【四】GKR 协议(原始版本)
- 白菜
- 发布于 2023-07-25 12:13
- 阅读 7074
GKR协议在InteractiveProtocol框架里是一套非常经典的协议,里面有很多细节值得关注一下,本系列专题主要通过手推的方式明确各个模块执行的时间成本:MultilinearExtensionsSum-CheckExtendedMUL/ADDOriginalGKRPr
GKR 协议在Interactive Protocol框架里是一套非常经典的协议,里面有很多细节值得关注一下,本系列专题主要通过手推的方式明确各个模块执行的时间成本:
- Multilinear Extensions
- Sum-Check
- Extended MUL/ADD
- [Original GKR Protocol]() ...
本章节重点detail 原始版本的GKR 协议,掌握它的详尽执行过程。
预备知识
- 主要为前三个章节的内容
问题描述
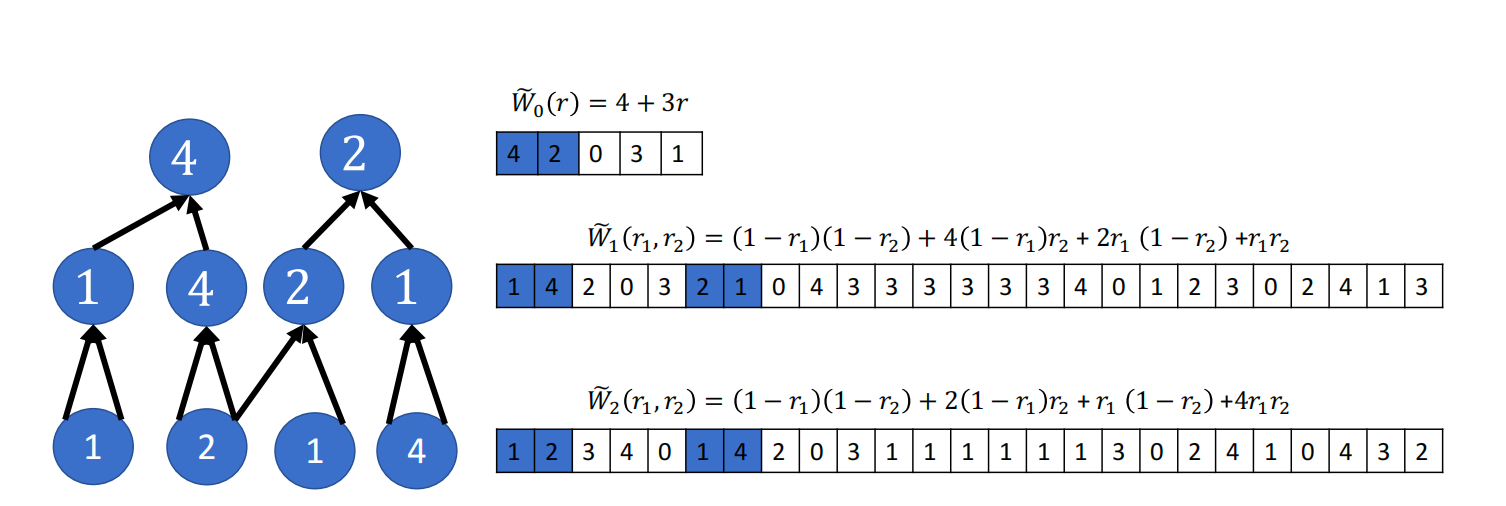
给定一个电路结构,Prover 给定电路的输出,Verifier 如何验证它?
