EIP-7594解析:PeerDAS和以太坊可扩展性路线图的技术深入研究
- Krieger69
- 发布于 2025-04-30 11:53
- 阅读 2224
这篇文章深入探讨了以太坊的扩展性问题,重点介绍了PeerDAS (EIP-7594)方案,它是以太坊实现数据可用性抽样(DAS)的第一个实践版本,旨在解决rollup在数据可用性方面的瓶颈。文章详细解释了PeerDAS的技术机制,包括数据结构、KZG承诺、网络交互和抽样策略,并分析了它对L2扩展性、网络效率和去中心化的影响。
以太坊上可扩展性的必要性
The Surge(巨浪):专注于大规模提高可扩展性,主要通过 Layer 2 rollups 和数据分片/可用性技术,目标是每秒 100,000+ 笔交易 (TPS)。
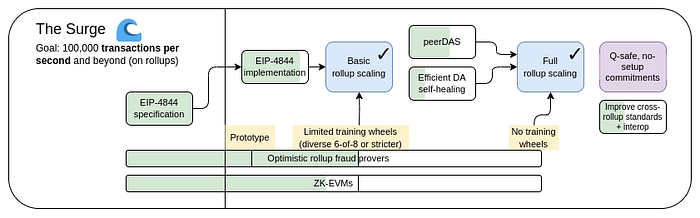
The Surge, 2023 年路线图版本 (作者: Vitalik Buterin)
随着以太坊朝着其以 rollup 为中心的扩展路线图 发展 (由 Vitalik Buterin 提出),旨在解决 “ 可扩展性三难困境 ” — 平衡 可扩展性、安全性 和 去中心化。Pectra 和 PeerDAS 代表着实现 The Surge(巨浪) 目标的下一个合乎逻辑且至关重要的步骤。EIP-4844 为 L2 数据 (blobs) 创建了空间,但其容量受到所有节点都需要下载所有内容的限制。
PeerDAS (EIP-7594) 通过引入 DAS 释放了该空间的可扩展性,打破了将总数据吞吐量与单个节点容量联系起来的约束。通过允许节点通过抽样验证可用性,PeerDAS 使网络能够安全地增加每个区块的 blob 数量,直接履行了 Surge 为 L2 rollups 提供廉价且充足的数据可用性的承诺。
PeerDAS(EIP-7594):以太坊的 DAS 实现
虽然 DAS 的核心思想 (深入文章) 提供了理论,但 以太坊的第一个实用版本 称为 PeerDAS,在 EIP-7594 中定义,并随 Fulu 升级一起发布。](https://ethereum.org/en/roadmap/danksharding/)(这将涉及更高级的 2D erasure coding)。
PeerDAS 技术机制:它是如何工作的
PeerDAS 引入了处理数据,网络和抽样的特定技术:
1. 数据结构和编码
- Blobs:PeerDAS 与 EIP-4844 中引入的 blobs 一起使用。一个区块可以包含多个 blobs(例如,Pectra 目标将每个区块的 目标 blobs 数量从 3 增加到 6,并将每个区块的 最大 blobs 数量从 6 增加到 9)。
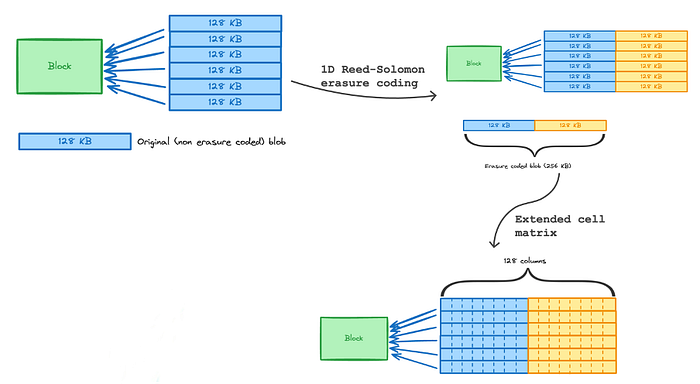
- 1D Reed-Solomon 编码: PeerDAS 将 1D Reed-Solomon coding (纠删码 的一种)独立地应用于每个 blob。每个 blob 的数据(例如,4096 个字段元素,通常组织成 64 个元素的 64 个单元格)被视为多项式并扩展,通常将其大小加倍(例如,由
[NUMBER\_OF\_COLUMNS](https://github.com/ethereum/consensus-specs/blob/8f8ab03acf1656c54f3a81ef18878f853a1cc4c6/specs/_features/eip7594/das-core.md#data-size)控制的每个 blob 64 个原始单元格扩展到 128 个编码单元格)。 - 矩阵概念:扩展后的 blobs 形成概念矩阵的行。如果一个区块有
M个 blobs,并且每个 blob 扩展到N个单元格(N = [NUMBER\_OF\_COLUMNS](https://github.com/ethereum/consensus-specs/blob/8f8ab03acf1656c54f3a81ef18878f853a1cc4c6/specs/_features/eip7594/das-core.md#data-size)),则矩阵的维度为M x N。
consensus-specs/specs/fulu/das-core.md at dev · ethereum/consensus-specs
def compute_matrix(blobs: Sequence[Blob]) -> Sequence[MatrixEntry]:
"""
返回完整的,扁平化的矩阵条目序列。
此帮助程序演示了 blobs 和单元格/证明矩阵之间的关系。
用于存储单元格/证明的数据结构取决于实现。
"""
matrix = []
for blob_index, blob in enumerate(blobs):
cells, proofs = compute_cells_and_kzg_proofs(blob)
