全面掌握Solidity智能合约开发
智能合约安全的新最低测试标准:Fuzz / Invariant Test
- 翻译小组
- 发布于 2023-11-28 22:39
- 阅读 6592
学习使用模糊测试(Fuzz Test)及不变性测试( Invariant Test)提高合约安全性。
什么是模糊测试(Fuzz Test)?什么是不变性测试( Invariant Test)?如何使用这些工具,了它们为什么至关重要,特别是对于安全性。未来,每个项目都应该具有有状态的模糊测试,并且审计人员可以使用理解不变性(invariant)来在代码部署之前找到关键错误。
向 Trail of Bits 和 Horsefacts 致敬,感谢他们提供的所有模糊测试内容。
介绍
大多数情况下,黑客攻击来自你没有考虑的情况,并未为其编写测试的场景。
如果我告诉你,你可以编写一个测试,可以检查几乎每种可能的情况,你会认为这可能么?
这就是要本文要介绍的模糊测试(Fuzz Test)?什么是不变测试( Invariant Test)
什么是模糊测试(Fuzz Test)?
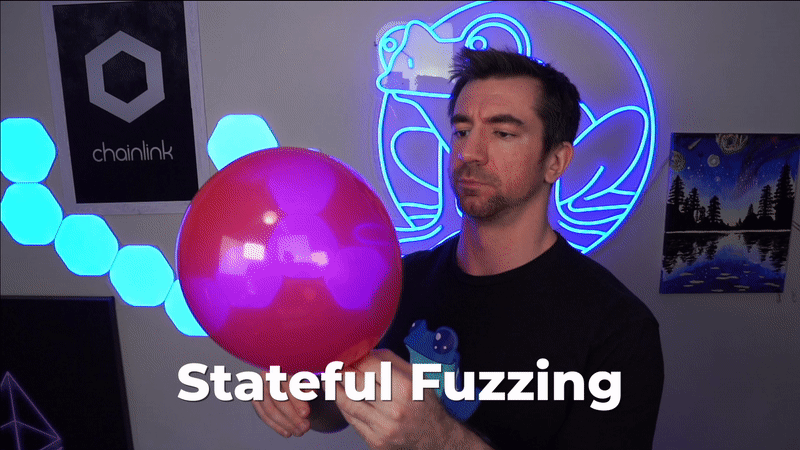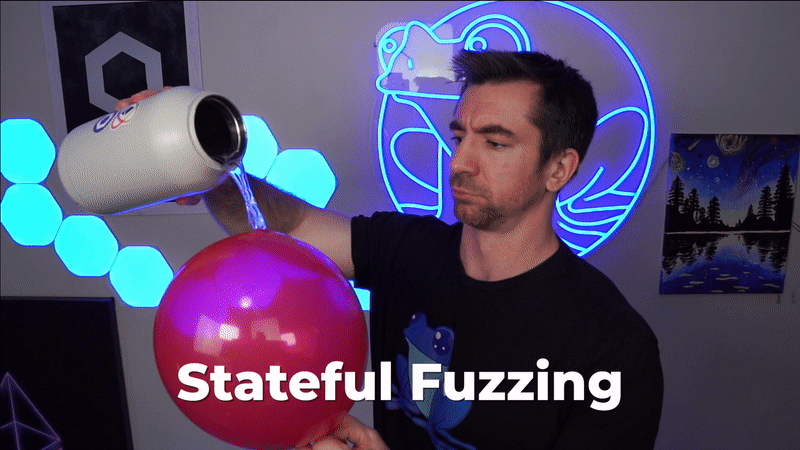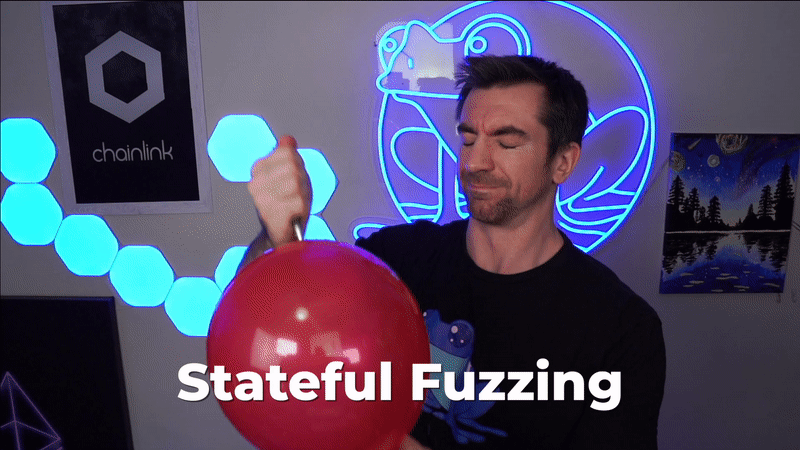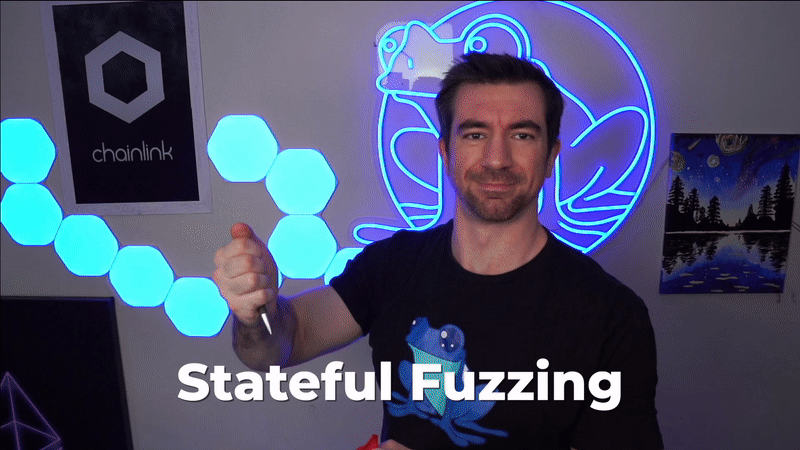
模糊测试是指向系统提供随机数据以尝试破坏它。
例如,如果这个气球是我们的系统/代码,那么模糊测试将涉及对气球进行随机操作以破坏它。
对气球进行随机操作 — 模糊测试的示例
那么,为什么我们要做这些呢?
让我们看一个例子:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract MyContract {
uint256 public shouldAlwaysBeZero = 0;
uint256 private hiddenValue = 0;
function doStuff(uint256 data) public {
if (data == 2) {
shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
}
if (hiddenValue == 7) {
shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
