预言机 Oracle 的原理和实现
- learnerL
- 发布于 2022-02-02 23:07
- 阅读 9043
阅读 geth 源代码是对预言机部分的学习,包括理论和源码解读
Oracle
oracle 翻译是预言机,英文中的意思是预卜先知,知晓消息的意思。在区块链里用于合约获取链外的数据。例如你想把比特币转换成美元,如果在链上进行,那么就需要从链外获取比特币和美元的汇率,例如price feed oracles。但是以太坊是封闭的系统,直接与外界交互很容易破坏 EVM 安全性,因此才用了预言机作为中间层,沟通链上和链外。详细可见chainlink的文档和官方文档。
在以太坊上,**oracle 是已经部署的智能合约和链外组件,它可以查询 API 提供的信息,然后给其他合约发消息,更新合约的数据**。但是只相信唯一的数据源也是很不可靠的方式,通常是多个数据源。我们可以自己创建,也可以直接使用服务商提供的服务。
一般 oracle 机制如下:
- 到了需要链外数据的时候,合约触发事件。
- 链外的接口监听事件的日志。
- 链外接口处理事务,然后交易的方式返回数据给合约。
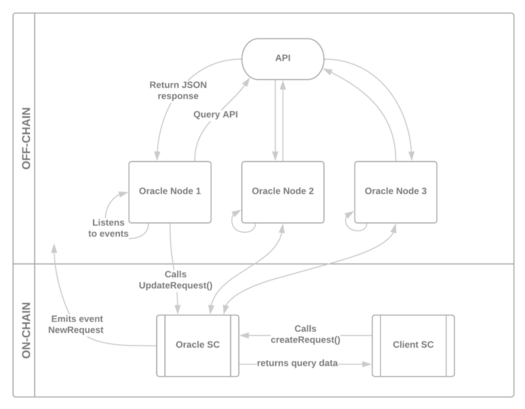
oracle 实例
下面是一个例子,从网络导入合约库,获取接口信息,然后创建合约类型 AggregatorV3Interface 的变量 priceFeed,然后结合获取的接口信息,在构造函数里创建在特定地址已经部署好的合约实例,调用函数priceFeed.latestRoundData(),返回的是元组,因此用多个数据接收。这样就获得了最新的 ETH 和 USD 的汇率。而我们导入的合约priceFeed 以及它在链外的配套接口,被称作预言机 oracle。类似的,我们也可以通过 oracle 解决链上难以产生可靠的随机数的问题。
**更多的例子可以看 chainlink 这些提供商,提供的文档,详细地说明了流程。也可以看这个[教程](https://github.com/pedroduartecosta/blockchain-oracle)。**
// This example code is designed to quickly deploy an example contract using Remix.
pragma solidity ^0.6.7;
import "https://github.com/smartcontractkit/chainlink/blob/master/evm-contracts/src/v0.6/interfaces/AggregatorV3Interface.sol";
contract PriceConsumerV3 {
AggregatorV3Interface internal priceFeed;
/**
* Network: Kovan
* Aggregator: ETH/USD
* Address: 0x9326BFA02ADD2366b30bacB125260Af641031331
*/
constructor() public {
priceFeed = AggregatorV3Interface(0x9326BFA02ADD2366b30bacB125260Af641031331);
}
/**
* Returns the latest price
*/
function getLatestPrice() public view returns (int) {
(
uint80 roundID,
int price,
uint startedAt,
uint timeStamp,
uint80 answeredInRound
) = priceFeed.latestRoundData();
return price;
}
}确保 oracle 安全的方式
Swiss-Cheese 模型
我们采用多层的结构保证数据的可信性,只有多层结构中只要有一个正常工作,则代表 oracle 提供的数据可信。这样也避免了单一数据来源的最脆弱环节失效容易导致漏洞的问题
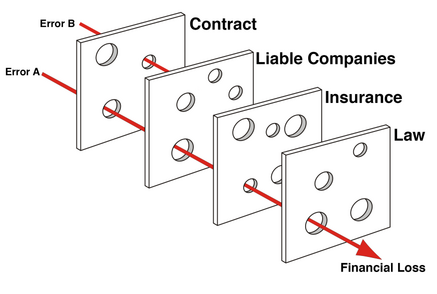
多数据源
可以在链上采用多个数据源,那么只有绝大多数数据都失效或者oracle合约本身存在漏洞时,oracle 才会失效。
实际上,多个可信的数据来源在链上处理是比较耗费 gas 的,因此提出了通过密码学手段,在链外汇总数据,然后发给合约。
多个 oracle
多用几个 oracle 一起验证安全性会提高很多,但是所有 oracle 都传入不正确的数据时,也可能出问题。当智能合约有多个 oracle 来源时,选择哪一个也是需要设计合理的共识机制的。一般而言,多个 oracle 需要满足:
- 每个 oracle 无法确认其他 oracle 的身份。这可以让他们无法串通。
- oracle 之间无法沟通,并且不会互相影响。例如,某个 oracle 有 40% 的投票权,他无法影响其他 oracle,让他们做出相同的选择。
- 当所有 oracle 都提供数据之前,每个 oracle 提供的数据都是无法确认的。这相当于在投票时,只有每个人都投完票之后,才公布结果。
- oracle 都带有权重,防止有人控制大量节点,成为分布式系统中的 “大多数”。
利益一致
完全区中心化的 oracle 是很危险的,我们无法预见数据提供者的行为。但是,可以尝试将 oracle 融入类似于挖矿的过程,如果执行者按规定执行,则给予奖励,否则就会产生损失。
