LayerZero跨链协议入门教程
- 翻译小组
- 发布于 2022-04-29 19:01
- 阅读 10299
在本教程中,我们将使用LayerZero 建立一个简单的跨链消息转账合约,并使用默认的UA配置,发送一个跨链消息。
前提条件
本教程用LayerZero 建立一个简单的跨链消息转账合约,需要你对Solidity Hardhat有一定的程度了解。
概述
首先,我们先来了解一下LayerZero, LayerZero是一个Omnichain互操作性协议,设计用于跨链的轻量级消息传递。LayerZero提供了无需信任、且真实的、有保证的、可配置的消息传递。LayerZero是由一套低费用(gas-efficient)、不可升级的智能合约实现。
1. 初始化hardhat项目
创建一个空目录,在目录下运行npm init,按照提示,填写项目信息,完成之后,运行npm install --save-dev hardhat 安装 Hardhat。
要创建Hardhat项目,在项目文件夹运行npx hardhat,如下图:
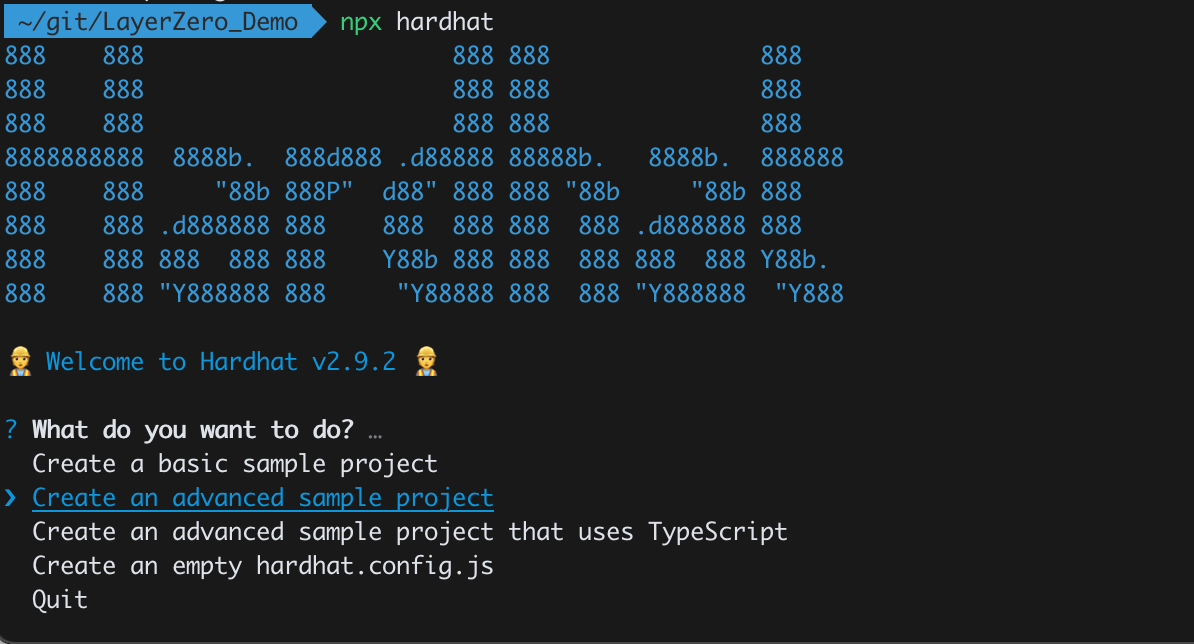
我们选择 Create an advanced sample project 为教程创建一个hardhat项目。
要发送跨链消息,合约在源链调用端点(endpoint)的send()方法,然后在目标链调用lzReceive()方法接收消息。为了使用端点合约,我们需要从 LayerZero 库 中导入接口。
备注:端点(endpoint)是在各链部署的合约,参考文档
2. 创建Solidity合约
创建合约文件LayerZeroDemo1.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.9;
pragma abicoder v2;
import "../interfaces/ILayerZeroEndpoint.sol";
import "../interfaces/ILayerZeroReceiver.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract LayerZeroDemo1 is ILayerZeroReceiver {
event ReceiveMsg(
uint16 _srcChainId,
address _from,
uint16 _count,
bytes _payload
);
ILayerZeroEndpoint public endpoint;
uint16 public messageCount;
bytes public message;
constructor(address _endpoint) {
endpoint = ILayerZeroEndpoint(_endpoint);
}
function sendMsg(
uint16 _dstChainId,
bytes calldata _destination,
bytes calldata payload
) public payable {
endpoint.send{value: msg.value}(
_dstChainId,
_destination,
payload,
payable(msg.sender),
address(this),
bytes("")
);
}
function lzReceive(
uint16 _srcChainId,
bytes memory _from,
uint64,
bytes memory _payload
) external override {
require(msg.sender == address(endpoint));
address from;
assembly {
from := mload(add(_from, 20))
}
if (
keccak256(abi.encodePacked((_payload))) ==
keccak256(abi.encodePacked((bytes10("ff"))))
) {
endpoint.receivePayload(
1,
bytes(""),
address(0x0),
1,
1,
bytes("")
);
}
message = _payload;
messageCount += 1;
emit ReceiveMsg(_srcChainId, from, messageCount, message);
}
// Endpoint.sol estimateFees() returns the fees for the message
function estimateFees(
uint16 _dstChainId,
address _userApplication,
bytes calldata _payload,
bool _payInZRO,
bytes calldata _adapterParams
) external view returns (uint256 nativeFee, uint256 zroFee) {