第0层
初始claims
<br /> Prover 发出两个claims:
$$ W_0(0) = 4 \ W_0(1) = 2 \ $$
<br />
Verifier 据此通过Lagrange Interploation 拿到第0层电路的MLE: $$ \widetilde{W}_0(r) = 4(1 - r) + 2r = 4 - 2r \mod 5 = 4 + 3r $$
<br />
为了证明Prover的两个claims,根据MLE 定理,Verifier 向Prover 发送一个随机的challenge factor,$r^{(0)} \in \mathbb{F^1}$,假定$r^{(0)} = 3$,Verifier 与 Prover 各自计算自己的MLE 取值:
$$ \text{For Verifier}: \widetilde{W}_0(3) = 3 \
\text{For Prover}: \widetilde{W'}_0(3) = ? \ $$
<br />
对于Verifier 而言他是看到不Prover 真实的MLE $\widetilde{W'}_0(r)$,所以接下来需要做的就是证明:
$$ \widetilde{W'}_0(3) = \widetilde{W}_0(3) = 3 $$
进入Sum-Check 协议
协议的推导细节可以参考之前章节,GKR 协议系列之Sum-Check
<br />
假定$\widetilde{W'}_0(r) = \widetilde{W}_0(r) $,我们把它的多项式展开:
$$ \widetilde{W}0(r^{(0)}) = \sum{x \in {0, 1}^{s1}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_1}} \widetilde{MUL}_1(r^{(0)}, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_1(x) * \widetilde{W}_1(y)) + \widetilde{ADD}_1(r^{(0)}, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_1(x) + \widetilde{W}_1(y)) $$
<br />
为了简化,我们这里只取乘法gate,上面的多项式变为:
$$ \widetilde{W}0(r^{(0)}) = \sum{x \in {0, 1}^{s1}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_1}} \widetilde{MUL}_1(r^{(0)}, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_1(x) * \widetilde{W}_1(y)) \
3 \overset{?} = \sum_{x \in {0, 1}^{s1}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_1}} \widetilde{MUL}_1(3, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_1(x) * \widetilde{W}_1(y)) \ $$
<br />
这是一个标准的Sum-Check 求解过程,根据上一章节内容Extended ADD/MUL,我们很容易得到如下展开式:
$$ \begin{aligned}
3 &\overset{?} = f3^{(0)}(x, y)= \sum{x \in {0, 1}^{s1}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_1}} \widetilde{MUL}_1(3, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_1(x) * \widetilde{W}_1(y)) \
&= \sum_{x1 \in {0, 1}} \sum{x2 \in {0, 1}} ... \sum{x_{s1} \in {0, 1}} \sum{y1 \in {0, 1}} \sum{y2 \in {0, 1}} ... \sum{y_{s_1} \in {0, 1}} \widetilde{MUL}_1(3, x_1, x2, ..., x{s_1}, y_1, y2, ..., y{s_1})
(\widetilde{W}_1(x_1, x2, ..., x{s_1}) * \widetilde{W}_1(y_1, y2, ..., y{s_1})) \
&= \sum_{x1 \in {0, 1}} \sum{x2 \in {0, 1}} ... \sum{x_{s1} \in {0, 1}} \sum{y1 \in {0, 1}} \sum{y2 \in {0, 1}} ... \sum{y_{s_1} \in {0, 1}} [-2 (1 - x_1) (1 - x_2) (1 - x_3) x_4 + 3 x_1 (1 - x_2) x_3 x_4] \
& [(1 - x_1)(1 - x_2) + 4 (1 - x_1) x_2 + 2 x_1 (1 - x_2) + x_1 x_2] \ & [(1 - x_3)(1 - x_4) + 4 (1 - x_3) x_4 + 2 x_3 (1 - x_4) + x_3 x_4] \
\end{aligned} $$
<br />
一共需要迭代$2s_1$ 个round,Verifier 会依次向Prover 发送$2s_1$ 个challenge factor,作为响应Verifier 会收到来自Prover的$2s_1$ 个单变量多项式
$$ z = (3, r{1}^{(0)}, r{2}^{(0)}, ..., r_{s1}^{(0)}, r{s1 + 1}^{(0)}, r{s1 + 2}^{(0)}, ..., r{2{s_1}}^{(0)}) \
\textcolor{red} {\Downarrow} \
(h_1^{(0)}(X), h2^{(0)}(X), ..., h{s1}^{(0)}(X), h{s1 + 1}^{(0)}(X), h{s1 + 2}^{(0)}(X), ..., h{2s_1}^{(0)}(X)) \ $$
<br />
其中$s_1 = \log{|S_1|}$,$S_1 $为第1层gate的个数,第0层 Sum-Check 具体的执行过程:
$$ \def\arraystretch{1.5}
\begin{array}{c:c:c:c:c} \text{Round i} & h_i^{(0)}(X) & h_i^{(0)}(0) + hi^{(0)}(1) & r{i}^{(0)} & hi^{(0)}(r{i}^{(0)}) \ \hline 0 & & & 3 & 3 \ \hdashline 1 & 8(X_1^2 - 1) + 3X_1(1 + X_1) & 3 \textcolor{red} \checkmark & 2 & 2 \ \hdashline 2 & 14(3 - 5X_2)(1 - X_2) & 2 \textcolor{red} \checkmark & 0 & 2 \ \hdashline 3 & 3(2 + 4X_3)(4 - 3X_3) & 2 \textcolor{red} \checkmark & 1 & 3 \ \hdashline 4 & 18X_4(2 - X_4) & 3 \textcolor{red} \checkmark & 4 & 4 \ \hdashline \end{array} $$
最后一个Round 的验证
<br />
在第0层Sum-Check最后一个Round,Verifier 会拿着$ = (r^{(0)}, u, v) = (3, 2, 0, 1, 4)$从Oracle 查询得到 $\widetilde{MUL}_1(z) = 6 * 4 = 24$,另外为了完成最后一步验证,需要Prover 提供两个claims:
$$ \widetilde{W}_1(u) = \widetilde{W}_1(2, 0) = 3 \
\widetilde{W}_1(v) = \widetilde{W}_1(1, 4) = -2 \ $$
<br />
Verifier 拿着这两个claims 进行第0层最后一步验证:
$$ \begin{aligned}
\widetilde{MUL}_1(z) (\widetilde{W}_1(u) \widetilde{W}_1(v)) & = 24 3 -2 \ &= -144 \mod 5 \ &= 4 \ &= h4^{(0)}(r{4}^{(0)}) \textcolor{red} \checkmark \
\end{aligned} $$
One More ...