}
hiddenValue = data;
}
}假设我们有一个名为doStuff的函数,它以整数作为输入。此外,我们有一个名为shouldAlwaysBeZero的变量,我们希望它始终为零。
这个变量应该始终为零的事实被称为我们的不变性(invariant),或者“系统应始终保持的属性”。
不变性(invariant):系统应始终保持的属性。
在我们的合约中,我们的不变性(invariant)(也称为属性 )是:
不变性(invariant):`shouldAlwaysBeZero` 必须始终为 0在我们的气球示例中,如果我们将气球标记为“不可摧毁”,我们的不变性(invariant)可能是“我们的气球永远不应该被戳破”。
不变性(invariant):`balloon`永远不应该被戳破在 DeFi 中,一个良好的不变性(invariant)可能是:
- 协议必须始终超额抵押
- 用户不应该能够提取比超过他们存入的资金
- 公平抽奖只能有 1 个赢家
Foundry 中的示例
让我们看一个 Foundry 中的普通单元测试。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import {MyContract} from "../src/MyContract.sol";
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContractTest is Test {
MyContract exampleContract;
function setUp() public {
exampleContract = new MyContract();
}
function testIsAlwaysZeroUnit() public {
uint256 data = 0;
exampleContract.doStuff(data);
assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0);
}
}通过这个单元测试testIsAlwaysZeroUnit,我们可能会认为代码已经有了足够的覆盖,但是如果我们再次查看doStuff函数,我们会发现如果我们的输入是 2,我们的变量将不为零。
function doStuff(uint256 data) public {
// WHAT IS THIS IF STATEMENT???
