合约创建指南: create、create2 和 create3
- Solichain
- 发布于 2024-10-30 12:42
- 阅读 3856
合约创建指南: create、create2 和 create3 的区别及应用场景
以太坊开发者使用称为操作码的特殊指令在与以太坊虚拟机(EVM)兼容的区块链上部署合约。在这些指令中:
- “CREATE”
- “CREATE2”
- “CREATE3”
前两个是实际的操作码,而 “create3” 是一个类似功能的有用库。本指南将为你快速概述每个操作码的功能及其重要性。
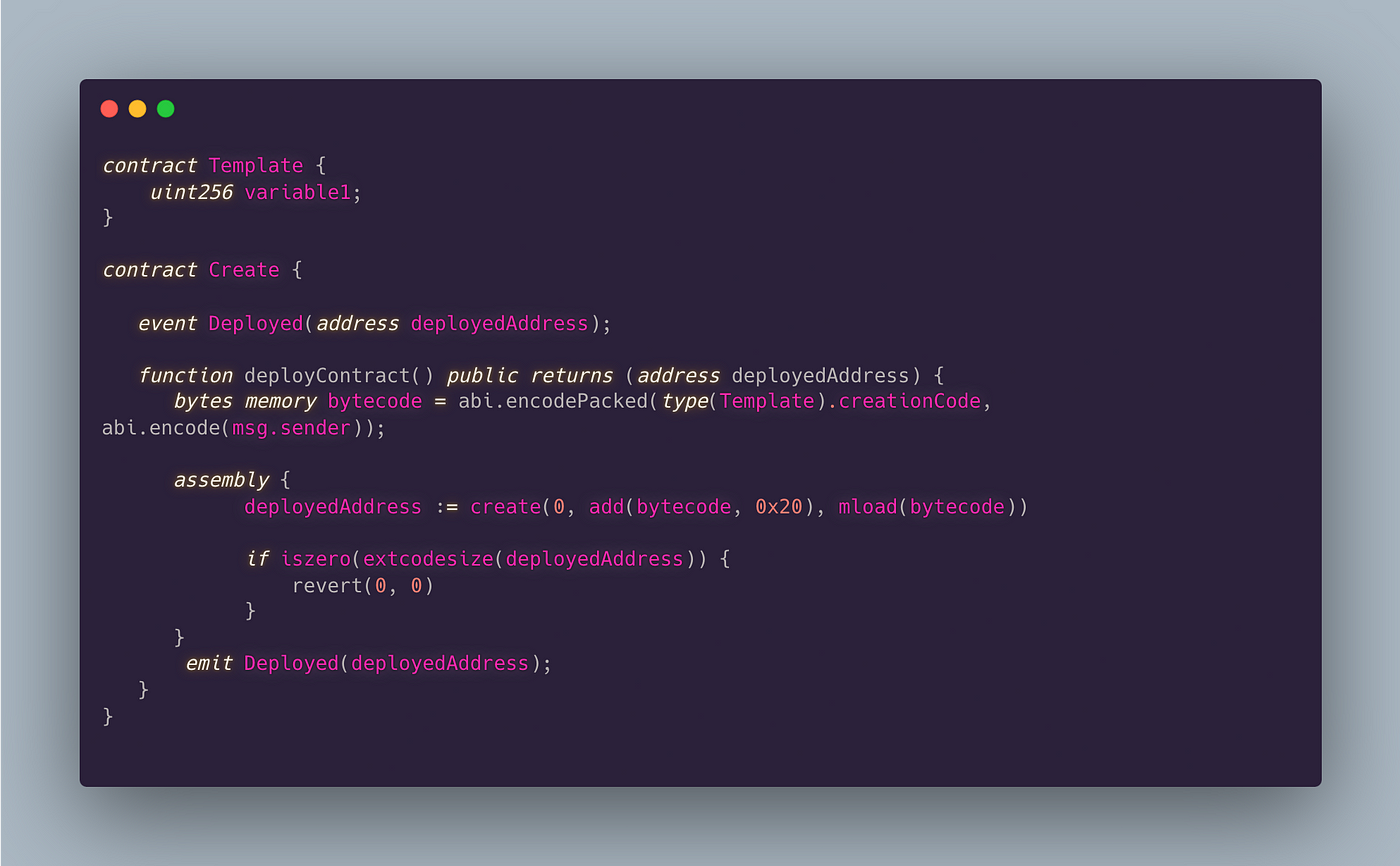
利用“create”操作码
create 操作码是最常用的合约创建操作码。当合约从脚本或其他开发环境中部署时,create 操作码是 EVM 执行的低级指令,用于部署和生成合约地址。
用例:
- 在合约中动态创建新合约。
- 对于部署多个合约更具成本效益。
- 当地址可预测性不是必需时。
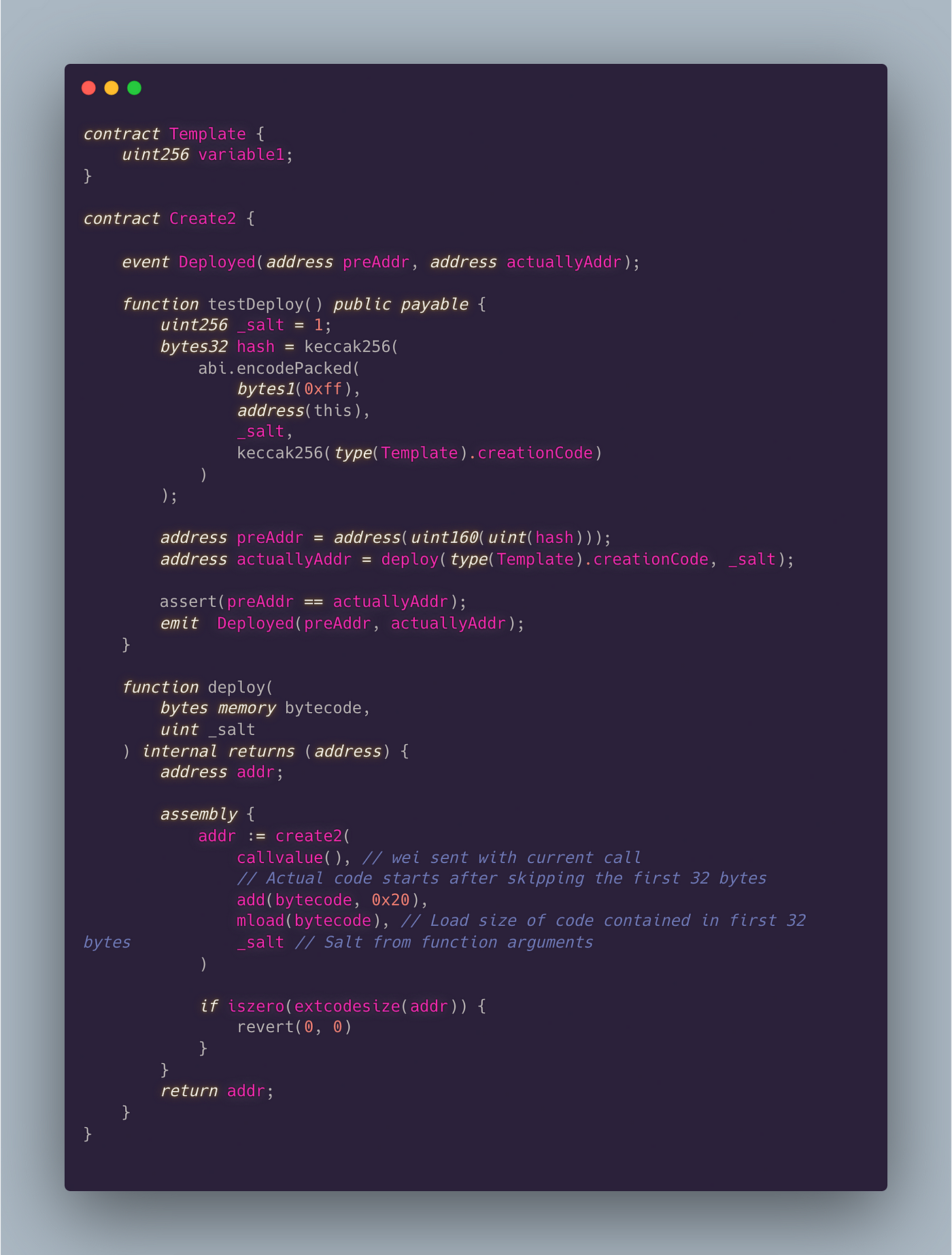
利用“create2”操作码
- 固定前缀,总是
0xFF。 - 发送者的地址确保合约与特定创建者绑定。
- 选择的盐值为合约地址增加唯一性。
- 字节码包含要部署的新合约的代码。
通过组合这些参数,CREATE2 为新合约计算出一个确定性的地址,即使区块链演变,该地址也保持不变。
用例:
- 确保新合约的确定性和可预测的地址。
- 在状态通道、合约钱包和链下交互中有用。
- 通过在部署前检查现有合约提供额外的安全层。
利用“create3” 库
CREATE3 类似于 CREATE2,但在地址推导公式中不包括合约 initCode。它可用于生成不与特定合约代码绑定的确定性合约地址。
CREATE3 是一种结合使用 CREATE 和 CREATE2 的方法,使字节码不再影响部署地址。— CREATE3 比 CREATE 或 CREATE2 更昂贵(固定额外成本约为 55k gas)。
//SPDX-License-Identifier: Unlicense
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
/**
@title A library for deploying contracts EIP-3171 style.
@author Agustin Aguilar <aa@horizon.io>
*/
library Create3 {
error ErrorCreatingProxy();
error ErrorCreatingContract();
error TargetAlreadyExists();
/**
@notice The bytecode for a contract that proxies the creation of another contract
@dev If this code is deployed using CREATE2 it can be used to decouple `creationCode` from the child contract address
0x67363d3d37363d34f03d5260086018f3:
0x00 0x67 0x67XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX PUSH8 bytecode 0x363d3d37363d34f0
0x01 0x3d 0x3d RETURNDATASIZE 0 0x363d3d37363d34f0
0x02 0x52 0x52 MSTORE