for cell_index, (cell, proof) in enumerate(zip(cells, proofs)):
matrix.append(MatrixEntry(
cell=cell,
kzg_proof=proof,
row_index=blob_index,
column_index=cell_index,
))
return matrix- 单元格和列:每个扩展行 (blob) 分为
N个 单元格(可以通过 KZG 证明验证的最小单元,通常每个单元格约 2KB)。列 (索引j) 由区块中每个M个扩展 blobs 中的j-th单元格组成。列数通常与每个扩展 blob 的单元格数匹配(例如,128 列)。
consensus-specs/specs/fulu/polynomial-commitments-sampling.md at dev · ethereum/consensus-specs
def compute_cells(blob: Blob) -> Vector[Cell, CELLS_PER_EXT_BLOB]:
"""
给定一个 blob,扩展它并返回扩展 blob 的所有单元格。
公共方法。
"""
assert len(blob) == BYTES_PER_BLOB
polynomial = blob_to_polynomial(blob)
polynomial_coeff = polynomial_eval_to_coeff(polynomial)
cells = []
for i in range(CELLS_PER_EXT_BLOB):
coset = coset_for_cell(CellIndex(i))
ys = CosetEvals([evaluate_polynomialcoeff(polynomial_coeff, z) for z in coset])
cells.append(coset_evals_to_cell(CosetEvals(ys)))
return cells2. KZG 承诺
PeerDAS 利用 KZG 承诺进行验证。每个 blob(行)都有自己的 KZG 承诺,这已经是 EIP-4844 结构的一部分。验证列中的单元格涉及根据其所属的特定 blob(行)的承诺检查其 KZG 证明。
consensus-specs/specs/fulu/polynomial-commitments-sampling.md at dev · ethereum/consensus-specs
def verify_cell_kzg_proof_batch(commitments_bytes: Sequence[Bytes48],
cell_indices: Sequence[CellIndex],
cells: Sequence[Cell],
proofs_bytes: Sequence[Bytes48]) -> bool:
"""
验证一组单元格是否属于其对应的承诺。
给定四个列表,表示 (``承诺``, ``单元格索引``, ``单元格``, ``证明``) 的元组,
该函数验证 ``证明``,该证明表明 ``单元格`` 是与 ``承诺`` 关联的多项式的评估,
在由 ``单元格索引`` 指定的域上进行评估。
此函数实现了此处介绍的通用验证公式:
https://ethresear.ch/t/a-universal-verification-equation-for-data-availability-sampling/13240
公共方法。
"""
assert len(commitments_bytes) == len(cells) == len(proofs_bytes) == len(cell_indices)
for commitment_bytes in commitments_bytes:
assert len(commitment_bytes) == BYTES_PER_COMMITMENT
for cell_index in cell_indices:
assert cell_index < CELLS_PER_EXT_BLOB
for cell in cells:
assert len(cell) == BYTES_PER_CELL
for proof_bytes in proofs_bytes:
assert len(proof_bytes) == BYTES_PER_PROOF
# 创建我们正在处理的去重承诺列表
deduplicated_commitments = [bytes_to_kzg_commitment(commitment_bytes)\
for commitment_bytes in set(commitments_bytes)]