// 👇👇👇👇👇👇
if (data == 2) {
shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
}
// 👆👆👆👆👆👆
// Ignore this one for now
if (hiddenValue == 7) {
shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
}
hiddenValue = data;
}这在我们的示例函数中似乎很明显,但往往情况并非如此,你可能会有一个看起来像这样的函数或系统:
function hellFunc(uint128 numberr) public view onlyOwner returns (uint256) {
uint256 numberrr = uint256(numberr);
Int number = Int.wrap(numberrr);
if (Int.unwrap(number) == 1) {
if (numbr < 3) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap(2) - number) * Int.wrap(100) / (number + Int.wrap(2)));
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 3) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap(numbr) - number) * Int.wrap(92) / (number + Int.wrap(3)));
}
if (Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(1)) / Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(numbr)))))))))) == 9) {
return 1654;
}
return 5 - Int.unwrap(number);
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 100) {
_numbaar(Int.unwrap(number));
uint256 dog = _numbaar(Int.unwrap(number) + 50);
return (dog + numbr - (numbr / numbir) * numbor) - numbir;
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 1) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 3) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap(2) - number) * Int.wrap(100) / (number + Int.wrap(2)));
}
if (numbr < 3) {
return (2 / Int.unwrap(number)) + 100 - (Int.unwrap(number) * 2);
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 12) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 6) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap(2) - number) * Int.wrap(100) / (number + Int.wrap(2)));
}
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 154) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 100) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 120) {
return (76 / Int.unwrap(number)) + 100 - Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(uint256(numbr))))))))))))) + Int.wrap(uint256(2)));
}
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 95) {
return Int.unwrap(Int.wrap((Int.unwrap(number) % 99)) / Int.wrap(1));
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 88) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap((Int.unwrap(number) % 99) + 3)) / Int.wrap(1));
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 80) {
return (Int.unwrap(number) + 19) - (numbr * 10);
}
return Int.unwrap(number) + numbr - Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(nunber) / Int.wrap(1));
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 7654) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 100000) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 1200000) {
return (2 / Int.unwrap(number)) + 100 - (Int.unwrap(number) * 2);
}
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) > 200) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 300) {
return (2 / Int.unwrap(number)) + Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(100) / (number + Int.wrap(2)));
}
}
}
}
if (Int.unwrap(number) == 0) {
if (Int.unwrap(number) < 3) {
return Int.unwrap((Int.wrap(2) - (number * Int.wrap(2))) * Int.wrap(100) / (Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(number)) + Int.wrap(2)));
}
if (numbr < 3) {
return (Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(2) - (number * Int.wrap(3)))) + 100 - (Int.unwrap(number) * 2);
}
if (numbr == 10) {
return Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(10));
}
return (236 * 24) / Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(Int.wrap(Int.unwrap(number)))))));
}
return numbr + nunber - mumber - mumber;
}这是 Cyfrin Security Challenges 之一。
在这里,如果有一个输入会导致回滚,情况就不那么明显了。为每个可能的整数或情景编写测试用例是不现实的,因此我们需要一种程序化的方法来找到任何异常情况。
有两种流行的方法可以通过程序找到这些边缘情况:
- 模糊/不变性测试(Fuzz / Invariant Tests)
- 形式验证/符号执行
我们将“形式验证”留在以后介绍。
在 Foundry 中,你可以编写一个类似下面的 solidity 模糊测试:
function testIsAlwaysZeroFuzz(uint256 randomData) public {
// uint256 data = 0; // commented out line
exampleContract.doStuff(randomData);
assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0);
}Foundry 将自动向randomData输入半随机值,并在多次运行后将它们输入到doStuff中,并检查断言是否成立。
这相当于编写许多测试,其中randomData具有不同的值,但现在都在一个测试中完成!
现在我说“半随机”,因为你的模糊器(在我们的例子中是 Foundry)选择随机数据的方式并不是真正随机的,它应该对它选择的随机数有一定的智能。Foundry 足够聪明,可以看到if data == 2的条件,并选择2作为输入。
Echidna logo
目前,我认为 Trail of Bits 的hybrid echidna 是最好的模糊器,因为其智能随机数选择,但在我看来,Foundry 的模糊器更容易编写代码。
无论如何,如果我们运行模糊测试,它会告诉我们哪个输入使测试失败:
$ forge test -m testIsAlwaysZeroFuzz
Failing tests:
Encountered 1 failing test in test/MyContractTest.t.sol:MyContractTest
[FAIL. Reason: Assertion violated Counterexample: calldata=0x47fb53d00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002, args=[2]] testIsAlwaysZeroFuzz(uint256) (runs: 6, μ: 27070, ~: 30387)我们可以看到,它发现如果将args=[2]传递给测试,它能够破坏assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0)。现在,回到我们的代码,意识到我们需要修复data == 2的边缘情况,现在我们就不再受到输入数据为 2 的攻击了!