Oracle 可能的漏洞
****单纯创建一个点对点的去中心化系统并不难,但是保证在去中心化系统中某些必要组件的可信性,却是一个难题。- 为了节省验证数据的计算开销,大节点可能在收集数据之后,在链外分享给它控制的节点。如果大节点收集的数据是错误的,那么拥有错误信息的节点容易占大多数,形成另类的女巫攻击。
- 恶意的 oracle 可能会抄袭别人的数据。
- 单一的 oracle的情况,如果数据有损坏,那么在链上是很难检测的。
- 区块链数据都是公开的,即使每个 oracle 的数据加密,执行过程中很难保证敏感的信息不会泄露。 详细可参考 Decentralised Oracles: a comprehensive overview
Oracle 的源码实现
从类型定义可见,checkpoint oracle 实际上是一个合约,它的方法也是和普通合约封装类似,
- 通过地址绑定到已部署的合约,调用该合约。
- 合约地址。
特殊的在于:
- 检查某个状态阶段的可信点(检查点)。
- 生成新的检查点。
附检查点的含义:oracle 的检查点,实际上是一个标记,用于确认这个状态和之前的状态是可信的。在区块链上,检查点往往是有足够的可信实体共同签名后,正式生成。它意味着检查点的状态是不可逆的,无条件可信的。这也是区块链防止造假的手段之一。
geth服务器代码:/contracts/checkpointoracle/contract/oracle.go:
// Package checkpointoracle is an on-chain light client checkpoint oracle.
package checkpointoracle
//go:generate abigen --sol contract/oracle.sol --pkg contract --out contract/oracle.go
//使用 abigen 工具根据目录contract 下的 oracle.sol,在 contract 包内 生成目录contract 下的 oracle.go 文件,
//里面是合约相关的 Golang语言的封装
import (
"errors"
"math/big"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/accounts/abi/bind"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/common"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/contracts/checkpointoracle/contract"
"github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/core/types"
)
// CheckpointOracle is a Go wrapper around an on-chain checkpoint oracle contract.
type CheckpointOracle struct {
address common.Address
contract *contract.CheckpointOracle //预言机类型封装,包括了调用内容、绑定的合约的封装、筛选器
}
//绑定作为检查点的合约,返回封装好的合约实例
// NewCheckpointOracle binds checkpoint contract and returns a registrar instance.
func NewCheckpointOracle(contractAddr common.Address, backend bind.ContractBackend) (*CheckpointOracle, error) {
c, err := contract.NewCheckpointOracle(contractAddr, backend)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &CheckpointOracle{address: contractAddr, contract: c}, nil
}
//获取地址
// ContractAddr returns the address of contract.
func (oracle *CheckpointOracle) ContractAddr() common.Address {
return oracle.address
}
//获取可直接用于调用函数的合约实例
// Contract returns the underlying contract instance.
func (oracle *CheckpointOracle) Contract() *contract.CheckpointOracle {
return oracle.contract
}
//查找某一段内生成检查点时的投票事件(即参与验证签名)
// LookupCheckpointEvents searches checkpoint event for specific section in the
// given log batches.