return
endpoint.estimateFees(
_dstChainId,
_userApplication,
_payload,
_payInZRO,
_adapterParams
);
}
}LayerZeroDemo1合约从源链向目标链发送一条消息,在合约构造时使用了端点地址,并且使用了两个接口:ILayerZeroEndpoint和ILayerZeroReceiver。
自定义函数sendMsg()封装了endpoint.send(…),其将在目标链上触发对lzReceive()的调用。
在源链调用endpoint.send(…)后,接收链上会自动调用重载的lzReceive函数。
自定义函数estimateFees()封装了endpoint.estimateFees(…),该函数将返回跨链消息的所需的费用。
3. 在不同的链上部署合约
Fantom 测试网络创建部署脚本:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const LayerZeroDemo1 = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("LayerZeroDemo1");
const layerZeroDemo1 = await LayerZeroDemo1.deploy(
"0x7dcAD72640F835B0FA36EFD3D6d3ec902C7E5acf"
);
await layerZeroDemo1.deployed();
console.log("layerZeroDemo1 deployed to:", layerZeroDemo1.address);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});在 Fantom 测试网上部署合约:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy_testnet.js --network testnetMumbai(Polygon测试网络)创建部署脚本:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const LayerZeroDemo1 = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("LayerZeroDemo1");
const layerZeroDemo1 = await LayerZeroDemo1.deploy(
"0xf69186dfBa60DdB133E91E9A4B5673624293d8F8"
);
await layerZeroDemo1.deployed();
console.log("layerZeroDemo1 deployed to:", layerZeroDemo1.address);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});在Mumbai测试网络部署合约:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy_mumbai.js --network mumbai成功部署两个合约后,我们得到了合约地址,例如:
Mubai测试网络: 0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b
Fantom 测试网络: 0xD67D01D6893cC4a2E17557765987d41E778fadca
4. 测试跨链消息传递
为 Mumbai 测试网络创建一个 javascript 测试脚本:
const hre = require("hardhat");
const { ethers } = require("ethers");
async function main() {
const LayerZeroDemo1 = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("LayerZeroDemo1");
const layerZeroDemo1 = await LayerZeroDemo1.attach(
"0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b"
);
const count = await layerZeroDemo1.messageCount();
const msg = await layerZeroDemo1.message();
console.log(count);
console.log(ethers.utils.toUtf8String(msg));
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});该脚本将合约实例关联到前面部署的合约地址:0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b。脚本将读取合约中的消息计数器和最后一条消息,现在返回的是0和空字符串。