<br />
为了把两个claims 压缩到一个claims里,这里用了一个技巧替代了上面的最后一步验证:
$$ \exists l^{(0)}: \mathbb{F^1} \longrightarrow \mathbb{F^{s_1}} \
l^{(0)}(t) = (a_1 t + b_1, a_2 t + b_2) \ $$
<br />
满足条件:
$$ \text{satisfies}:
\begin{cases}
l^{(0)}(0) = u = (2, 0) \ l^{(0)}(1) = v = (1, 4) \
\end{cases} \
\Longrightarrow l^{(0)}(t) = (-t + 2, 4t) \ $$
<br />
把 $\widetilde{W}_1(x_1, x_2)$ 由$\mathbb{F^{s_1}}$ 降维到 $\mathbb{F^1}$,得到:
$$
q(t) = \widetilde{W}_1(l^{(0)}(t)) = (1 - 4t)(3 - t) + 4t(3t - 2) \
\Longrightarrow
\begin{cases}
q(0) = \widetilde{W}_1(u) = \widetilde{W}_1(2, 0) = 3 \
q(1) = \widetilde{W}_1(v) = \widetilde{W}_1(1, 4) = -2 \
\end{cases} $$
<br />
把基于$\mathbb{F^1}$的多项式$q(t) $作为$\widetilde{W}_1(x_1, x_2) $的替代传递给Verifier,这样Verifiery 就可以拿着它进行最后一步校验了:
$$ \begin{aligned}
\widetilde{MUL}_1(z) (q(0) q(1)) & = 24 3 -2 \ &= -144 \mod 5 \ &= 4 \ &= h4^{(0)}(r{4}^{(0)}) \textcolor{red} \checkmark \
\end{aligned} $$
新的claims
<br />
接下来第1层的迭代就会去校验上面的claims,Verifier 随机采样一个challenge factor $t \in \mathbb{F^1}$
$$ \text{assumes}: t = 3 \
r^{(1)} = l(t) = (-1, 12) \mod 5 = (4, 2) \ $$
<br />
如果不用上面的策略的话,这里的challenge factor 会是 $t \in \mathbb{F^2}$。基于这个采样点,拿到下一层Sum-Check 的claims值:
$$ q(t) = q(3) = 12 * 7 = 84 \mod 5 = 4 $$
第1层 ...
同样运用Sum-Check 协议来验证:
$$ \widetilde{W}1(r^{(1)}) = \sum{x \in {0, 1}^{s2}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_2}} \widetilde{MUL}_2(r^{(1)}, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_2(x) * \widetilde{W}_2(y)) \
4 \overset{?} = \sum_{x \in {0, 1}^{s2}} \sum{y \in {0, 1}^{s_2}} \widetilde{MUL}_2(4, 2, x, y) (\widetilde{W}_2(x) * \widetilde{W}_2(y)) \ $$
后面的逻辑跟第0层一样,这里不再赘述。
参考文献
【1】Libra: Succinct Zero-Knowledge Proofs with Optimal Prover Computation 【2】Proofs, Arguments, and Zero-Knowledge
- 原创
- 学分: 6
- 分类: 零知识证明
- 标签: interactive protocol sumcheck GKR
- ZK/SEC季度报告 700 浏览
- ZK/SEC 季刊 661 浏览
- ZK/SEC 季度报告 635 浏览
- ZK/SEC 季度刊 536 浏览
- ZK/SEC 季度报 562 浏览
- ICICLE 迈向 Metal:v3.6 1533 浏览
- 构建 Jolt:一个快速、易于使用的 zkVM 3857 浏览
- 你check 过你的 sum 吗? 2072 浏览
- Spartan 预备知识:GKR with ZK Argument 8946 浏览
- 【三】GKR 协议系列之Extended MUL/ADD 5856 浏览
- 【二】GKR 协议系列之Sum-Check 6461 浏览