0x03 0x60 0x6008 PUSH1 08 8
0x04 0x60 0x6018 PUSH1 18 24 8
0x05 0xf3 0xf3 RETURN
0x363d3d37363d34f0:
0x00 0x36 0x36 CALLDATASIZE cds
0x01 0x3d 0x3d RETURNDATASIZE 0 cds
0x02 0x3d 0x3d RETURNDATASIZE 0 0 cds
0x03 0x37 0x37 CALLDATACOPY
0x04 0x36 0x36 CALLDATASIZE cds
0x05 0x3d 0x3d RETURNDATASIZE 0 cds
0x06 0x34 0x34 CALLVALUE val 0 cds
0x07 0xf0 0xf0 CREATE addr
*/
bytes internal constant PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE = hex"67_36_3d_3d_37_36_3d_34_f0_3d_52_60_08_60_18_f3";
// KECCAK256_PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE = keccak256(PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE);
bytes32 internal constant KECCAK256_PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE = 0x21c35dbe1b344a2488cf3321d6ce542f8e9f305544ff09e4993a62319a497c1f;
/**
@notice Returns the size of the code on a given address
@param _addr Address that may or may not contain code
@return size of the code on the given `_addr`
*/
function codeSize(address _addr) internal view returns (uint256 size) {
assembly { size := extcodesize(_addr) }
}
/**
@notice Creates a new contract with given `_creationCode` and `_salt`
@param _salt Salt of the contract creation, resulting address will be derivated from this value only
@param _creationCode Creation code (constructor) of the contract to be deployed, this value doesn't affect the resulting address
@return addr of the deployed contract, reverts on error
*/
function create3(bytes32 _salt, bytes memory _creationCode) internal returns (address addr) {
return create3(_salt, _creationCode, 0);
}
/**
