SUI Move开发必知必会<Let's Move>
SUI Move开发必知必会——SUI Move 2024迁移指南及新语法实践
- rzexin
- 发布于 2024-04-04 23:42
- 阅读 4386
SUI Move开发必知必会——SUI Move 2024迁移指南及新语法实践
SUI Move开发必知必会——SUI Move 2024迁移指南及新语法实践
rzexin 2024.04.04
1 前言
SUI Move在2024年迎来重大更新,引入了许多新功能,涵盖新特性,例如:方法语法(method syntax)、位置域(positional fields)、循环标签(loop labels)等,以及不兼容更新,例如:数据类型可见性(Datatype visibility requirements)、 可变性要求(Mutability requirements) 等。这些更新为Move编程语言引入了新的定义数据和调用函数的方式等,使得在Sui上构建应用程序更加高效灵活,也为未来要推出的新功能铺平道路。
本文中SUI Move 2024新增功能内容参考自:https://blog.sui.io/move-2024-migration-guide/,主要包括:
-
新特性(
New features)可以向前兼容的特性,即新旧语法都能进行正常编译
- 方法语法(Method syntax)
- 索引语法(Index syntax)
- 位置域(Positional fields)
- 可嵌套
use别名(Nesteduse) - 常用标准库默认引入(standard library defaults)
- 等式中的自动引用(Automatic referencing in equality)
- 循环标记(Loop labels)
- 带值跳出循环(
breakwith value)
-
不兼容更新(
Breaking changes)无法向前兼容,即不再支持旧语法,若编译会报错
- 数据类型可见性(Datatype visibility requirements)
- 可变性要求(Mutability requirements)
- 移除
friends和public(friend) - 新关键字(New keywords)
- 修订路径和名字空间(Revised paths and namespaces)
除此之外还有很多新特性在路上,例如:语法宏(syntactic macros)、具有模式匹配的枚举(enums with pattern matching)和其他用户定义的语法扩展。
2 迁移指南
要完成历史传统Move合约迁移到SUI Move 2024特别的简单,只需要2步:
2.1 第一步:升级SUI版本
需要使用sui 1.22.0及以上版本。
2.2 第二步:执行迁移命令
在合约根目录里执行sui move migrate命令
- 终端会显示要进行的更改的合约差异,如果接受更改,会自动将现存 历史版本(
legacy) 的合约,迁移成 新版合约(2024.beta) 代码,并会更新Move.toml文件,同时也会生成一个migration.patch文件,将变更差异记录在其中。 - 主要修改的代码就是上面提到的 不兼容更新(
Breaking changes) 部分
2.3 自动迁移实操
$ sui --version
sui 1.22.0-0362997459
$ sui move migrate
Please select one of the following editions:
1) 2024.beta
2) legacy
Selection (default=1): 1
Would you like the Move compiler to migrate your code to Move 2024? (Y/n)
Generated changes . . .
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY Sui
INCLUDING DEPENDENCY MoveStdlib
BUILDING nfts_num
The following changes will be made.
============================================================
--- sources/num.move
+++ sources/num.move
@@ -7 +7 @@
- struct Num has key, store {
+ public struct Num has key, store {
@@ -12 +12 @@
- struct NumIssuerCap has key {
+ public struct NumIssuerCap has key {
============================================================
Apply changes? (Y/n)
Updating "sources/num.move" . . .