模糊测试基础总结
总之,为了编写一个模糊测试,我们做了以下工作:
- 我们理解了不变性(invariant)或“我们系统必须始终保持的属性”
- 我们编写了一个测试,将随机值输入到我们的函数中,以尝试破坏我们的不变性(invariant)
有状态 vs 无状态模糊测试
无状态模糊测试
现在你可能会注意到还有另一种情况,即我们的代码可能存在问题,即hiddenValue == 7。为了发生这种回滚,你必须首先将hiddenValue设置为7,通过使用值7调用doStuff来设置hiddenValue为7,然后再次调用此函数。
uint256 hiddenValue = 0;
function doStuff(uint256 data) public {
// 注释掉这些,解决问题
// if (data == 2) {
// shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
// }
// 等等,这是什么
// 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
if (hiddenValue == 7) {
shouldAlwaysBeZero = 1;
}
// 👆👆👆👆👆👆👆
hiddenValue = data;
}我们的不变性(invariant)在 2 次调用后被破坏:
- 使用
7调用doStuff - 使用任何其他数字再次调用
doStuff
我们上面编写的模糊测试永远无法找到这个例子,因为按照当前的编写方式,我们的测试是所谓的“无状态模糊测试”,即上一次运行的状态被丢弃,不会影响下一次运行。
无状态模糊测试:模糊测试,上一次运行的状态被丢弃。
两次无状态模糊运行的示例
如果我们回到气球的例子,无状态模糊测试类似于对气球 A 进行一次随机尝试来破坏它,然后再吹一个新的气球 B 并尝试以不同的方式破坏它。
在气球的例子中,你永远不会尝试破坏你过去已经尝试过破坏的气球。这似乎有点愚蠢,因为如果我们的气球的不变性(invariant)是“气球不能被戳破”,我们希望在同一个气球上进行多次尝试。
有状态模糊测试
因此,在软件工程中,我们可以使用“有状态模糊测试”。有状态模糊测试是指上一次运行的状态是下一次运行的起始状态。
有状态模糊测试:上一次模糊运行的状态是下一次模糊运行的起始状态。
有状态模糊运行的示例,一次运行中进行多次尝试
单个有状态模糊运行类似于在同一个测试中使用所有你的资产。
function testIsAlwaysZeroUnitManyCalls() public {
uint256 data = 7;
exampleContract.doStuff(data);
assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0);
data = 0;
exampleContract.doStuff(data);
assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0); // this would fail
}顺便说一句,这是不好的做法,请不要在同一个测试中编写多个断言。
在 Foundry 中编写有状态模糊测试,你需要使用invariant关键字,并且需要进行一些额外的设置。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import {MyContract} from "../src/MyContract.sol";
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
import {StdInvariant} from "forge-std/StdInvariant.sol";
contract MyContractTest is StdInvariant, Test {
MyContract exampleContract;
function setUp() public {
exampleContract = new MyContract();
targetContract(address(exampleContract));
}
function invariant_testAlwaysReturnsZero() public {
assert(exampleContract.shouldAlwaysBeZero() == 0);
}
}与只是将随机数据传递给函数调用不同,有状态模糊测试(不变测试)将自动使用随机数据调用随机函数。
我们使用targetContract函数告诉 Foundry 它可以使用exampleContract中的任何函数。对于这个示例,只有一个函数,所以它将使用不同的值调用doStuff。
如果我们运行这个测试,我们可以看到输出如下,我们可以看到它发现如果你两次调用doStuff(一次使用值 7),它将抛出错误!
$ forge test -m invariant_testAlwaysReturnsZero
Failing tests:
Encountered 1 failing test in test/MyContractTest.t.sol:MyContractTest
[FAIL. Reason: Assertion violated]
[Sequence]
sender=0x000000000000000000000000000000000000018f addr=[src/MyContract.sol:MyContract]0x5615deb798bb3e4dfa0139dfa1b3d433cc23b72f calldata=doStuff(uint256), args=[7]
sender=0x0000000008ba49893f3f5ba10c99ef3a4209b646 addr=[src/MyContract.sol:MyContract]0x5615deb798bb3e4dfa0139dfa1b3d433cc23b72f calldata=doStuff(uint256), args=[2390]等等,到时什么是不变性(invariant)?
现在,重要的一点是 Foundry 如何使用术语invariant。正如我们所描述的,不变性(invariant)是系统必须始终保持的属性,但 Foundry 使用这个术语来表示“有状态模糊测试”。请记住这一点。
- Foundry Invariant 测试 == 有状态模糊测试
- Foundry Fuzz 测试 == 无状态模糊测试
- 不变性(invariant) == 系统必须始终保持的属性
因此,在实际的智能合约中,你的不变性(invariant)不会是气球不应该被戳破或某个函数应该始终为零;它会是像这样的东西:
- 新铸造的代币 < 通货膨胀率
- 随机抽奖只能有 1 个赢家
- 用户不应该能够提取比超过他们存入的资金
现在,你已经了解了模糊测试的所有基础知识!恭喜!也许现在你可以休息一下,尝试自己编写一些测试。
这是新的安全最低标准
这是 Web3 安全的新标准。这是系统化的做法,任何人都可以学会,它可以避免很多麻烦。
- 理解你的不变性(invariant)
- 为它们编写有状态的模糊测试
- 在此之前不要在进行审计。
- 如果你这样做了,请确保你的审计人员帮助你理解你的不变性(invariant)!
现在你已经了解了模糊测试和不变测试的基础知识,你可以使用你喜欢的工具!要了解更多关于高级有状态模糊测试的信息此外,请阅读 Foundry 文档中关于 H高级测试的方法的内容,因为这是构建最复杂的有状态模糊测试的推荐方法。
这篇文章来自 Horsefacts,也提供了一个令人惊叹的演示。
本翻译由 DeCert.me 协助支持, 在 DeCert 构建可信履历,为自己码一个未来。