@notice Creates a new contract with given `_creationCode` and `_salt`
@param _salt Salt of the contract creation, resulting address will be derivated from this value only
@param _creationCode Creation code (constructor) of the contract to be deployed, this value doesn't affect the resulting address
@param _value In WEI of ETH to be forwarded to child contract
@return addr of the deployed contract, reverts on error
*/
function create3(bytes32 _salt, bytes memory _creationCode, uint256 _value) internal returns (address addr) {
// Creation code
bytes memory creationCode = PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE;
// Get target final address
addr = addressOf(_salt);
if (codeSize(addr) != 0) revert TargetAlreadyExists();
// Create CREATE2 proxy
address proxy; assembly { proxy := create2(0, add(creationCode, 32), mload(creationCode), _salt)}
if (proxy == address(0)) revert ErrorCreatingProxy();
// Call proxy with final init code
(bool success,) = proxy.call{ value: _value }(_creationCode);
if (!success || codeSize(addr) == 0) revert ErrorCreatingContract();
}
/**
@notice Computes the resulting address of a contract deployed using address(this) and the given `_salt`
@param _salt Salt of the contract creation, resulting address will be derivated from this value only
@return addr of the deployed contract, reverts on error
@dev The address creation formula is: keccak256(rlp([keccak256(0xff ++ address(this) ++ _salt ++ keccak256(childBytecode))[12:], 0x01]))
*/
function addressOf(bytes32 _salt) internal view returns (address) {
address proxy = address(
uint160(
uint256(
keccak256(