Changes complete
Wrote patchfile out to: ./migration.patch
Recorded edition in 'Move.toml'3 新语法实战
以下会通过一个合约示例,展示
SUI Move 2024主要新增的语法特性,考虑到合约实现逻辑的连贯性,会混合使用新特性和不兼容更新的语法。为了一目了然会标题旁做一下标记,以区分:新特性(🎉) 和 不兼容更新(💥),并附上官方文档链接,方便大家查阅。
3.1 可嵌套use别名(Nested use)🎉
支持嵌套使用别名,可以带来代码编写的简洁。
module bityoume::sui_move_2024 {
// legacy code
// use sui::balance;
// use sui::coin::{Self, Coin};
// Move 2024 code
use sui::{balance, coin::{Self, Coin}};
}3.2 常用标准库默认引入(standard library defaults)🎉
以下声明将会自动包含在每个模块中,不需要再写了。这些定义很常用,几乎每个模块都会用到,默认引入,可以减少开发者重复去编写。
// legacy code
use std::vector;
use std::option::{Self, Option};
use sui::object::{Self, ID, UID};
use sui::transfer;
use sui::tx_context::{Self, TxContext};
// Move 2024 code
<空,默认引入>3.3 数据类型可见性(Datatype visibility requirements)💥
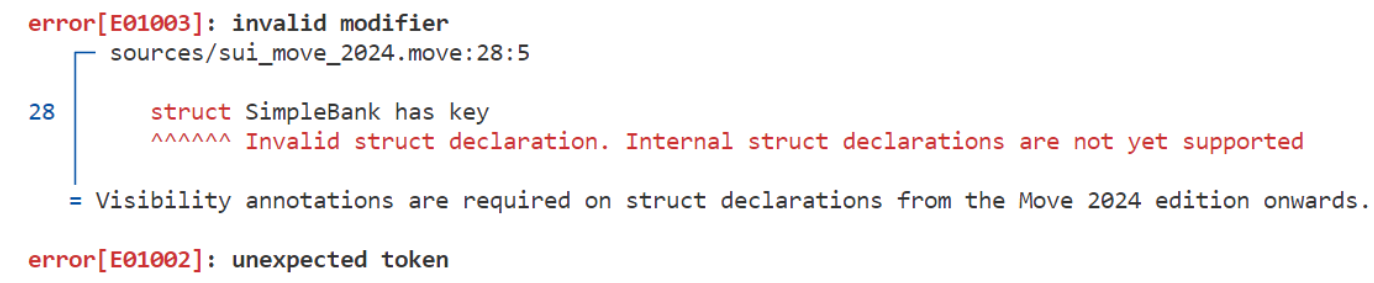
Move 2024要求所有结构体都必须使用public关键字声明,当前Move中的所有结构体都是公开的- 未来的版本可能引入新的可见性标识符,但当前若不使用
public,编译就会报错 - 由于
UID和vector都已经默认引入了,所以不需要再额外引入,结构体中都能正确使用
module bityoume::sui_move_2024 {
use sui::{balance::{Self, Balance}, coin::{Self, Coin}};
use sui::vec_map::{Self, VecMap};
use sui::sui::SUI;
// legacy code
// struct SimpleBank has key
// Move 2024 code
public struct SimpleBank has key {
id: UID,
balances: VecMap<address, Balance<SUI>>,
coin_values: vector<u64>,
}
}- 这是不兼容更新,如果使用旧的写法将会报错:
3.4 方法语法(Method syntax)🎉
- 可以调用与接收器(示例中的
simple_bank和amount)类型相同的模块中定义的任何函数作为方法 - 必要时会自动借用(添加
&和&mut) - 对于在模块外定义的函数,可以使用
public use fun和use fun声明方法 - 从以下代码对比中,不难看出,新语法实现,代码会简洁不少
// legacy code
public entry fun deposit_legacy (
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
amount: &mut Coin<SUI>,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
assert!(coin::value(amount) > 0, EInvalidAmount);
let value = coin::value(amount);
let paid = coin::split(amount, value, ctx);
let sender = tx_context::sender(ctx);
let totalBalance;
if ( vec_map::contains(&simple_bank.balances, &sender) ) {
let myBalance = vec_map::get_mut(&mut simple_bank.balances, &sender);
totalBalance = balance::join(myBalance, coin::into_balance(paid));
} else {
vec_map::insert(&mut simple_bank.balances, sender, coin::into_balance(paid));
totalBalance = value;
};
vector::push_back(&mut simple_bank.coin_values, value);
}
// Move 2024 code
public entry fun deposit_2024 (
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
amount: &mut Coin<SUI>,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
assert!(amount.value() > 0, EInvalidAmount);
let value = amount.value();
let paid = amount.split(value, ctx);
let sender = tx_context::sender(ctx);
let totalBalance;