使用hardhat运行脚本:
npx hardhat run scripts/demo1_mumbai.js --network mumbai
接着在 Fantom 测试网创建一个 javascript 测试脚本:
const { formatBytes32String } = require("ethers/lib/utils");
const { ethers } = require("ethers");
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const LayerZeroDemo1 = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("LayerZeroDemo1");
const layerZeroDemo1 = await LayerZeroDemo1.attach(
"0xD67D01D6893cC4a2E17557765987d41E778fadca"
);
const fees = await layerZeroDemo1.estimateFees(
10009,
"0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b",
formatBytes32String("Hello LayerZero"),
false,
[]
);
console.log(ethers.utils.formatEther(fees[0].toString()));
await layerZeroDemo1.sendMsg(
10009,
"0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b",
formatBytes32String("Hello LayerZero"),
{ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("1") }
);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});Fantom 测试网测试脚本将合约实例关联上地址 0xD67D01D6893cC4a2E17557765987d41E778fadca。该脚本会从 Fantom 测试网向Mumbai测试网上的合约(地址:0x37587469690CC37EE19Ff6163ce7275BB1b17d3b) 发送一条消息“Hello LayerZero” ,并估算了消息费用(演示目的)。最后发送带有费用的消息, 为简单起见,这里为 1FTM。如果源交易比提供的金额少,它将把额外的金额退还到我们传递的地址 _refundAddress。
使用 Hardhat 运行脚本:
npx hardhat run scripts/demo1_testnet.js --network testnet脚本完成后,我们可以在 FTMScan 测试网中查找合约0xd67d01d6893cc4a2e17557765987d41e778fadca上的交易:
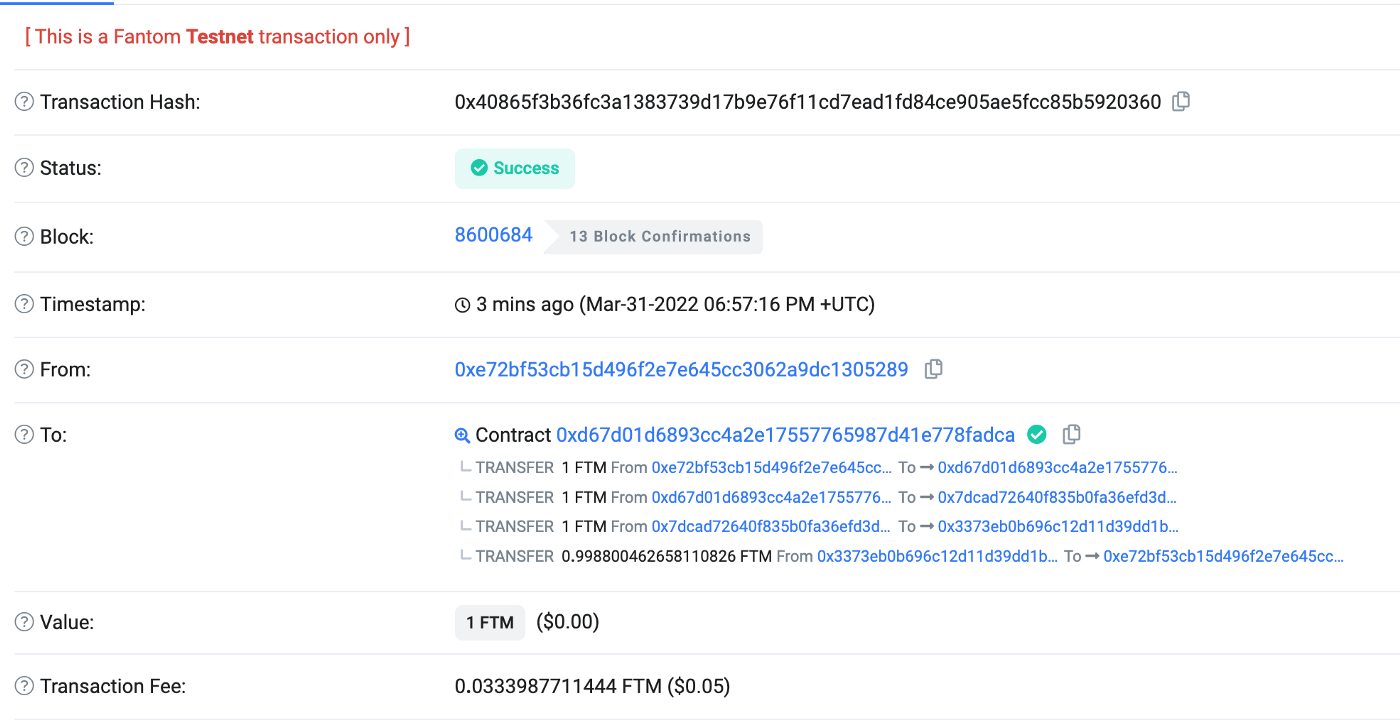
再次运行 Mumbai 测试脚本,控制台将打印:

小结
教程完成了,Mumbai测试网络的合约收到Fantom测试链发来的消息,增加计数器。LayerZero 使整个过程变得非常简单。
教程源码:https://github.com/The-dLab/LayerZero-Demo
LayerZero 测试网地址: https://layerzero.gitbook.io/docs/technical-reference/testnet/testnet-addresseshttps://medium.com/@Tim4l1f3/layerzero-tutorial-for-beginners-d3fe9326e8b7
本翻译由 Duet Protocol 赞助支持。
- 并行执行的谎言:为什么SOL和ZERO不是在与ETH竞争,而是在输给它的L2 464 浏览
- Layer Zero 发布 Zero 链:去中心化的多核世界计算机 440 浏览
- 第22章:跨链协议与跨链桥 1956 浏览
- 2026年互操作性发展现状 1182 浏览
- Uniswap Tribunal 审计 895 浏览
- 跨链治理:DAO如何在多链上进行投票(而不会崩溃) 786 浏览
- Layerzero:OFT-adapter 952 浏览
- LayerzeroV2:message跨链 1740 浏览
- 当社交媒体开始为用户付费时:Overherd 如何将注意力转化为收入 785 浏览
- 区块链桥接安全 - 介绍与第一部分 1203 浏览
- 让以太坊所有的 Layer2 再次感觉像一条链 3737 浏览
- zERC20:基于零知识燃烧证明的跨链隐私型 ERC-20 - ERC标准 71 浏览

