实现一套 DID 之总体设计 | Move dApp 极速入门(五)
- 李大狗
- 发布于 2022-09-19 19:39
- 阅读 3259
从本篇开始,我们将通过一个实战案例更深入的讲解 MOVE 语言以及 MOVE dApp 的开发 ——这也是 MOVE 生态上的首个 DID 的实现。
前文链接:
第一个 Move dApp | Move dApp极速入门(二)
在之前的文章里,我们通过精简的方式对 MOVE 语言以及 Starcoin dApp 开发进行了快速入门。
从本篇开始,我们将通过一个实战案例更深入的讲解 MOVE 语言以及 MOVE dApp 的开发 ——这也是 MOVE 生态上的首个 DID 的实现。
0x01 DID & Verifiable Credential 科普
DID 是由 w3c 推出的数字身份协议。
Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) are a new type of identifier that enables verifiable, decentralized digital identity. A DID refers to any subject (e.g., a person, organization, thing, data model, abstract entity, etc.) as determined by the controller of the DID.
Verifiable Credential 是由 w3c 推出的可验证凭证协议。
Credentials are a part of our daily lives; driver's licenses are used to assert that we are capable of operating a motor vehicle, university degrees can be used to assert our level of education, and government-issued passports enable us to travel between countries. This specification provides a mechanism to express these sorts of credentials on the Web in a way that is cryptographically secure, privacy respecting, and machine-verifiable.
在现有的实践中,二者经常被一同实践。但实际上,这两套协议也并非绑定的,我们完全可以用 DID + SBT来替代DID + VC。
0x02 设计思路
像羽毛一样轻。
一个MVP(最小可用版本)的 DID 至少包含如下几个组成部分:
-
DID Syntax(DID 标识符)
https\://www.w3.org/TR/did-core/#did-syntax
-
DID Document in JSON(JSON 格式的 DID 描述文档)
-
- Address Aggregator 地址聚合器
- Endpoint Aggregator 终端服务聚合器
在进行任意的 dApp 实践的时候,设计者都首先要问自己一个问题:
把哪些部分放到链上?把哪些部分放到链下?
这个问题遵循一个即可:
让链上设计尽可能的轻
以 DID 为例,我们可以看到很多 DID 的实现都会把链上搞得过重。事实上,对于 MVP 版本来说,我们在链上实现如下两个模块即可:
- Addr Aggregator:地址的增删改查
- Endpoint Addrgator:终端服务的增删改查
然后我们会在链下实现一个 did_sdk,里面包含如下模块:
- Contract Interactor:和链上合约进行交互
- DID Handler:将链上数据转化为符合
w3c标准的格式
0x03 系统架构
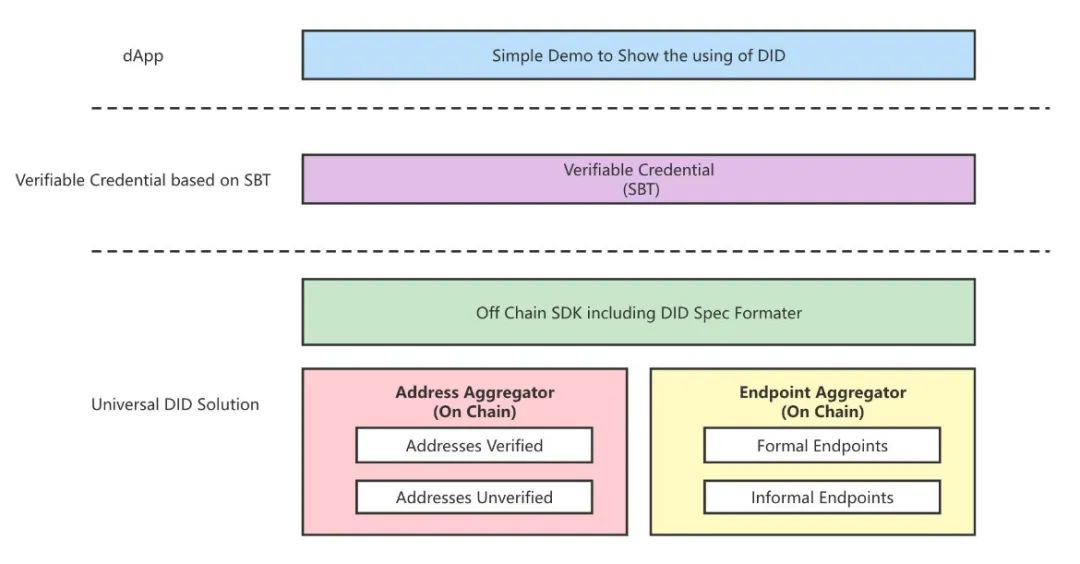
包含如下三个层级:
- dApp 层:一个简单的对 DID 应用的 dApp 的实现
- VC 层:基于 SBT 的可验证凭证的实现
- 通用 DID 层:通用 DID 的实现
0x04 文件结构
本项目持续 buidl 中,完全开源:
文件结构如下
.
├── README.md
├── did
│ ├── Move.toml
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── build
│ ├── dapp
│ ├── release
│ └── sources
├── sbt-as-vc
│ ├── Move.toml
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── build
│ ├── dapp
│ ├── release
│ └── sources
└── did_handler
├── README.md
├── _build
├── deps
├── lib
├── mix.exs
├── mix.lock
└── test其中,did和sbt-as-vc包含 MOVE 合约及纯前端 dApp,did_handler 是使用 elixir 语言实现的 SDK。
- Move 对比 Rust 对比 Solidity:终极 L1 区块链安全对比 (2026) 131 浏览
- DApp生存法则:来自Solana租金回收市场的启示 471 浏览
- Web3 实操入门 3674 浏览
- 102:从 ERC 到多链:鸟瞰各公链标准体系 1229 浏览
- 第12章. 去中心化应用 2124 浏览
- dApp开发入门教程:从零开始构建链上留言板 1417 浏览
- 101:账户模型是标准的根:UTXO vs Account vs Object 1994 浏览
- 第3章:以太坊 2852 浏览
- 第2章:什么是去中心化金融 (DeFi)? 1888 浏览
- Monad主网上线后必看的dApp 357 浏览
- 从 EVM 迁移到 Move,第一部分 2323 浏览
- 从零开始构建你的第一个 Web3 DApp —— 5. Dapp前端部署 2520 浏览