if ( simple_bank.balances.contains(&sender) ) {
let myBalance = simple_bank.balances.get_mut(&sender);
totalBalance = myBalance.join(paid.into_balance());
} else {
simple_bank.balances.insert(sender, paid.into_balance());
totalBalance = value
};
simple_bank.coin_values.push_back(value);
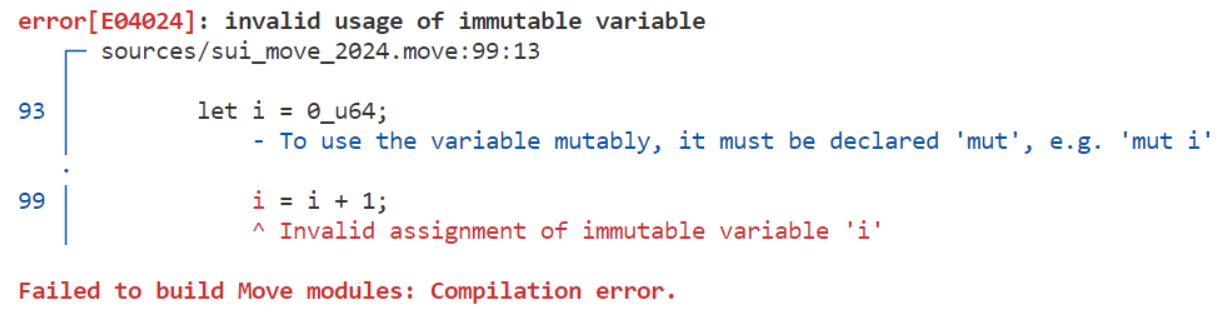
}3.5 可变性要求(Mutability requirements)💥
- 遗产版本所有变量都是隐式可变(
implicitly mutable) - 2024版必须显式声明其可变性,否则编译器将会报错:
public entry fun increase_coin_values(
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
// legacy code
// let i = 0_u64;
// Move 2024 code
let mut i = 0_u64;
while ( i < total_length ) {
i = i + 1;
}
}3.6 索引语法(Index syntax)🎉
-
可以为函数添加
#[syntax(index)]注解,这样便能使用v[i]风格进行方法调用 -
官方的
vector库中,有添加该注解的示例:#[syntax(index)] #[bytecode_instruction] /// Acquire an immutable reference to the `i`th element of the vector `v`. /// Aborts if `i` is out of bounds. native public fun borrow<Element>(v: &vector<Element>, i: u64): ∈ #[syntax(index)] #[bytecode_instruction] /// Return a mutable reference to the `i`th element in the vector `v`. /// Aborts if `i` is out of bounds. native public fun borrow_mut<Element>(v: &mut vector<Element>, i: u64): &mut Element;说明我们可以如下方式进行调用:
&x[i] // 展开为 x.borrow(i) &mut x[i] // 展开为 x.borrow_mut(i) -
这种简化后的语法更易于阅读,也避免了使用复杂索引操作容易出现的问题
public entry fun increase_coin_values(
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
let mut i = 0_u64;
while ( i < total_length ) {
// legacy code
*vector::borrow_mut(&mut simple_bank.coin_values, i) =
*vector::borrow(&simple_bank.coin_values, i) + 1;
// Move 2024 code
*&mut simple_bank.coin_values[i] = simple_bank.coin_values[i] + 1;
i = i + 1;
}
}3.7 位置域(Positional fields)🎉
- 2024版可以定义具有位置字段的结构体,这些字段由从零开始的索引访问
public struct Pair(address, u64) has copy, drop, store;
public struct SimpleBank has key {
id: UID,
balances: VecMap<address, Balance<SUI>>,
coin_values: vector<u64>,
pairs: vector<Pair>,
}
public entry fun increase_coin_values(
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
let mut i = 0_u64;
while ( i < total_length ) {
*&mut simple_bank.coin_values[i] = simple_bank.coin_values[i] + 1;
// Move 2024 code
*&mut simple_bank.pairs[i].1 = simple_bank.pairs[i].1 + 1;
event::emit(EventPair {
sender: simple_bank.pairs[i].0,
amount: simple_bank.pairs[i].1,
});
i = i + 1;
}
}3.8 等式中的自动引用(Automatic referencing in equality)🎉
==和!=的两侧如果一侧是引用另一边不是,不是的这边会自动转成引用
public entry fun increase_coin_values(
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
let mut i = 0_u64;
while ( i < total_length ) {
......