# 创建索引列表,将初始承诺(可能包含重复项)映射到去重承诺
commitment_indices = [CommitmentIndex(deduplicated_commitments.index(commitment_bytes))\
for commitment_bytes in commitments_bytes]
cosets_evals = [cell_to_coset_evals(cell) for cell in cells]
proofs = [bytes_to_kzg_proof(proof_bytes) for proof_bytes in proofs_bytes]
# 进行实际验证
return verify_cell_kzg_proof_batch_impl(
deduplicated_commitments,
commitment_indices,
cell_indices,
cosets_evals,
proofs)3. 对等点发现和网络交互
- 列子网:p2p 网络分为子网,每列一个子网(例如,128 列对应 128 个子网)。
consensus-specs/specs/fulu/das-core.md at dev · ethereum/consensus-specs
def get_custody_groups(node_id: NodeID, custody_group_count: uint64) -> Sequence[CustodyIndex]:
assert custody_group_count <= NUMBER_OF_CUSTODY_GROUPS
current_id = uint256(node_id)
custody_groups: List[CustodyIndex] = []
while len(custody_groups) < custody_group_count:
custody_group = CustodyIndex(
bytes_to_uint64(hash(uint_to_bytes(current_id))[0:8])
% NUMBER_OF_CUSTODY_GROUPS
)
if custody_group not in custody_groups:
custody_groups.append(custody_group)
if current_id == UINT256_MAX:
# 防止溢出
current_id = uint256(0)
else:
current_id += 1
assert len(custody_groups) == len(set(custody_groups))
return sorted(custody_groups)- 保管要求:每个节点(验证者或完整节点)确定性地被分配保管 一小部分列子网。
[CUSTODY\_REQUIREMENT](https://github.com/ethereum/consensus-specs/blob/8f8ab03acf1656c54f3a81ef18878f853a1cc4c6/specs/_features/eip7594/das-core.md#custody-setting)参数定义了每个节点必须下载、验证和临时存储的 不同列数。示例:如果[CUSTODY\_REQUIREMENT](https://github.com/ethereum/consensus-specs/blob/8f8ab03acf1656c54f3a81ef18878f853a1cc4c6/specs/_features/eip7594/das-core.md#custody-setting) = 8,则节点负责 128 列中的 8 列。 - 对等点发现:
由于保管分配是确定性的(使用节点的唯一 ID 和区块的元数据),因此需要列 j 的节点可以有效地找到负责列 j 的潜在对等点。
- 对等点连接:这种确定性分配使高效的对等点发现成为可能。需要对列
j进行抽样的节点可以识别出其节点 ID 将它们映射到保管子网j的潜在对等点。网络模拟表明,节点可能只需要与相对少量的不同对等点(例如,< 50,取决于参数)保持连接,以确保覆盖所有必需的子网。 - Gossip + RPC:初始列数据通过 gossiped 传播,但抽样使用 直接 RPC 请求 以提高效率。
4. 抽样策略
- 何时:预计节点在每个Slot(约 12 秒)执行 DAS 抽样。
- 抽样内容:节点从其对等点处对整个_列_进行抽样。
- 要抽样多少:
每个节点必须 成功地在每个Slot抽样一定数量的不同列。此数字由 SAMPLES_PER_SLOT 参数定义。
示例:如果 SAMPLES_PER_SLOT = 40,则节点在给定Slot中抽样 40 个不同的列。
- 抽样方法:
子网抽样(初始):节点订阅为其分配的列的 gossip 主题(效率较低)。
对等点抽样(目标):节点使用直接 RPC 从负责这些列的对等点处请求特定列(效率更高)。