abi.encodePacked(
hex'ff',
address(this),
_salt,
KECCAK256_PROXY_CHILD_BYTECODE
)
)
)
)
);
return address(
uint160(
uint256(
keccak256(
abi.encodePacked(
hex"d6_94",
proxy,
hex"01"
)
)
)
)
);
}
}
contract Child {
function hola() external view returns (string memory) {
return "mundo";
}
}
contract Deployer {
function deployChild() external {
Create3.create3(keccak256(bytes("<my salt>")), type(Child).creationCode);
}
}
contract Child2 {
uint256 meaningOfLife;
address owner;
constructor(uint256 _meaning, address _owner) {
meaningOfLife = _meaning;
owner = _owner;
}
}
contract Deployer2 {
function deployChild() external {
Create3.create3(
keccak256(bytes("<my salt>")),
abi.encodePacked(
type(Child).creationCode,
abi.encode(
42,
msg.sender
)
)
);
}
}特点:
- 基于msg.sender + salt的确定性合约地址。
- 相同的合约地址适用于不同的 EVM 网络。
- 支持任何兼容 EVM 的链,支持 CREATE2。
- 可支付的合约创建(转发到子合约)— 支持构造函数。
用例:
当目标是在多个区块链上部署合约到相同地址时,影响部署地址的因素较少,使得实现这一目标更容易。因此,在这种情况下,CREATE3 比 CREATE2 更好用。
结论
“Create”、“create2”和“create3”是任何从事以太坊合约工作的人必备的工具。每个工具提供不同的合约部署方式,“create”简单直接,“create2”提供可预测的合约地址,而“create3”通过库方法提供多链兼容性。有关详细信息,请查看:
- 基本合约部署:Create1 Gist
- 可预测的合约地址创建:Create2 Gist
- 一致的多链部署:Create3 Gist
有关以太坊开发和见解的更多信息,请访问 smart-contracts-developer.com 和solichain.com。在 Twitter、LinkedIn和 GitHub 上与我联系。
- 确定性部署,第三部分:其他方法 241 浏览
- Uniswap V2 代码解析 126 浏览
- Uniswap V2 — 理解DeFi协议的完整指南 298 浏览
- 智能合约:CREATE,CREATE2,CREATE3区别 1190 浏览
- 部署时节省 gas 1843 浏览
- Solidity合约内部创建合约 2424 浏览
- 工厂模式 - 智能合约如何部署其他合约 1012 浏览
- CREATE2:确定性合约地址 38 浏览
- 部署与确定性地址(CREATE vs CREATE2) 4237 浏览
- 工厂合约 370 浏览
- 理解合约部署、代理和CREATE2——第二部分 3268 浏览
- 利用Wake的引导模糊测试检测抢跑漏洞 1515 浏览