func (oracle *CheckpointOracle) LookupCheckpointEvents(blockLogs [][]*types.Log, section uint64, hash common.Hash) []*contract.CheckpointOracleNewCheckpointVote {
var votes []*contract.CheckpointOracleNewCheckpointVote
for _, logs := range blockLogs { //需检索的日志
for _, log := range logs {
event, err := oracle.contract.ParseNewCheckpointVote(*log) //解析日志中的事件
if err != nil {
continue
}
if event.Index == section && event.CheckpointHash == hash { //事件包含在需要检索的段,并且哈希值正确。
votes = append(votes, event)
}
}
}
return votes
}
//创建检查点,创建时获取发起的签名,然后调用根据 oracle 合约生成的封装好的代码,给合约发消息
// RegisterCheckpoint registers the checkpoint with a batch of associated signatures
// that are collected off-chain and sorted by lexicographical order.
//
// Notably all signatures given should be transformed to "ethereum style" which transforms
// v from 0/1 to 27/28 according to the yellow paper.
func (oracle *CheckpointOracle) RegisterCheckpoint(opts *bind.TransactOpts, index uint64, hash []byte, rnum *big.Int, rhash [32]byte, sigs [][]byte) (*types.Transaction, error) {
var (
r [][32]byte
s [][32]byte
v []uint8
)
for i := 0; i < len(sigs); i++ {
if len(sigs[i]) != 65 { //检查签名长度
return nil, errors.New("invalid signature")
}
r = append(r, common.BytesToHash(sigs[i][:32]))
s = append(s, common.BytesToHash(sigs[i][32:64]))
v = append(v, sigs[i][64])
}
return oracle.contract.SetCheckpoint(opts, rnum, rhash, common.BytesToHash(hash), index, v, r, s) //调用生成的 oracle.go 中的 SetCheckpoint方法,它是通过 abigen 根据合约代码生成的封装好的调用方法
}合约代码:/contracts/checkpointoracle/contract/oracle.sol
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
//注意,合约并不管生成检查点的具体内容,只负责管理创建、生成检查点的事件,然后交给链外组件完成。这一点与状态机模型是一致的
/**
* @title CheckpointOracle
* @author Gary Rong<garyrong@ethereum.org>, Martin Swende <martin.swende@ethereum.org>
* @dev Implementation of the blockchain checkpoint registrar.
*/
contract CheckpointOracle {
/*
Events
*/
//事件:生成新的检查点时,管理员之一完成签名
// NewCheckpointVote is emitted when a new checkpoint proposal receives a vote.
event NewCheckpointVote(
uint64 indexed index,
bytes32 checkpointHash,
uint8 v,
bytes32 r,
bytes32 s
);
//构造检查点,管理员地址(需要管理员签名才可以生成检查点)、每一段的大小(每个这么一段的区块数)、需要确认的区块数、最少签名人数(阈值)
/*
Public Functions
*/
constructor(
address[] memory _adminlist,
uint256 _sectionSize,
uint256 _processConfirms,
uint256 _threshold
) public {
for (uint256 i = 0; i < _adminlist.length; i++) {
admins[_adminlist[i]] = true;
adminList.push(_adminlist[i]);
}
sectionSize = _sectionSize;
processConfirms = _processConfirms;
threshold = _threshold;
}
/**
* @dev Get latest stable checkpoint information.
* @return section index
* @return checkpoint hash
* @return block height associated with checkpoint
*/
function GetLatestCheckpoint()
public
view
returns (
uint64,
bytes32,
uint256
)
{
return (sectionIndex, hash, height);
}
//注册检查点,最近的区块号和它的哈希值(用于防止链分叉时的重放攻击(第三方拿之前的凭证,谎称自己有签名,冒充身份))、段的索引、段的哈希、签名
// SetCheckpoint sets a new checkpoint. It accepts a list of signatures
// @_recentNumber: a recent blocknumber, for replay protection
// @_recentHash : the hash of `_recentNumber`
// @_hash : the hash to set at _sectionIndex
// @_sectionIndex : the section index to set
// @v : the list of v-values
// @r : the list or r-values
// @s : the list of s-values
function SetCheckpoint(
uint256 _recentNumber,
bytes32 _recentHash,
bytes32 _hash,
uint64 _sectionIndex,
uint8[] memory v,
bytes32[] memory r,
bytes32[] memory s
) public returns (bool) {
//已授权
// Ensure the sender is authorized.