验证:节点根据相应 blob 的 KZG 承诺检查每个抽样的单元格。
consensus-specs/specs/fulu/p2p-interface.md at dev · ethereum/consensus-specs
def verify_data_column_sidecar_kzg_proofs(sidecar: DataColumnSidecar) -> bool:
"""
验证 KZG 证明是否正确。
"""
# 列索引也表示单元格索引
cell_indices = [CellIndex(sidecar.index)] * len(sidecar.column)
# 批量验证单元格是否与相应的承诺和证明匹配
return verify_cell_kzg_proof_batch(
commitments_bytes=sidecar.kzg_commitments,
cell_indices=cell_indices,
cells=sidecar.column,
proofs_bytes=sidecar.kzg_proofs,
)数据重建: 由于 1D RS 编码(通常每个 blob 扩展2 倍),节点需要获取至少 50% _列_对应的数据,才能重建 整个 原始数据矩阵(所有原始 blobs)。如果节点需要完全重建但抽样比例小于 50%,则可以使用对等点发现机制从负责的对等点处请求缺少的列。
PeerDAS 集成的好处
预计通过 Fulu 升级在 EIP-7594 中集成 PeerDAS 将带来几个关键好处:
- 增强的 L2 可扩展性:PeerDAS(通过 Fulu 升级中的 EIP-7594)增加了每个区块的 blobs 数量,为 rollups 提供了更多的数据空间并降低了 L2 交易费用。
- 改进的网络效率:节点无需下载所有 blobs,只需处理其负责的部分,从而减少了平均带宽和存储需求。
- 保持去中心化:通过保持较低的资源需求,PeerDAS 允许家庭质押者和小型运营商继续参与而无需昂贵的硬件。
对节点运营商的影响:
- 完整节点/验证者:处理更少的数据,但必须与 PeerDAS 网络交互。
- 超级节点:验证所有数据的实体将需要更高的带宽和存储。
- 轻客户端:可以以非常低的资源使用率安全地验证数据可用性。
参考
https://github.com/ethereum/EIPs/blob/master/EIPS/eip-7594.md
https://github.com/ethereum/consensus-specs/blob/dev/specs/fulu/das-core.md
Fraud and Data Availability Proofs: Maximising Light Client Security and Scaling Blockchains with Dishonest Majorities — arXiv, https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.09044
EIP-7594: PeerDAS — Peer Data Availability Sampling — Ethereum Magicians, https://ethereum-magicians.org/t/eip-7594-peerdas-peer-data-availability-sampling/18215
http://vitalik.eth.limo/general/2024/10/17/futures2.html
https://hackmd.io/@manunalepa/r1H8CtZlR#The-novel-PeerDAS-approach-Fulu
- 原文链接: medium.com/@Krieger69/un...
- 登链社区 AI 助手,为大家转译优秀英文文章,如有翻译不通的地方,还请包涵~
- 通过创建新的状态形式来实现超大规模状态扩展 270 浏览
- Vitalik的L2重置:以太坊为何需要此航向修正 276 浏览
- Vitalik: 重新评估以太坊 Layer2 382 浏览
- 通过实时证明实现 Rollup 间的同步组合 - Layer 2 251 浏览
- 外部跨链桥 vs Rollup 的安全委员会 728 浏览
- Vitalik: 结合预确认与Based Rollup的架构,实现同步可组合性 496 浏览
- Celestia 2.0 愿景:所有市场上链 703 浏览
- 区块链 101:数据处理 1161 浏览
- 以太坊上的PeerDAS和ZK-EVM、ERC-8004代理、Ambire自定义Bundler、稳定币结算 510 浏览
- 为什么许多团队的Layer 2迁移会失败(以及如何正确地进行迁移) 526 浏览
- Ethereum Fusaka 升級介紹 1240 浏览
- 区块链扩容 1840 浏览