// Move 2024 code
check(99, &simple_bank.pairs[i].1);
i = i + 1;
}
}
fun check(x: u64, r: &u64): bool {
// legacy code
// &x == r
// Move 2024 code
x == r
}3.9 循环标记(Loop labels)🎉
- 嵌套循环中,可以直接为外部循环命名,可以直接
break到外部命名的位置,而无需一层一层的break
public entry fun loop_break (
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
let mut i = 0_u64;
let mut j = total_length - 1;
'outer: while ( i < total_length ) {
while ( j >= 0 ) {
if (check(i, &j)) {
break 'outer
};
j = j - 1;
};
i = i + 1;
};
}3.10 带值跳出循环(break with value)🎉
- 在
loop循环中,可以带值break出循环 - 也可以使用循环标记带值
break出多层循环
public entry fun break_with_value (
simple_bank: &mut SimpleBank,
ctx: &mut TxContext) {
let total_length = simple_bank.coin_values.length();
// Move 2024: break with value
let mut i = 0_u64;
let x: u64 = loop {
if ( i >= total_length ) {
break 0
};
if (simple_bank.coin_values[i] > 100) {
break simple_bank.coin_values[i]
}
};
// Move 2024: break with label value
let mut i = 0_u64;
let mut j = total_length - 1;
let y = 'outer: loop {
while ( j >= 0 ) {
if (check(simple_bank.coin_values[i], &simple_bank.coin_values[j])) {
break 'outer 100
};
j = j - 1;
};
i = i + 1;
if (i==total_length-1) break 0
};
}3.11 移除friends和public(friend)💥
- 以下方式使用方式,在
2024版将会报错
module pkg::m {
friend pkg::a;
public(friend) fun f() { ... }
}
module pkg::a {
fun calls_f() { ... pkg::m::f() ... }
}- 如果希望模块方法仅在包内可见,需要使用
public(package)
module pkg::m {
public(package) fun f() { ... }
}
module pkg::a {
// this now works directly
fun calls_f() { ... pkg::m::f() ... }
}3.12 新关键字(New keywords)💥
-
Move 2024 Beta在语言中添加了以下关键字:
enumformatchmuttype
-
但是在以前的版本中可能被用作标识符。为了帮助开发者迁移现有代码,新的语法规则允许使用反引号将这些关键字作为标识符使用,例如:
let `type` = 0; `type` + 1;
3.13 修订路径和名字空间(Revised paths and namespaces)
-
Move 2024为全局限定引入了前缀操作 -
传统版本
use sui_system::sui_system; ... #[expected_failure(abort_code = sui_system::validator_set::EInvalidCap)] -
2024版本
use sui_system::sui_system; ... #[expected_failure(abort_code = ::sui_system::validator_set::EInvalidCap)] // ^ note `::` here
4 更多
欢迎关注微信公众号:Move中文,开启你的 Sui Move 之旅!