require(admins[msg.sender]);
//分叉时,之前的区块位置可能被顶替,区块号相同但是区块哈希不同
// These checks replay protection, so it cannot be replayed on forks,
// accidentally or intentionally
require(blockhash(_recentNumber) == _recentHash);
//通过签名长度检查签名是否有效
// Ensure the batch of signatures are valid.
require(v.length == r.length);
require(v.length == s.length);
//还没到下一段,不用新建检查点
// Filter out "future" checkpoint.
if (
block.number < (_sectionIndex + 1) * sectionSize + processConfirms
) {
return false;
}
//这一段已经生成过了,错误。
// Filter out "old" announcement
if (_sectionIndex < sectionIndex) {
return false;
}
//这一段已经开始生产或者已经生成,没必要再次尝试创建
// Filter out "stale" announcement
if (
_sectionIndex == sectionIndex && (_sectionIndex != 0 || height != 0)
) {
return false;
}
//检查点哈希异常,哈希无效
// Filter out "invalid" announcement
if (_hash == "") {
return false;
}
//生成签名哈希
// EIP 191 style signatures
//
// Arguments when calculating hash to validate
// 1: byte(0x19) - the initial 0x19 byte
// 2: byte(0) - the version byte (data with intended validator)
// 3: this - the validator address
// -- Application specific data
// 4 : checkpoint section_index(uint64)
// 5 : checkpoint hash (bytes32)
// hash = keccak256(checkpoint_index, section_head, cht_root, bloom_root)
bytes32 signedHash = keccak256(
abi.encodePacked(
bytes1(0x19),
bytes1(0),
this,
_sectionIndex,
_hash
)
);
address lastVoter = address(0);
//签名按照顺序依次验证, ecrecover函数用于验证签名是否来自可信地址,这里采用的是 EIP191 标准的签名,
//更进一步了解可见 https://soliditydeveloper.com/ecrecover
// In order for us not to have to maintain a mapping of who has already
// voted, and we don't want to count a vote twice, the signatures must
// be submitted in strict ordering.
for (uint256 idx = 0; idx < v.length; idx++) {
address signer = ecrecover(signedHash, v[idx], r[idx], s[idx]);
require(admins[signer]); //签名生成的地址属于管理者
require(uint256(signer) > uint256(lastVoter)); //按照地址排序,在前一个人之后验证
lastVoter = signer;
emit NewCheckpointVote(
_sectionIndex,
_hash,
v[idx],
r[idx],
s[idx]
);
//签名人数已足够
// Sufficient signatures present, update latest checkpoint.
if (idx + 1 >= threshold) {
hash = _hash;
height = block.number;
sectionIndex = _sectionIndex;
return true;
}
}
//如果未达到签名人数的阈值,则回滚
// We shouldn't wind up here, reverting un-emits the events
revert();
}
/**
* @dev Get all admin addresses
* @return address list
*/
function GetAllAdmin() public view returns (address[] memory) {
address[] memory ret = new address[](adminList.length);
for (uint256 i = 0; i < adminList.length; i++) {
ret[i] = adminList[i];
}
return ret;
}
/*
Fields
*/
//管理员列表中有权参与的人的标记
// A map of admin users who have the permission to update CHT and bloom Trie root
mapping(address => bool) admins;
//管理员列表
// A list of admin users so that we can obtain all admin users.
address[] adminList;
//最新一段的编号
// Latest stored section id
uint64 sectionIndex;
// The block height associated with latest registered checkpoint.
uint256 height;
//注册检查点时的哈希
// The hash of latest registered checkpoint.
bytes32 hash;
//每过这一段大小就生成一个检查点
// The frequency for creating a checkpoint
//
// The default value should be the same as the checkpoint size(32768) in the ethereum.
uint256 sectionSize;
//构造预言机的检查点时,需要的可信签名的个数,多一些人验证可以防止因为链重组造成的异常
// The number of confirmations needed before a checkpoint can be registered.
// We have to make sure the checkpoint registered will not be invalid due to
// chain reorg.
//
// The default value should be the same as the checkpoint process confirmations(256)
// in the ethereum.
uint256 processConfirms;
//生成可信检查点需要验证的最小的签名个数
// The required signatures to finalize a stable checkpoint.
uint256 threshold;
}
