报价无效。这也需要由市场实施。
- 通过外部智能合约将订单提交到分散市场,该合约在验证订单签名之前执行上述逻辑。这样可以实现安全的转账,无需市场支持。
- 在代币绑定账户实现中,实施一个锁定机制,防止恶意所有者在账户被锁定时提取资产
防止欺诈行为超出了本提案的范围。
所有权循环
如果创建了所有权循环,所有存放在代币绑定账户中的资产可能会变得无法访问。最简单的例子是将ERC-721代币转移到其自己的代币绑定账户中。如果发生这种情况,ERC-721代币和存储在代币绑定账户中的所有资产将永久无法访问,因为代币绑定账户无法执行转移ERC-721代币的交易。
可以在任何具有n>0个代币绑定账户的图中引入所有权循环。由于需要无限的搜索空间,链上防止这些循环是很难强制执行的,因此超出了本提案的范围。鼓励应用客户和账户实施采纳此提案的措施,以限制所有权循环的可能性。
版权
版权和相关权利通过CC0放弃。
- NFT 进阶开发!ERC6551 场景应用 + 理论代码全解析 753 浏览
- NFT即钱包的ERC-6551 真有那么神奇吗? 4422 浏览
- 如何使用 NFTScan NFT 数据创建一个 ERC-6551 账户? 3534 浏览

